Geography Paper 1 Memorandum - Grade 12 June 2021 Exemplars
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1: WEATHER AND CLIMATE
1.1
1.1.1 Cumulonimbus (1)
1.1.2 southern
1.1.3 easterly (1)
1.1.4 Clear skies (1)
1.1.5 outside (1) (5 x 1) (5)
1.2
1.2.1 Isotherms (1)
1.2.2 12 ⁰C (1)
1.2.3 rural areas (1)
1.2.4 CBD (1)
1.2.5 A to B (1) (5 x 1) (5)
1.3
1.3.1 Air pressure (1) (1 x 1) (1)
1.3.2
- South Atlantic high further north indicating the northward migration of the ITCZ (1)
- South Indian high further from the land (1) Clear skies over the interior (1)
- Kalahari high dominant over the interior (1)
(Any ONE) (1 x 1) (1)
1.3.3 Descending air is stronger than the convection stream during winter (2) The inversion layer will be pushed towards/beyond the plateau (2) (2 x 2) (4)
1.3.4
- West to east/Easterly/eastwards (1) (1 x 1) (1)

(4 x 1) (4)- Clockwise movement of air around a low pressure is causing south-westerly winds at D and north-westerly winds at E (2) Onshore winds experienced at D and offshore winds at E (2) (2 x 2) (4)
1.4
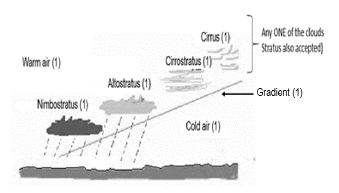
1.4.1 Meeting of warm, moist air and cold, dry air over the interior of South Africa (2) (CONCEPT) (1 x 2) (2)
1.4.2 Summer (1) (1 x 1) (1)
1.4.3
- Anti-clockwise movement of air from pressure system A causes cold, dry air to move towards the interior of South Africa (2)
- Anti-clockwise movement of air from pressure system B causes warm, moist air to move towards the interior of South Africa (2)
- The cold, dry air meets the warm, moist air over the interior forming the moisture front (2)
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
1.4.4 Negative impact
- Cumulonimbus clouds cause heavy rainfall and flooding will destroy infrastructure (2)
- Heavy rainfall will cause soil erosion, which makes soil infertile and affects crop production (2)
- Productivity decreases due to strong winds (2) Lightning may cause crops to catch fire (2)
- Fields can become waterlogged after torrential/heavy rain, which decreases crop production (2)
- Strong and gusty winds destroy crop plantations and infrastructure (2)
Positive impact
- Rains will fill dams, which increases water availability through irrigation (2)
- Long term effects of floods will make the soil fertile (2) Productivity will increase (2)
(Any FOUR) (4 x 2) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 2: GEOMORPHOLOGY
2.1
2.1.1 dendritic (1)
2.1.2 acute angles (1)
2.1.3 Uniform (1)
2.1.4 3 (1)
2.1.5 interfluve (1) (5 x 1) (5)
2.2
2.2.1 Laminar (1)
2.2.2 Turbulent (1)
2.2.3 Laminar (1)
2.2.4 Turbulent (1)
2.2.5 Turbulent (1) (5 x 1) (5)
2.3
2.3.1 High lying area between two drainage basins (1) (CONCEPT) (1 x 2) (2)
2.3.2 River A is flowing over softer rock (1) River A is flowing at a lower level (1) (Any ONE) (1 x 1) (1)
2.3.3
- It lowers the watershed (1)
- It causes a gap in the watershed (1) (Any ONE) (1 x 1) (1)
2.3.4
- Increase in water volume (2) River is longer (2)
- River has more erosive power (2)
- Starts to erode vertically again (2) (Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
2.3.5 The valley through which it flows is too big (2) Stream has too little water (2) (Any ONE) (1 x 2) (2)
2.3.6
- Elbow of capture (1) (1 x 1) (1)
- Tourist attraction because of the knickpoint waterfall (2)
Due to falling water, hydro-electricity can be generated (2) (2 x 2) (4)
2.4
2.4.1 Permanent/Perennial (1) (1 x 1) (1)
2.4.2
- Upper level of the groundwater, where soil and rocks are permanently saturated with water (1) (CONCEPT) (1 x 2) (2)
- In sketch A the water table is higher than in sketch B (2) (1 x 2) (2)
- Continuous pumping of water from the well, will lower the water table (2)
The well makes the ground less saturated and decreases flooding/overflow of the river (2)
(Any ONE) (1 x 2) (2)
2.4.3
- More soil erosion will cause more silt deposits in the river, thus decreasing water capacity (2)
- Silting of the river might cause it to become non perennial (2)
- Less infiltration will lower the water table, with a decrease in groundwater flow hence decreasing the volume of water (2)
