TECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2020
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupTECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NOVEMBER 2020
MEMORANDUM
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
QUESTION 1
1.1 D ✓✓(2)
1.2 D ✓✓ (2)
1.3 A ✓✓ (2)
1.4 B ✓✓ (2)
1.5 B ✓✓ (2)
1.6 A ✓✓ (2)
1.7 B ✓✓(2)
1.8 B ✓✓ (2)
1.9 A ✓✓ (2)
1.10 C ✓✓ (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 An object continues in a state of rest or uniform (moving with constant) velocity unless it is acted upon by a net (resultant) force ✓
OR
An object will remain at rest or continue moving at a constant velocity unless a non-zero resultant /net force acts on it.✓ (2)
2.2 OPTION 1
Fnet = ma
Fnet = 0 N
Fnet = F Cos 40° + fk
F Cos 40° + fk = 0 N
Fnet = FH + fk
FH + fk = 0 N
(Choose right to be positive)
F Cos 40° + fk = 0
80 Cos 40° + fk = 0
61,28 + fk = 0
fk = - 61,28
fk = 61,28 N (to the left)
OPTION 2
Fnet = ma
Fnet = 0 N
Fnet = F Cos 40° + fk
F Cos 40° + fk = 0 N
Fnet = FH + fk
FH + fk = 0 N
(Choose left to be positive)
F Cos 40° + fk = 0
- 80 Cos 40° + fk = 0
- 61,28 + fk = 0
fk = 61,28 N (to the left) (3)
2.3.1 Inertia is a property/tendency of an object/body to resist a change in its state of rest or motion (in a straight line). (2)
2.3.2 Apply Negative marking
Increase. ✓
Inertia of an object is directly proportional to its mass. ✓
When the mass of an object increases, its inertia also increases. ✓ (3)
[10]
QUESTION 3
3.1.1
- Tension is a (pulling) force acting in a string or rope.
- Force applied by Zane (FZane)/F160/160 N (3)
3.1.2 Decrease (2)
3.1.3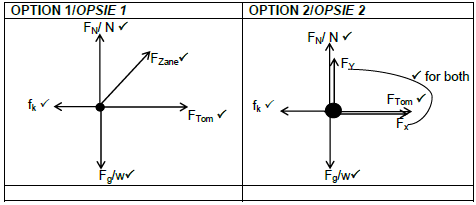
ACCEPTABLE LABELS:
- Fg/w/weight
- fk/f/friction
- FTom/ F200/ 200 N/Force by Tom
- FZane/ Force by Zane/F160/160 N/Tension /T
- FN/N/Normal force/Normaalkrag
- FY/FV/Vertical component of force by Zane
- FX/FH/ Horizontal component of force by Zane
- FA /Fzane/FTom
NOTE:
Penalise once if
- Force diagram used
- Arrows are not shown
- If force does not touch the dot
- An additional force
- Using broken lines (5)
3.2 OPTION 1
Choose east to be positive
Fnet = Fx + FTom + fk
Fnet = FZane Cos 65° + FTom + fk
205 = 200 + 160 Cos 65° + fk
fk = - 62,62 N
fk = k μ N
fk = k μ (Fg - FZane Sin 65°)
fk = k μ (mg - FZane Sin 65°)
62,62 = k μ (350 x 9,8 – 160 Sin 65°)
62,62 = k μ (3284,99)
k μ = 0,019/ 0,02
OPTION 2
Fnet = Fx + FTom + fk
Fnet = FZane Cos 65° + FTom + fk
205 = 200 + 160 Cos 65° + fk
fk = - 62,62 N
N = Fg - FZane Sin 65)
= mg - FZane Sin 65°)
= 350 x 9,8 – 160 Sin 65°
= 3284,99 N
fk = k μ N
62,62 = k μ (3284,99)
k μ = 0,019/ 0,02
OPTION 3
Choose east to be positive
fk = k μ N
Fnet – (FZane Cos 65° + FTom) = k μ N
Fnet – (FZane Cos 65° + FTom) = k μ (mg - FZane Sin 65°)
205 – 200 – 160 Cos 65° = k μ (350 x 9,8 – 160 Sin 65°)
- 62,62 = k μ (3284,99)
(Ignoring direction)
62,62 = k μ (3284,99)
k μ = 0,019 /0,02 (6)
[16]
QUESTION 4
4.1.1 Momentum (of an object) is the product of the object's mass and its velocity (in a straight line). ✓
4.1.2 OPTION 1
vi truck = 120 x 1000
3600
= 33,33 m.s-1, east
OPTION 2
vi truck = 120 x1/3,6
= 33,33 m.s-1, east (2)
4.1.3 p = mcar vi car
= 1 050 x 16,67
= 17 503,5 kg.m.s-1, west (3)
4.2.1 The total linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant (is conserved) in magnitude and direction.
OR
The total linear momentum of an isolated system before collision/explosion is equal to total linear momentum after collision/explosion. (2)
4.2.2 POSITIVE MARKING FROM 4.1.2
ΣEki = ½mtruck i.e v2i truck i.e + ½mcarv2icar
= ½ (1350)(33,33)2 + ½ (1 050)(-16,67)2
= 895 741,68 J
½mtruck i.e v2i truck i.e + ½mcarv2icar
= ½ (1350)(33,33)2 + ½ (1 050)(5,32)2
= 293 019,51 J
ΣEki ≠ ΣEkf /(Kinetic energy is not conserved)
Therefore, collision was inelastic
NOTE: If a learner starts: ΣEki = ΣEkf take 1 mark(5)
4.3.1 Inversely proportional.
OR
Fnet ∞ 1/Δt
OR
When the contact time increases/decrease, the net force decreases/increase.
