MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY (FITTING AND MACHINING) GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2020
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: FITTING AND MACHINING
GRADE 12
NOVEMBER 2020
MEMORANDUM
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
1.1 A ✓(1)
1.2 D ✓ (1)
1.3 A ✓ (1)
1.4 C ✓ (1)
1.5 B ✓ (1)
1.6 B ✓ (1)
[6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Work procedures on machine:
Switch off machine. ✓ (1)
2.2 The horizontal band saw:
- No adjustments to machine or work piece✓
- Ensure sufficient coolant on work piece and blade. ✓
- Do not leave machine unattended while in operation. ✓
- Do not lean on machine.✓
- Keep hands clear from blade. ✓
(Any 2 x 1)(2)
2.3 Surgical gloves:
- Prevent contamination of wound✓
- To prevent transmission of HIV/AIDS or any blood related diseases to the first aid helper. ✓(2)
2.4 Personal protective equipment (PPE) during arc welding:
- Welding helmet / Helmet✓
- Safety goggles / Face shield ✓
- Leather apron / Apron✓
- Leather gloves / Gloves ✓
- Leather spat / Spats ✓
- Safety boots / Safety shoes ✓
- Over-all ✓
- Skull cap✓
- Neck protection ✓
- Ear plugs / Ear muffs. ✓
- Respirator ✓
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5 Responsibility of the employer regarding the health and safety:
- Sufficient lighting ✓✓
- Sufficient ventilation✓✓
- Provide first-aid equipment✓✓
- Provide a safe / clean working environment ✓✓
- Provide personal protective equipment (PPE) ✓✓
- Provide safety training to employees ✓✓
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
2.6 Responsible for administering first aid:
A qualified / trained first aid person ✓(1)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Tests to identify various metals:
3.1.1 Sound test:
- Tapping the metal with a hammer (any metal object) ✓ and identify the sound. ✓
- Dropping the metal on the floor ✓and identify the sound.✓
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.1.2 File test:
File the metal and pay attention to the bite of the file into the metal.✓The bigger the bite the softer the metal. OR The smaller the bite the harder the metal.✓ (2)
3.2 Purpose of heat treatment of steel:
- To change ✓ the properties ✓ of steel.
- To change ✓the grain structure ✓ of steel.
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.3 Purpose of case hardening on steel:
To create a hard / wear resistance surface / case ✓ with a tough core. ✓ (2)
3.4 The tempering process for steel:
- Heat the steel to a temperature (temper colour) below the critical temperature. ✓
- Soak it at that temperature for a period.✓
- Quench / cool in an appropriate quenching agent. ✓ (water, brine, or oil) (3)
3.5 THREE factors for heat treatment of steel:
- Heating temperature / Carbon content ✓
- Soaking (Time period at temperature) / Work piece size✓
- Cooling rate / Quenching rate (Quenching medium) ✓ (3)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 C ✓ (1)
4.2 B ✓ (1)
4.3 A ✓ (1)
4.4 A / B ✓ (1)
4.5 C ✓ (1)
4.6 B ✓ (1)
4.7 C ✓ (1)
4.8 C ✓ (1)
4.9 D ✓ (1)
4.10 A ✓ (1)
4.11 C ✓ (1)
4.12 B ✓ (1)
4.13 B ✓ (1)
4.14 C ✓ (1)
[14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (LATHE AND MILLING MACHINE) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Taper turning:
5.1.1 Taper: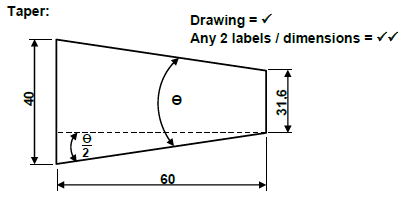
(3)
5.1.2 Included angle:
Tan θ/2 =D - d
