Life Sciences Memorandum - Grade 12 June 2021 Exemplars
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupPRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES
- If more information than marks allocated is given.
Stop marking when maximum mark is reached and put a wavy line and ‘max’ in the right-hand margin. - If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given.
Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/ incorrect. - If whole process is given when only a part of it is required. Read all and credit the relevant part.
- If comparisons are asked for, and descriptions are given. Accept if the differences/similarities are clear.
- If tabulation is required but paragraphs are given. Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating.
- If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required. Candidates will lose marks.
- If flow charts are given instead of descriptions. Candidates will lose marks.
- If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense.
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit. - Non-recognised abbreviations.
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation, but credit the rest of the answer if correct. - Wrong numbering.
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions, but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable. - If language used changes the intended meaning. Do not accept.
- Spelling errors.
If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context. - If common names are given in terminology.
Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting. - If only the letter is asked for, but only the name is given (and vice versa).
Do not credit. - If units are not given in measurements.
Candidates will lose marks. Marking guideline will allocate marks for units separately. - Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.
- Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption. - Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts)
A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learners' assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited, if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 A √√
1.1.2 D √√
1.1.3 A √√
1.1.4 B √√
1.1.5 C √√
1.1.6 B √√
1.1.7 C √√
1.1.8 C √√
1.1.9 D √√ (9 x 2) (18)
1.2
1.2.1 Blastocyst √
1.2.2 Internal √fertilisation
1.2.3 Peptide √bonds
1.2.4 Umbilical vein √
1.2.5 Gene √
1.2.6 Grommets √
1.2.7 Chromatin network √ (7 x 1) (7)
1.3
1.3.1 B only √√
1.3.2 B only √√
1.3.3 Both A and B √√ (3 x 2) (6)
1.4
1.4.1
- PpLI √√ (2)
- Ppll √√ (1)
1.4.2 25% √√ (2)
1.5
1.5.1
- A √ – Dendrite √(2)
- D √ – Synapse √ (2)
- E √ – Interneuron √/Connector neuron (2)
1.5.2
- B √ (1)
- C √ (1)
1.6
1.6.1
- Prostate gland √ (1)
- Epididymis √ (1)
1.6.2
- G √ – urethra √ (2)
- E √ – testis √ (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1
- Nuclear membrane √/(nucleus) (1)
- DNA √ (1)
2.1.2
- Carries the coded message from DNA √ in the nucleus to the ribosomes for protein synthesis (1)
2.1.3 Translation √*
- The anticodon on the tRNA/molecule Z matches the codon on the mRNA √
- tRNA brings the required amino acid √
- to the ribosome √/structure F
- Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds √
- to form the required protein √ (*1 compulsory + 5) (6)
2.1.4
- Adenine √ (1)
- UUU-CAU-GAC-GCG √√ (correct sequence) (2)
- GUA √√ (2)
2.2.1 Prophase I √ (1)
2.2.2
- Crossing over √*
- Chromosomes pair up √/ homologous chromosomes / bivalents form
- Chromosomes overlap √/cross over
- at points called chiasmata √
- Exchange of genetic material occurs between chromatids √ /adjacent chromosome pairs
(*1 compulsory + 4) (5)
2.2.3
- Brings about variation √ in the gametes
- by ensuring that no two gametes are the same √(2)
2.3
2.3.1 Pedigree diagram √/ Genetic lineage (1)
2.3.2
- 1 √ (1)
- 2 √ (1)
2.3.3
- XHXh √ (1)
- XhY √ (1)
2.3.4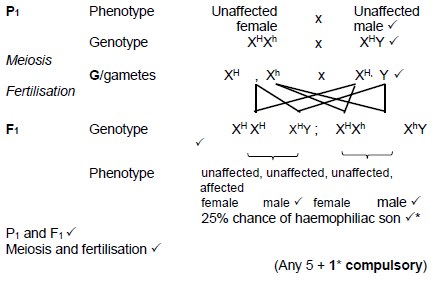
