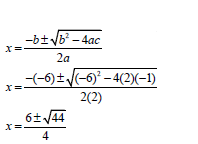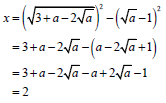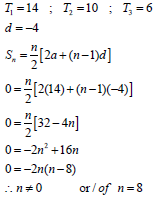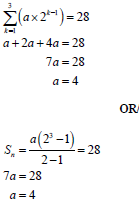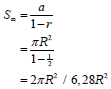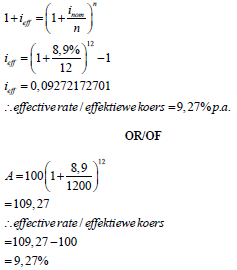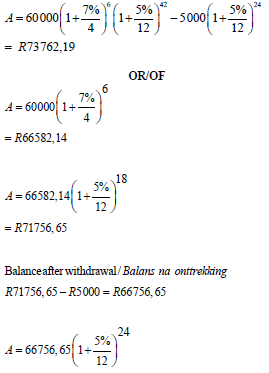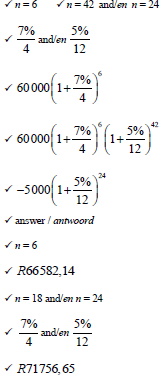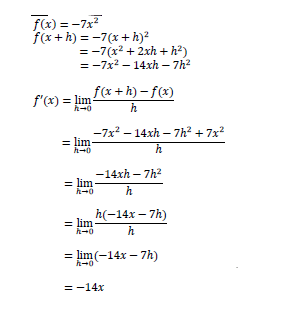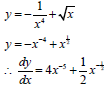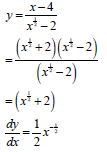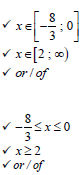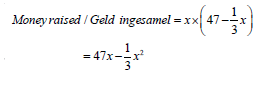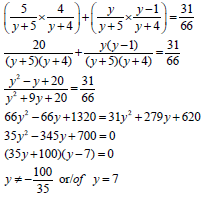Mathematics Paper 1 Memorandum - Grade 12 June 2021 Exemplars
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupNOTE:
- If a candidate answered a question TWICE, mark the FIRST attempt ONLY.
- Consistent accuracy (CA) applies in ALL aspects of the marking guideline.
- If a candidate crossed out an attempt of a question and did not redo the question, mark the crossed-out attempt.
- The mark for substitution is awarded for substitution into the correct formula.
QUESTION 1 | ||
1.1.1 | 2x(x +1) = 0 | x = 0 |
1.1.2 | 2x(x - 3) = 1 Penalise 1 mark for incorrect rounding off. | standard form |
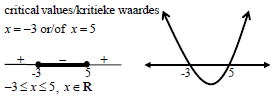
1.1.3 | x2 - 2x - 15 ≤ 0 | factors OR x ∈[-3 ; 5] (3) |
1.1.4 |
| 3 + a - 2√a | (3) |
1.2 | x - 2 y = 3 .......................(1) | x = 2y + 3 | (6) |
1.3.1 | For equal roots Δ = 0 | Δ = 0 | (4) |
1.3.2 | Consider axis of symmetry | method | (2) |
[24] | |||
QUESTION 2 | |||
2.1 | 23 ; 21 ; 19 ; . . . ; – 47 | substitution | (2) |
2.2.1 | T2 - T1 = T3 - T2 | method | (3) |
2.2.2 |
| first term and common difference
| (4) |
2.3.1 | 25 ; 48 ; 69 ; 88 ; x ; y | √ x = 105 | (2) |
2.3.2 | 2a = -2 3a + b = 23 a + b + c = 25 | value of a | (4) |
2.3.3 | n = -b = -(26) = 169 | method | (3) |
2.4 |
| expanding answer | (2) |
[20] | |||
QUESTION 3 | |||||
3.1 | Alevel1 = 1 × πR2 OR a = πR2 ; r = ½ OR Alevel 4 = 8 × π(1/8R)2 | √√√ Areas for levels 1 to 3 answer value of a value of r substitution | (4)
(4) | ||
3.2 |
| formula | (3) | ||
[7] | |||||
QUESTION 4 | ||||