2L
Tanθ/2 =40 - 31.6
2 x 60
θ/2 = 4.004º
θ = 8º (4)
5.1.3 Angle of compound slide:
Half the included angle:
θ/2 = 4º (1)
5.2 Parallel key:
Width:
Width W = diameter
4
= 30
4
= 7,5 mm
Length:
Length L = 1,5 diameter
= 1,5 x 30
= 45 mm (4)
5.3 Centring a milling cutter:
X = diameter of workpiece - thickness of cutter
2
= 60 - 15
2
= 45
2
= 22,5 mm (3)
5.4 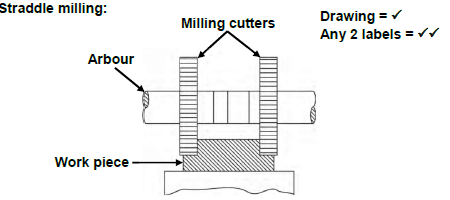
[18]
QUESTION 6: TERMINOLOGY (INDEXING) (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Spur gear terminology:
6.1.1 Outside diameter:
Outside diameter = PCD + 2m
= mT + 2m
= (3 x 51) (2 x 3)
= 153 + 6
= 159 mm
OR
Outside diameter = m(T + 2)
= 3(51 + 2)
= 3(53)
= 159 mm
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
6.1.2 Cutting depth:
Cutting depth = 2,157m
= 2,157 x 3
= 6,471 mm
OR
Cutting depth = 2,25m
= 2,25 x 3
= 6,75 mm
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
6.1.3 Simple indexing:
Simple Indexing = 40/N
=40/51
0 full turns and 40 holes on the 51-hole circle (3)
6.2 Differential indexing:
6.2.1 Differential indexing: (Choose 80 divisions)
Simple indexing = 40/n
SI = 40/83 (indexing not possible , choose 80)
DI = 40/80
= ½ x 12/12
= 12/24
No full turns and 12 holes on the 24 hole circle
No full turns and 14 holes on the 28 hole circle
No full turns and 15 holes on the 30 hole circle
No full turns and 17 holes on the 34 hole circle
No full turns and 19 holes on the 38 hole circle
No full turns and 21 holes on the 42 hole circle
No full turns and 23 holes on the 46 hole circle
No full turns and 27 holes on the 54 hole circle
No full turns and 29 holes on the 58 hole circle
No full turns and 31 holes on the 62 hole circle
No full turns and 33 holes on the 66 hole circle
(Any 1 x 4) (4)
6.2.2 Change-gears:
Driver =A - N x 40
Driven A 1
=80 - 83 x 40
80 1
= -3/80 x 40/1
= -120/80
= -12/8 x 6/6
= -72/48
OR
Driver =A - N x 40
Driven A 1
=80 - 83 x 40
80 1
= -3/80 x 40/1
= -120/80
= -12/8 x 4/4
= -48/32
ALTERNATIVE FORMULA
Change-gears:
Driver = A - N x 40
Driven A
= 80 - 83 x 40/80
= -3 x ½
=- 3 x 24
2 x 24
= - 72/48
OR
Driver = A - N x 40
Driven A
= 80 - 83 x 40/80
= -3 x ½
=- 3 x 16
2 x 16
= - 48/32
(Any 1 x 5) (5)
6.2.3 The rotation of the index plate relative to the index crank:
Index plate rotates in the opposite direction to the index crank. (1)
6.3 Dove tail: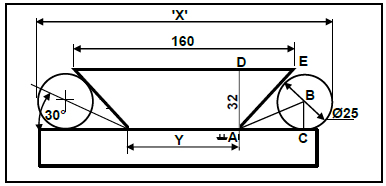
Calculate X:
X = Y + 2(AC+r)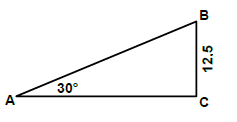
Calculate AC:
Tan θ = BC/AC
AC = BC
Tan θ
= 12.5
Tan 30º
= 21,65 mm
OR Calculate AC:
Sin30° = BC/AB
AB = BC
Sin 30°
= 12,5
Sin 30°
= 25mm
AC2 = AB2 - BC2
AC = √252 - 12.52
= 21,65mm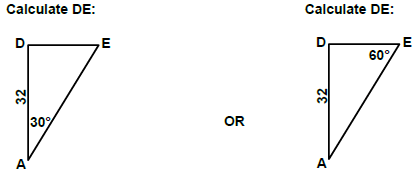
Tan 30º =DE/AD
DE = Tan30º x AD
= Tan30º x 32
= 18,48 mm
OR
Tan 60° = AD/DE
DE = AD
Tan 60°
= 32
Tan 60°
=18,48mm
Calculate Y:
Y = 160 2(DE)
= 160 -2(18,48)
= 160 - 36,96
Y = 123,04mm
Calculate X:
X = Y + 2(AC + r)
= 123,04 + 2(21,65 + 12,5)
= 123,04 + 68,3
X = 191,34mm (9)
6.4 Reasons for balancing a work piece on a lathe:
- Prevent unnecessary bearing loads ✓
- Prevent excessive vibration✓
- To obtain a good finish✓
- To prevent clatter on the gear teeth ✓
- To prevent the spindle from bending ✓
- To ensure accuracy✓
- Ensure the safety of the worker ✓
- Prevent damage to the cutting tool / equipment ✓
- Ensure that the work piece is perfectly round ✓
- Prevent work piece from slipping from the chuck ✓