NOTE: GIVE full mark for mathematical expression (2)
4.3.2 Equal to (1)
4.3.3
- Impulse remains constant.
- Airbags increase the contact time during the crash.
- The longer the contact time, the smaller the force exerted by the driver on the car and the lesser is the extent of injuries. (3)
4.3.4 OPTION 1
Let the direction towards the tree be positive
FnetΔt = Δp
FnetΔt = m(vf – vi)
- 57 500Δt = 1 150(0 – 15)
Δt = 0,30 s
OPTION 2
Let the direction towards the tree be negative
FnetΔt = Δp
FnetΔt = m(vf – vi)
57 500Δt = 1 150{0 – (-15)}
Δt = 0,30 s (4)
[24]
QUESTION 5
5.1.1 Wlearner = Fapp Δy Cosθ
= (25)(0,9)(Cos 0°)
= (25)(0,9)(1)
= 22,5 J (3)
5.1.2 OPTION 1
Choose up to be positive
Fnet = Fa + Fg
Fnet = Fa + mg
= 25 + 2(- 9,8)
= 5,4 N
Wnet = Fnet Δy Cos θ
= (5,4) (0,9)(Cos 0°)
= (5,4)(0,9)(1)
= 4,86 J
OPTION 2
Positive marking from 5.1.1
Wg = Fg Δy Cosα
= mg Δy Cos α
= (2)(9.8)(0,9)(Cos 180°)
= (2)(9.8)(0,9)(-1)
= - 17,64 J
Wnet = Wlearner+ Wg
= 22,5 + (- 17,64)
= 4,86 J
OPTION 3
Wnet = Fnet Δy Cos θ
= (Fa + mg) Δy Cos θ
= {25 + 2(- 9,8) } (0,9)(Cos 0°)
= (5,4)(0,9)(1)
= 4,86 J
OPTION 4
Wnet = Wlearner + Wg
= Wlearner + mg Δy Cos α
= 22,5 + (2)(9.8)(0,9)(Cos 180°)
= 22,5 + (2)(9.8)(0,9)(-1)
= 4,86 J (4)
5.2.1 The total mechanical energy of an isolated system is constant.
OR
The sum of gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy in an isolated system remains constant. (2)
5.2.2 OPTION 1
ME = Ep + Ek
= mgh + ½mv2
= (6)(9,8)(5) + ½ x 6 x 02
= 294 J
Accept:
0 for ½ x 6 x 02
OPTION 2
Ek = ½mv2
= ½ x 6 x 02
= 0 J
Ep = mgh
= (6)(9,8)(5)
= 294 J
ME = Ep + Ek
= 294 + 0
= 294 J (4)
5.2.3 POSITIVE MARKING FROM 5.2.2
OPTION 1
In an isolated system Ep(Top) = Ek(Bottom)
NOTE: If the above statement is omitted, learner will lose 1 mark
Ek = ½mv2
294 = ½ x 6 x v2
v2 = 98
v = 9,90 m.s-1
OPTION 2
ME(A) = ME(B)
ME(A) = (Ep + Ek)B
ME(A) = (mgh + ½mv2)B
294 = 0 + ½ (6)(v2)
v2 = 98
v = 9,90 m.s-1 (4)
5.2.4 POSITIVE MARKING FORM 5.2.2
OPTION 1
ME = Ek + Ep (At C)
Ek at C = ME – Ep at C
= ME – mgh
= 294 - (6x9,8x3)
= 294 - 176,4
= 117,6 J
½mv2 = 117,6 at point C
½(6)v2 = 117,6
v2 = 39,2
v = 6,26 m.s-1 (4)
OPTION 2
ME (At B) = ME (At C)
½mv2 + mgh (At B) =½mv2 + mgh (At C)
½(6)(9,9)2 + (6)(9,8)(0) = ½(6)(v)2 + (6)(9,8)(3)
294 = 3(v)2 + 176,4
v2 = 39,2
v = 6,26 m.s-1
OPTION 3
ME (At A) = ME (At C)
½mv2 + mgh (At A) = ½mv2 + mgh (At C)
½(6)(0)2 + (6)(9,8)(5) =½(6)(v)2 + (6)(9,8)(3)
294 = 3(v)2 + 176,4
v2 = 39,2
v = 6,26 m.s-1
[21]
QUESTION 6
6.1.1 Stress is the internal restoring force per unit area of body (2)
6.1.2 Strain is the ratio of change in dimension/length to the original dimension/length.✓✓ (2)
6.2.1 Κ = σ/ε
190 x 109 = 250 x 106
ε
ε = 1,32 x 10-3/ 0,00132 (3)
6.2.2 OPTION 1
Area = πd2
4
Area =π(0,06)2
4
= 2,827433 x 10-3m2
σ = F
A
250 x 106 = F
2,8274333 x 10-3
F = 706 858,35 N
ACCEPT: 706 500 N OR 707 500 N
OPTION 2
Area = πr2
Area = π(0,03)2
= 2,827433 x 10-3m2
σ = F
A
250 x 106 = F
2,8274333 x 10-3
F = 706 858,35 N
ACCEPT: 706 500 N OR 707 500 N (4)
6.3 As the temperature increases, (viscosity of a fluid) decreases. (2)
6.4 A body which does not show a tendency to regain its original shape and size when the deforming force is removed. (2)
6.5
- Clay
- Wax
- Putty
- Aluminium
- Mild Steel (2)
6.6 In a continuous liquid at equilibrium, the pressure applied at any point is transmitted equally to other parts of the liquid. (2)
6.7 OPTION 1
F1 = F2
A1 A2
F1 = 20 000
0,05 0,8
F1 = 1 250 N✓
NOTE: Give full marks if F2 is calculated.
