Technical Sciences Paper 2 Questions - Grade 12 June 2021 Exemplars
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupINSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SEVEN questions. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two sub-questions, for example, between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Round off your FINAL numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions etc. where required.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1–1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 D.
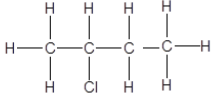
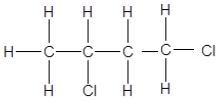
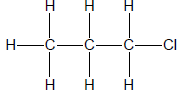
1.1 The positional isomer of the molecule below is …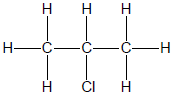



 (2)
(2)
1.2 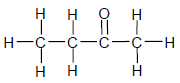
The IUPAC name for the compound above is …
- butanal.
- butanol.
- butanone.
- butanoic acid. (2)
1.3 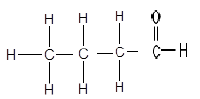
The structure above represents a/an …
- ketone.
- aldehyde.
- ester.
- carboxylic acid. (2)
1.4 Which of the following groups of elements can be used for doping?
- Group 3 and Group 5 elements
- Alkali metals (Group 1) and alkali earth metals (Group 2)
- All transition metals since they can conduct electricity
- Halogens (Group 7) and inert gases (Group 8) (2)
1.5 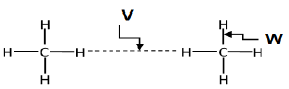
The correct labels for V and W are respectively:
V | W | |
A | Intramolecular forces | Intermolecular forces |
B | Intermolecular forces | Intramolecular forces |
C | Inter atomic forces | Chemical bonds |
D | Chemical bonds | Inter-atomic forces |
(2) [10]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a new page.)
Give ONE word for each of the following statements.
2.1 When a hydrocarbon burns in oxygen. (1)
2.2 Organic molecules with the same molecular formula, but different structural formulae. (1)
2.3 A large molecule composed of smaller monomer units covalently bonded to each other in a repeating pattern. (1)
2.4 A semiconductor doped with phosphorus (P), arsenic (As) or antimony (Sb) as an impurity. (1)
[4]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a new page.)
The diagram below represents the model of propene.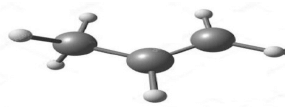
Propene is one of the most important organic compounds that is used in the industry to manufacture various products such as propanol and esters.
3.1
3.1.1 Define the term organic compound. (2)
3.1.2 Write down the general formula for alkenes. (1)
3.1.3 To which homologous series does propanol belong? (1)
3.1.4 What is the NAME of the functional group which propanol belongs to? (1)
3.1.5 Draw the structural formula of propan-2-ol. (2)
3.2 Propyl methanoate is the ESTER that is a product of an industrial process mentioned in the statement above. Use this information and answer the following questions.
3.2.1 Name the type of intermolecular forces found between esters and between alcohols. (2)
3.2.2 Write down the NAME of the carboxylic acid used to form the propyl methanoate. (1)
3.2.3 Draw the structural formula of the functional isomer of propyl methanoate. (2)
3.2.4 Draw the structural formula for the FUNCTIONAL GROUP of the isomer mentioned in QUESTION 3.2.3 above. (1)
3.3 Consider the organic compounds given below and answer the questions that follow.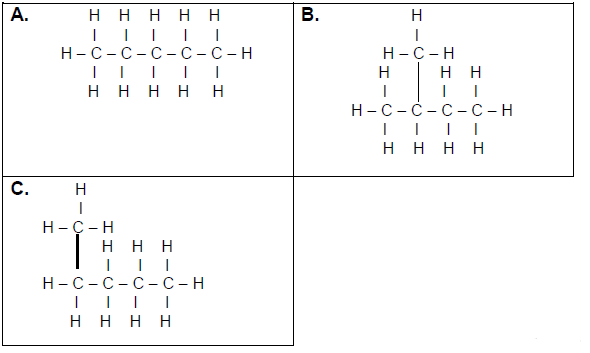
Write down:
3.3.1 ONE similarity between compounds A, B and C (1)
3.3.2 ONE observable difference between A and B (1)
3.3.3 The homologous series to which these compounds belong (1)
3.4 Write down the IUPAC names of the compounds represented by the following letters:
3.4.1 A (1)
3.4.2 B (2)
3.4.3 C (1)
3.4.4 Which of these compounds has the smallest surface area? Write only A, B or C. (1)
3.4.5 Explain your answer to QUESTION 3.4.4 above. (2)
3.5
3.5.1 Define the term plastic in words. (2)
3.5.2 Choose TWO industrial uses of polyethene from the list given in the table below.
USES | |
A | Electroplating |
B | Food packaging plastics |
C | Squeezable bottles |
D | Electrorefining |
E | Flexible water pipes |
F | Aluminium extraction |
(2 x 1) (2)
[27]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a new page.)