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
[28]
QUESTION 7: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
7.1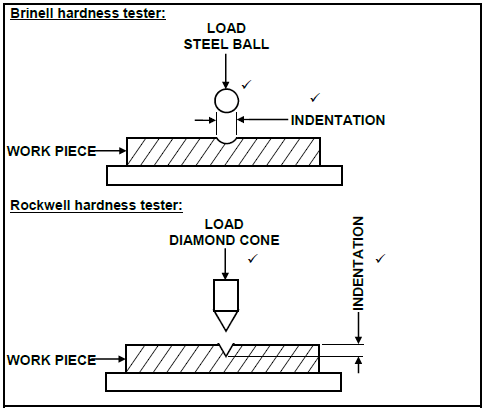 (4)
(4)
7.2 Function of tensile tester:
To demonstrate the fundamentals / tensile properties ✓of different materials. ✓ (2)
7.3 Precision measuring instruments:
- Outside micrometer✓
- Inside micrometer✓
- Depth micrometer ✓ (3)
7.4Properties determined by a tensile test:
- Tensile strength✓
- Elasticity ✓
- Ductility✓
- Plasticity ✓
- Strain ✓
(Any 3 x 1) (3)
7.5 Measuring instrument for root diameter on a screw thread:
- Screw thread micro meter ✓
- Vernier calliper✓
(Any 1 x 1) (1)
[13]
QUESTION 8: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Resultant: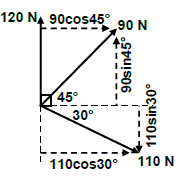
ΣHC = 90cos45º + 110cos30º
= 63,64 + 95,26
= 158,90 N
OR
ΣVC = 120 + 90sin45º - 110sin30º
= 120 + 63,64 - 55
= 128,64N
| Horizontal components | Magnitudes | Vertical components | Magnitudes |
| 120 | 120 N | ||
| 90Cos45° | 63,64 N | 90Sin45° | 63,64 N |
| 110Cos30° | 95,26 N | -110Sin30° | -55 N |
| TOTAL | 158,90 N | TOTAL | 128,64 N |
R2 = HC2 + VC2
R = √158,902 + 128,642
R = 204,44N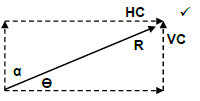
Tanθ = VC
HC
= 128,64
158,90
θ = 38,99 or 38 59'24"
OR
Tanα = HC
VC
= 158,90
128,64
α = 51,01 or 50 00'36"
R 204,44N at 51,01 east of north
OR
R 204,44N at 38,99 north of east
Can also state cos 330° instead of cos 30°/ and sin 330° instead of sin 30°
(13)
8.2 Moments:
Take moments about “O”.
ΣRHM = ΣLHM
500 x "X" = 3000 x 1,5
500 x "X" = 4500
"X" = 4500
500
"X" = 9m (4)
8.3 Stress and Strain:
8.3.1 Type of stress:
Compressive stress (1)
8.3.2 Stress:
A = L x B
= 0,03 x 0,016
= 0,48 x 10-3 m2
σ = F/A
= 50 x 10 3
0,48 x 10-3
σ = 104,17 x 106 Pa
σ = 104,17 MPa (6)
8.3.3 Change in length:
E =σ/ε
ε = σ/E
= 104,17 x 106
90 x 109
= 1,16 10
ε = ΔL
L
ΔL = ε x L
= (1,16 x 10-3) x 80
= 0,09 mm
8.3.4 Safe working stress:
Safety factor = Break stress
Safe working stress
Safe working stress = Break stress
Safety factor
= 600
4
= 150 MPa (3)
[33]
QUESTION 9: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Preventative maintenance of a belt drive system:
- Checking for wear and tear on belt.✓
- Checking belt alignment. ✓
- Checking the tension setting. ✓
- Checking the tensioning device, e.g. jockeys. ✓
- Checking for wear on the pulleys.✓
- Checking for wear on pulley bushes. ✓
- Check for dirt on the system. ✓
(Any 3 x 1) (3)
9.2 Results of a lack of preventative maintenance on a gear drive system:
- A loss / lack of lubrication. ✓
- Loose components. ✓
- Misalignment of gear components.✓
- Contamination of lubricants. ✓
- Noisy operation. ✓
- Excessive wear on components.✓
- Excessive vibration in the system. ✓
- Excessive heat generated.✓
- Malfunctioning of gear system ✓
- Loss of production ✓
- Risk of injuries / death✓
- Financial loss✓
(Any 3 x 1) (3)
9.3 Procedures to reduce wear on a chain drive system:
- Adjust the chain alignment. ✓
- Adjust the chain tension / mechanism. ✓
- Prevent overloading of the system.✓
- Keep the sprockets and chain clean.✓
- Repair or replace worn sprockets and chains.✓
- Ensure adequate lubrication.✓
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.4 Replace the belt on a flat belt drive system:
- Switch off the machine ✓
- Release the tension on the belt. ✓
- Remove the belt from the pulleys. ✓
