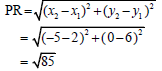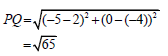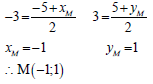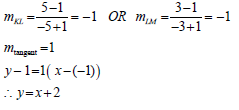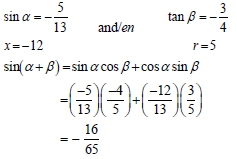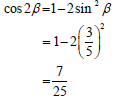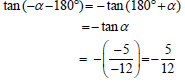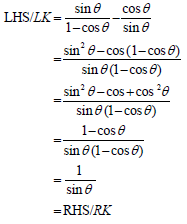Mathematics Paper 2 Memorandum - Grade 12 June 2021 Exemplars
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMEMORANDUM
| QUESTION 1 | ||
1.1 | a = 62 | value of a |
(5) | ||
1.2 | Skewed to the right OR Positively skewed | answer |
(1) | ||
1.3 | Yes | Yes |
(2) | ||
[8] | ||
| QUESTION 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.1 | Positive impact The number of learners obtaining lower marks decreased while those obtaining higher marks increased in the Post Test. | positive impact reason | (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.2 | 20 < x ≤ 30 | answer | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.3 | Less | answer | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Frequency Cummulative frequency | (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.5 | 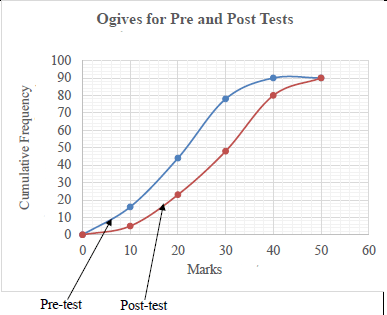 | Grounding Upper limits used Shape | (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2.6 | Pre: 90 – 78 = 12 learners obtained 60% and more | 12 | (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
[14] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QUESTION 3 | ||
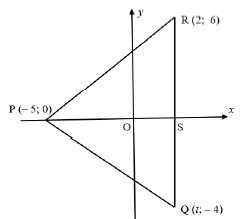 | ||
3.1 | t = 2 | value of t |
(1) | ||
3.2.1 |
| substitution answer (2) |
3.2.2 | mPR =y2 - y1 = 0 - 6 | substitution gradient of PR (2) |
3.3 | tan RPS = 6/7 | tanθ = 6/7 |
3.4 | mPR = 6/7 ∴ ΔPRQ is not right angled at R OR RQ2 =100 | substitution OR
substitution |
3.5 | mnewline = mPQ = - 4/7 | gradient of new line | (3) |
3.6 | SP = 7 units | length of SP | (5) |
[22] | |||
| QUESTION 4 | |||
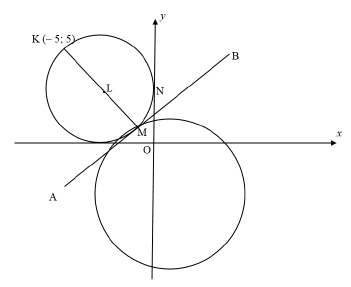 | |||
4.1.1 | x2 + y2 + 6x - 6y + 9 = 0 | method | (4) |
4.1.2 |
| method | (3) |
4.1.3 |