In the table below FIVE substances, as well as their molecular formula and viscosity, are given. Use the table to answer the questions which follow.
SUBSTANCE | MOLECULAR FORMULA | VISCOSITY | |
A | Pentane | C5H12 | X |
B | Chlorohexane | C6H11Cl | 0,695 |
C | Pent-2-ene | C5H10 | 0,210 |
D | Ethanol | C2Hn6O | 1,074 |
E | Propan-1-ol | C3H8O | 1,945 |
4.1 Define the term vapour pressure. (2)
4.2 Identify the TYPE of intermolecular force in:
4.2.1 Chlorohexane (1)
4.2.2 Pent-2-ene (1)
4.3 Use the table above to answer these questions.
How does the viscosity of chloro-hexane compare with the viscosity of pentane? Write only HIGHER or LOWER. Explain your answer. (2)
4.4 Explain, by referring to intermolecular forces and energy, which of the organic compounds from the table above will have the highest vapour pressure. (3)
4.5 Which intermolecular forces are common between pent-2-ene and ethanol? (2)
[11]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a new page.)
Hydrocarbons are famous for being the primary constituents of fossil fuels. Energy is obtained from fossil fuels through combustion of the fuel. Hydrocarbon combustion is the primary process in the burning of fossil fuels. Regardless of the type of hydrocarbon, the combustion produces the same products and large amounts of thermal heat are released.
5.1 Define the term hydrocarbon. (1)
5.2 Write down:
5.2.1 A balanced chemical reaction for the complete combustion of methane using a molecular formula (3)
5.2.2 The reaction conditions for the complete combustion of methane (1)
[5]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a new page.)
6.1 Consider the flow diagram below and answer the questions that follow.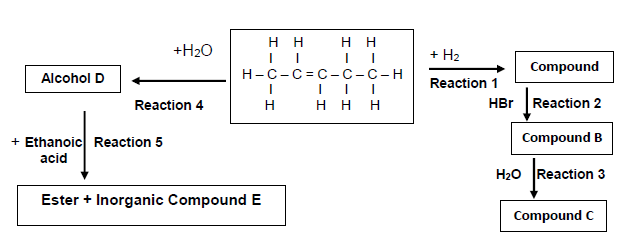
Write down the NAME/TYPE of the following:
6.1.1 Reaction 3 (1)
6.1.2 Reaction 4 (1)
6.1.3 Reaction 5 (1)
6.2 Write down the IUPAC name for the following compounds:
6.2.1 Secondary alcohol D (1)
6.2.2 Minor product compound B (1)
6.2.3 Inorganic compound E (1)
6.3 Write down the reaction conditions for the following reactions:
6.3.1 Reaction 1 (1)
6.3.2 Reaction 2 (1)
6.4 Draw the structural formula of compound C. (2)
6.5 Write down:
6.5.1 A balanced chemical reaction for Reaction 5 using structural formulae (4)
6.5.2 The NAME of the ester formed in Reaction 5 (1)
6.5.3 A balanced chemical reaction for Reaction 1 using structural formulae (3)
[18]
TOTAL: 75
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
DATA FOR TECHNICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Avogadro’s constant | NA | 6,02 × 1023 mol-1 |
Molar gas constant | R | 8,31 J.K-1.mol-1 |
Standard pressure | pq | 1,013 × 105 Pa |
Molar gas volume at STP | Vm | 22,4 dm3∙mol-1 |
Standard temperature | Tθ | 273 K |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE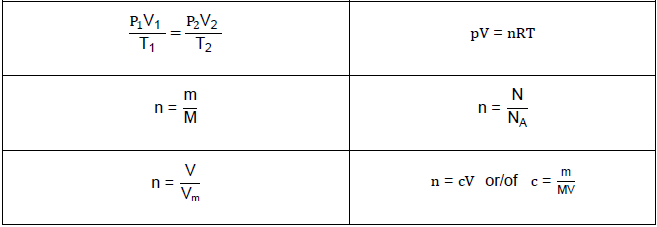
TABLE 3:THE PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS
TABLE 4A: STANDARD REDUCTION POTENTIAL
TABLE 4B:STANDARD REDUCTION POTENTIALS
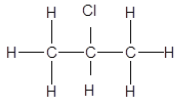
 (2)
(2)