OPPTION 2
P2 = F2
A2
P2 = 20000
0,8
P2 =25000 Pa
P2 = 25×103 Pa
P2 = 25 kPa
But P1 =P2 =, then
P1 = F1/A1
25 x 103 = F1
0.05
F1= 1 250 N (4)
6.8 The normal force exerted by a liquid at rest on a given surface in contact with it.(2)
[25]
QUESTION 7
7.1.1 A is the p-type/ Positive type (semiconductor)
B is an n-type/ Negative type (semiconductor) (2)
7.1.2 ![]()
ACCEPT: If the arrow is not shaded (2)
7.1.3 Four/4 (1)
7.2 A device that stores electrical charge. (2)
7.3 The capacitance is directly proportional to the charge between the plates.
OR
C ∞ Q (2)
7.4
- Decrease surface area of the plates. ✓
- Increase distance between the plates.✓
- Use dielectric material with a low dielectric constant/ permittivity. (2)
7.5 OPTION 1
P = V2/R
P =1202
60
P =240W
P =0,24 kW
Energy used:
E =Pt
E =0,24×2
E =0,48 kWh
Cost of energy used:
Cost = E used x tariff
Cost = 0,48x1,75
Cost = R0,84
OPTION 2
P =VI
P =120×2
P =240W
P =0,24 kW
Energy used:
E =Pt
E =0,24×2
E =0,48 kWh
Cost of energy used:
Cost = E used x tariff
Cost = 0,48x1,75
Cost = R0,84
OPTION 3
P =I2R
P =22 × 60
P =240W
P =0,24 kW
Energy used
E =Pt
E =0,24×2
E =0,48 kWh
Cost of energy used:
Cost = E used x tariff
Cost = 0,48x1,75
Cost = R0,84 (7)
OPTION 4
W = V2Δt
R
=(1202) (2)
60
= 480 W
= 0,48 kWh
Cost = Eused x tariff
= (0,48)(1,75)
= R0,84
OPTION 5
W = VIΔt
= (120)(2)(2)
= 480 W
= 0,48 kWh
Cost = Eused x tariff
= (0,48)(1,75)
= R0,84
OPTION 6
W = I2RΔt
= (22)(60)(2)
= 480 W
= 0,48 kWh
Cost = Eused x tariff
= (0,48)(1,75)
= R0,84
[18]
QUESTION 8
8.1 This is the process of generating electricity from motion.
OR
The production of an emf or voltage across an electrical conductor due to relative motion between the conductor and magnetic field. (2)
8.2
- The strength of the magnetic field.
- The number of turns on the coil.
- The speed at which the magnet and coil are moved relative to each other.
(ANY TWO)(2)
8.3 (Lenz's law states that) the direction of the induced emf (in the coil) opposes the effect that produces it. ✓✓✓✓(2)
8.4
- Electromagnetic braking in trains/rotating machinery. ✓
- Electric motors✓
- Electric generators. ✓
- Induction cooking pots where the pot is heated by magnetic induction.✓
(ACCEPT ANY OTHER CORRECT APPLICATIONS) (3)
[9]
QUESTION 9
9.1.1
- – (carbon) brushes✓
- – commutator/ split ring ✓✓
- – magnet ✓(3)
9.1.2 DC motor ✓✓ (1)
9.2 OPTION 1
V2 = Ns
VP NP
20 = 110
VP 1 200
VP = 1 200 x 20
110
VP= 218,18 V
OPTION 2
Vp = Np
Vs Ns
VP = 1 200 x 20
110
VP = 218,18 V (3)
[7]
TOTAL: 150