| mLM OR mKM | (4) |
4.1.4 | ( x + 3)2 + ( y - 3)2 = 9 | value of x | (2) |
4.2.1 | L ( – 3 ; 3) | value of x |
4.2.2 | mML/ = -4 - 1 = - 5 Not passing through the origin | mML/ |
[19] |
| QUESTION 5 | ||
5.1.1 |
| value of x |
5.1.2 |
| expansion |
5.1.3 |
| reduction |
5.2.1 | 1- cosθ = 0 or sinθ = 0 OR θ = 360º.k or θ =180º + 360º.k (k∈θ) | method |
5.2.2 |
| common denominator |
| 5.3 | LHS/LK = sin (x - y) | identity |
| [20] | ||
| QUESTION 6 | ||
6.1.1 | 1 | 1 (1) |
6.1.2 | 120° | 120° (1) |
6.2 | f (x) = g(x) | cos(x - 60º) - cos(90º - 3x) |
6.3 | 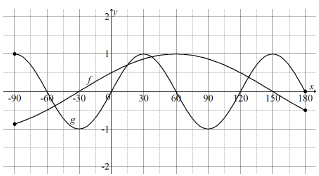 | f: g: |
6.4 | x = -30º or x = 150º | both values of x beide waardes van x |
(1) | ||
6.5 | f (x) = cos(x - 60º + 15º) | h(x) = cos (x – 45°) |
(1) | ||
[15] | ||
| QUESTION 7 | ||
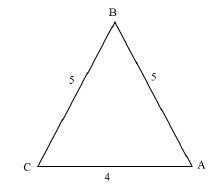 | ||
52 = 42 + 52 - 2(4)(5) cos A | substitution into cosine rule | (5) |
[5] | ||
| QUESTION 8 | |
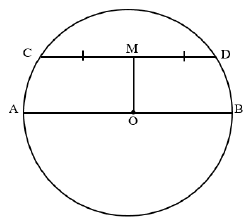 | |
OM ⊥ CD (line from centre which bisects the chord) | S/R |
[5] | |
| QUESTION 9 | ||
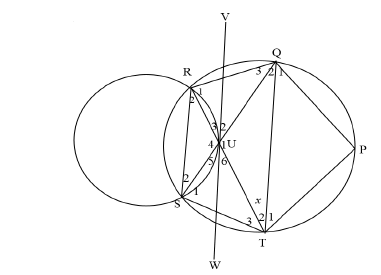 | ||
9.1 | R2 = Q2 ( ∠s in the same segment) | S/R |
9.2 | S2 = T2 = x (∠s in the same seg) | S/R |
9.3.1 | R1 + x + 90º - x = 180º ( sum of ∠s of Δ) | S |
9.3.2 | P = 90º (∠in thesemicircle) | S |
| 9.4.1 | Q2 = T2 = x (∠s opp. equal sides) ∴ Q2 = S2 ∴RS||QT (Alt ∠s are equal) | S/R R (2) |
| 9.4.2 | U2 = Q2 = x VW is a tangent to circle passing through QUT (Converseof tan-chord theorem) | S R (2) |
| [17] | ||
| QUESTION 10 | ||
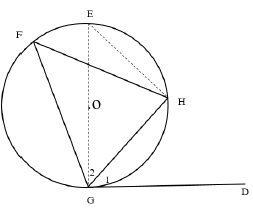 | ||
10.1 | Construction: Draw diameter GOE. Join EH | construction |
(5) | ||
10.2 | 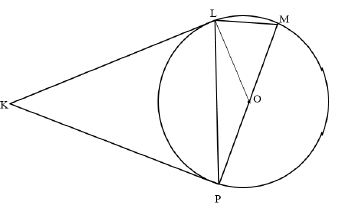 | |
10.2.1 | Kite | answer (1) |
10.2.2 | KLO = 90º (tan ⊥ rad.) | S/R |
10.2.3 | KLO + KPO = 90º + 90º | S |
10.2.4 | K + LOP =180º (Opp.∠sof cyclicquad.) OR M = 67º ( ∠s opp. = sides) | S/R OR S/R |
[18] | ||
| QUESTION 11 | ||
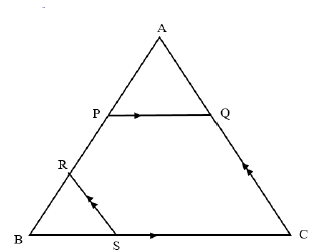 | ||
AP = 3 (Prop. theorem; PQ||BC) | S/R | |
[7] | ||
| TOTAL: | 150 | |