4.1 | -x2 - 4x + 5 = 0 | solving for x-intercepts | (4) | |
4.2 | x = (-5 + 1) = -2 or x = -(-4) = -2 | x-value | (3) | |
4.3 | a = 1 and q = 5 | a = 1 | (2) | |
4.4 | Length of ND = 9 (from 4.2) | ND = 9 TD = 3 NT = 6 | (3) | |
4.5 | S( -4 ; 5) m = f'(-4) | coordinates of S | (5) | |
[17] | ||||
QUESTION 5 | |||
5.1 | A(1 ; 0) | answer | (1) |
5.2 | f (x) = k g(x) = log p x 2 = logp 9 | k = 6 p2 = 9 | (3) |
5.3 | y = log3x | interchanging x and y | (2) |
5.4 | Range of g -1 | √√ answer | (2) |
5.5 | 6 = log3x + 1 | (3 ; 1) point on g | (2) |
[10] | |||
QUESTION 6 | |||
6.1 | g(x) = (x + 2)( y + 3) = k | standard form | (3) |
6.2 | - 5 = k - 3 2 0 + 2 1 = k 2 2 | substitution | (2) |
6.3 | y = -(x + 2) - 3 | substitution | (2) |
[7] | |||
QUESTION 7 | |||
7.1 |
| formula substitution
| (3)
(3) |
| 7.2 | 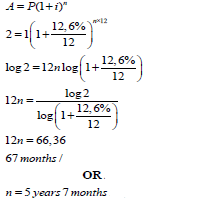 | substitution use of logs solving for n answer | (4) |
| 7.3 | 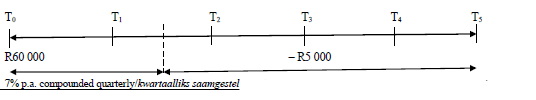 | ||
= R73762,18 |
subtraction | ||
QUESTION 8 | ||
8.1 |
Answer only = 0 marks | −7?2 − 14?ℎ − 7ℎ2 |
8.2.1 |
| √ x-4 + x½ |
8.2.2 |
| (x½ + 2)(x½ - 2) |
[10] | ||
QUESTION 9 | ||||
9.1 | g(-5) = (-5)3 + (-5)2 -16(-5) + 20 | substitution | (2) | |
9.2 | g(x) = x3 + x2 -16x + 20 | (x2 - 4x + 4) | (3) | |
9.3 | g'(x) = 3x2 + 2x -16 = 0 | g'(x) | (4) | |
9.4 | 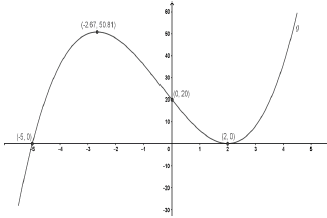 | intercepts with the axes | (3) | |
9.5 | g''(x) = 6x + 2 OR g''(x) = 6x + 2 = 0 | g''(x) substitution conclusion g''(x) x = - 1/3 conclusion | (3) | |
9.6 |
OR -8/3 ≤ x ≤ 0 or x ≥ 2 |
| (3) | |
[18] | ||||
QUESTION 10 | ||||
10.1 |
| multiplication | (2) | |
10.2 | 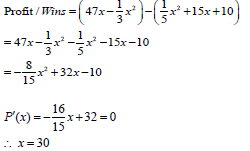 | method | (5) | |
[7] | ||||
QUESTION 11 | |||
11.1.1 | P( A or B) = P( A) + P(B) - P( A and B) | P(B) = 0,4 | (3) |
11.1.2 | P( A and/en B) = 0, 2 | P(A) x P(B) = 0,2 | (3) |
11.2.1 | P(R or G) = 1 OR (100%) | answer | (1) |
11.2.2 | 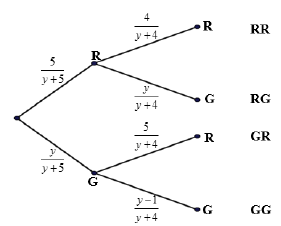 | first branch with labels second branch with labels third branch with labels outcomes | (4) |
11.2.3 |
| method | (5) |
[16] | |||
TOTAL: | 150 | ||