- Less evapo-transpiration will decrease rainfall, which will affect the volume of water in the long term (2) (4 x 2) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: RURAL AND URBAN SETTLEMENTS
3.1
3.1.1 F (1)
3.1.2 C (1)
3.1.3 D (1)
3.1.4 E (1)
3.1.5 A (1) (5 x 1) (5)
3.2
3.2.1 Threshold population (1)
3.2.2 Invasion (1)
3.2.3 Urban hierarchy (1)
3.2.4 Urban sprawl (1)
3.2.5 Urban profile (1) (5 x 1) (5)
3.3
3.3.1 The manner in which farms and houses are arranged (1) (CONCEPT) (1 x 2) (2)
3.3.2 Nucleated (1) (1 x 1) (1)
3.3.3
- Flat land made it easier to expand (2)
- Fertile soil allows farmers to stay together with enough land surrounding them to farm (2) (2 x 2) (4)
3.3.4
- T-shape (1) (1 x 1) (1)
- Main roads joining in a T-shape (1) (1 x 1) (1)
- Easy access to most farmland (1)
Easy access to markets (1)
(Any ONE) (1 x 1) (1)
3.3.5
- Land is fragmented, therefore hampering initiative and expansion (2)
- Traveling between cultivated lands have extra financial implications (2)
- Profits might be shared between farmers due to communal ownership (2)
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
3.4
3.4.1 The physical growth of the urban area (2) (CONCEPT) (1 x 2) (2)
3.4.2 An increase in the number of people in urban areas will necessitate the building of more living quarters, the extension of infrastructure and the construction of more industries (2) (1 x 2) (2)
3.4.3
- Fertile soil is being removed (2)
- Natural habitats of species are being removed (2)
- Biodiversity and ecosystems are being disturbed (2)
- Increase of the heat island effect due to artificial production of heat (2)
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
3.4.4
- Infrastructure needs constant maintenance (2)
- Industrial development creates more job opportunities (2)
- Better infrastructure attracts investment with more employment opportunities (2)
- Construction of new buildings creates more job opportunities (2)
- Upskilling of people creates more job opportunities (2)
Not positive
- Unskilled people will struggle to find jobs (2)
- Expansion into the rural urban fringe will leave people living there with no livelihood (2)
(Any FOUR) (4 x 2) (8)
[40]
SECTION B
QUESTION 4: CALCULATIONS AND MAP SKILLS
4.1
4.1.1
- Formula: Gradient = Vertical Interval (V.I.)
Horizontal Equivalent (H.E.) - Gradient = ( 346,5 – 328,8) m range (1950 – 2050) m
(4(1) cm x 500) m - Gradient = 17,7(1)
2000(1) - Gradient = 17,7
2000 - Gradient = 17,7 : 2000 (1)
17,7 17,7 - Gradient= 1 : 112,9 OR 1 : 113 (1) (Range: 1 : 110 – 1 : 115,8) (5 x 1) (5)
4.2
4.2.1 C (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.2.2 D (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.2.3
- 3 cm x 1,3 cm
(3 x 100) x (1,3 x 100)
300(1) m x 130(1) m
Area: 39 000 m² (1) (3 x 1) (3)
4.3
4.3.1
- Mediterranean (1)
- Caledon is in the Western Cape (2)
- Latitude 34° S (2) (western part of South Africa)
(Any ONE) (1 + 2) (3)
4.4
4.4.1 B (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.4.2 Most rivers are seasonal, and they are in contact with the water-table only in the rainy season (2) (1 x 2) (2)
4.5 4.5.1 Dendritic (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.5.2 The rivers flow in the V-shaped valleys (2) The rivers flow over a uniform steep slope (2) (Any ONE) (1 x 2) (2)
4.5.3 North Westerly/NNW direction (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.5.4 Dam wall (Basil Newman Reservoir) is in the northwest (2) Tributaries join the main river downstream in the NW/NNW (2) Generally, contour lines bend towards NW/NNW direction (2)
(Any ONE) (1 x 2) (2)
4.6
4.6.1 D (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.7 4.7.1 Raster (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.7.2 Captured images/objects are represented in pixels (2) (1 x 2) (2)
4.7.3
- The use of vector data on a topographic map makes map interpretation more user friendly (2)
- It is easier to obtain data at a glance/quick referencing (2) It makes it easier for data layering (2)
- Data can be rendered at any scale, as symbols are not drawn to scale (2)
- Zooming in and out does not change the quality of the topographic data representation (2)
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
[30]
TOTAL: 150