(Any 5 + 1* compulsory) (6)
OR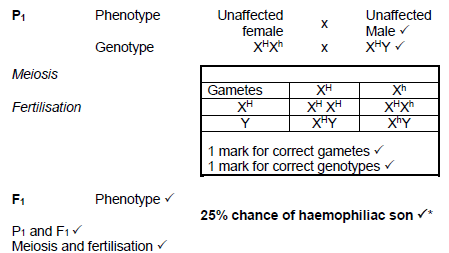
(Any 5 + 1* compulsory) (6)
2.4.1 Accommodation √ (1)
2.4.2
- B √/ D (1)
- E √ (1)
2.4.3
- The ciliary muscles relax √
- Suspensory ligaments become taut √/ stretched
- and the lens becomes less convex √/ flatter
- decreasing the refractive power of the lens √
- maintaining a clear image (4)
2.5
2.5.1
- Corpus luteum √ (1)
- Ovulation √ (1)
2.5.2 Oestrogen √(1)
2.5.3
- FSH will not be released √therefore
- no follicles will develop √in the ovaries
- LH will not be released √therefore
- no ovulation √will occur
- The female will be infertile √/ cannot have babies (Any 4) (4)
2.5.4
- It continues secreting progesterone √
- To further increase the thickness of the endometrium√
- For possible implantation √ (3)
[50]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1
- 2 – Semi-circular canals √
- 3 – Auditory nerve √ (2)
3.1.2
- 5 – Equalises pressure on either side of the tympanic membrane √
- 6 – Transmits vibrations (sound waves) to the ossicles (middle ear) √ (2)
3.1.3
- A change in the position of the head
- stimulates the maculae √
- in the utriculus and sacculus √
- to convert the stimulus into an impulse √
- The impulse is sent to the cerebellum √
- through the auditory nerve √
- The cerebellum sends impulses to the skeletal muscles √
- to restore balance √ (Any 5) (5)
3.1.4
- Vibrations are not transmitted to the inner ear √
- Pressure waves not generated in cochlea √
- Organ of Corti is not stimulated √
- No impulse is transmitted to cerebrum √
- resulting in impaired hearing √ (Any 3) (3)
3.2
3.2.1
- Its larvae eat the contents of maize stems √
- this weakens the stems causing the plants to collapse √ (2)
3.2.2
- The spray may not reach all the larvae √ as
- they develop inside the stem √ and therefore
- are shielded from the spray √ (3)
3.2.3
- Type of treatment √/ protection (1)
- Number of maize plants collapsed √ (1)
3.2.4
- As a control √
- for comparison of results √ with and without treatment (2)
3.2.5 Average number of plants collapsed
- Plot B = 0+0+22+0+1+11+2+0+1+6+13+17 √
12
= 6,08 √/ 6,1/ 6
Plot C = 1+0+21+0+0+12+1+1+0+0+1+0 √
12
= 3,08 √/3,1/3
(4)
3.2.6 Using genetically modified Bt corn is more effective √ in protecting the maize against the corn borer moth than spraying the corn with Bt toxin √ (2)
3.2.7
- Long period of investigation √/ 12 weeks
- Large sample used √/ Several hundreds of seedlings used (2)
3.2.8 Different scientists used for counting √/ each scientist may have counted differently from the other (1)
3.3
3.3.1
- For the body to be able to react to stimuli √
- To co-ordinate the various activities of the body √ (2)
3.3.2
- E √ – corpus callosum √ (2)
- C √ – spinal cord √ (2)
3.3.3
- The medulla oblongata regulates vital life processes √ like breathing rate √/heart rate (2)
- The right cerebral cortex controls the left-hand side of the body √ A blood clot in the right cerebral cortex will inhibit voluntary action on the left-hand side of the body √ (2)
3.4
3.4.1
- Placenta √(1)
- Umbilical cord √ (1)
3.4.2
- It provides the fluid medium for free movement of fetus √
- It acts as a shock absorber
- It protects the fetus against dehydration √
- It protects the fetus against temperature changes√ Promotes lung development √
- Holds waste √
(Mark first ONE only) (Any 1) (1)
3.4.3 Respiratory √/Gaseous exchange system Digestive √system
Excretory √ system
(Mark first TWO only) (Any 2) (2)
3.4.4
| Vein | Artery |
| Oxygen content – High√ | Oxygen content – Low√ |
| Nutrient content – High√ | Nutrient content – Low√ |
| CO2 content – Low√ | CO2 content – High√ |
| Nitrogenous waste – Low√ | Nitrogenous waste – High√ |
(Mark first ONE only) 1 for table + Any (1 x 2 ) (3)
3.4.5
- High levels of progesterone √
- inhibit the secretion of FSH√ (2)
[50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 100
GRAND TOTAL: 150