- Fit the correct size replacement belt onto the pulleys.✓
- Check the pulley's condition and alignment.✓
- Apply adequate tension to the belt and lock the system.✓
- Check for proper functioning. ✓
(Any 5 x 1) (5)
9.5 Properties of Bakelite:
- Non-conductive (Heat and Electricity) ✓
- Heat-resistant ✓
- Brittle✓
- Hard✓
- Can’t be deformed by heat (Thermo-hardened / Thermosetting) ✓
- Cast easily ✓
- Resistance to chemicals ✓
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.6 Properties that make Vesconite an outstanding bearing material:
- Wear resistance / Longer lifespan ✓
- Very versatile✓
- High load bearing strength / strong✓
- High temperature limits✓
- Little to no water absorption✓
- High chemical resistance ✓
- Very low co-efficient of friction ✓
- Resistance to fuels, oils and hydrocarbons✓
- Very good machinability ✓
- Tough ✓
(Any 3 x 1) (3)
[18]
QUESTION 10: JOINING METHODS (SPECIFIC)
10.1 Square thread:
10.1.1 The lead of the thread:
Lead = pitch x no of starts
= 6 x 3
= 18 mm (2)
10.1.2 The helix angle of the screw thread:
Pitch diameter = OD - (P/2)
= 58 - 6/2
= 55 mm
Pitch circumference = π x Pitch diameter
= π x 55
= 172,79 mm
Helix angle tanθ = Lead
Pitch circumference
= 18
172,79
θ = 5,95º or 5 57'
OR
Helix angle tanθ = Lead
π x (OD - P/2)
= 18
π x (58 - 6/2)
= 18
172,79
θ = 5,95º or 5º57' (5)
10.1.3 Leading angle:
Leading angle = 90º - (helix angle + clearanceangle)
= 90º -(5,95º + 3º)
= 81,05º (2)
10.1.4 Following angle:
Following angle = 90 + (helix angle - clearanceangle)
= 90º + (5,95º - 3º)
= 92,95 (2)
10.2 M20 x 2,5. Drill size:
Drill diameter = OD - P
= 20 - 2,5
= 17,5 mm (3)
10.3 Pitch of a screw thread:
The pitch is the axial distance ✓measured from any given point ✓on the screw thread to a corresponding point ✓ on an adjacent thread. ✓ (4)
[18]
QUESTION 11: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (DRIVE SYSTEMS) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 Advantages of a belt drive system compared to a gear drive system:
- Silent operation ✓
- Cheaper parts✓
- Transmit power over a longer distance✓
- Can change direction without additional parts✓
- Easy to replace parts✓
- No lubrication needed ✓
- Belt drive slip may prevent system damages or injuries ✓
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
11.2 Belt drive system:
11.2.1 Rotation frequency of driven pulley in r/sec:
NDR x DDN = NDR x DDR
DDN = NDR x DDR
DDN
=1100 x 0.24
0.36
= 733.33r/min
= 12.22 r/sec (4)
11.2.2 The power transmitted in kW:
P= (T1 - T2)πDN
60
P = (200 - 90)π x 0.24 x 1100
60
= 1520,53 Watt
= 1,52 kW
OR
P= (T1 - T2)πDN
60
P = (200 - 90)π x 0.36 x 733.33
60
= 1520,53 Watt
= 1,52 kW (4)
11.2.3 The belt speed in m.s-1:
v = πDN
60
= π x 0.24 x 1100
60
= 13.82m.s-1
OR
v = πDN
60
= π x 0.36 x 733.33
60
= 13.82m.s-1 (3)
11.3 Hydraulics:
11.3.1 Fluid pressure:
AA = πDA2
4
AA = π(0.04)2
4
AA =1.26 x 10-3m2
P = FA
AA
P = 80
0.00126
P = 63,49 x 103 Pa OR 63,66 x 103 Pa
P = 63,49 kPa OR 63,66 kPa (4)
11.3.2 Diameter of piston B in millimetres:
FA = FB
AA AB
AB =FB x AA
FA
= 320 x 0,00126
80
= 5,04 x 10-3 m2
AB =π x DB2
4
DB √AB x 4
π
= √(5,04 x 10-3) x 4
π
= 0,0801 m
= 80,11mm
Calculation without rounding off:
AB =π x DB2
4
DB √AB x 4
π
= √(5,026548246 x 10-3) x 4
π
= 0,08 m x 1000
= 80 mm (7)
11.4 Gear drive system:
Rotition frequency of driven gear:
NF =TA x TC x TE
NA TB x TD x TF
NF =TA x TC x TE x NA
TB x TD x TF
NF =20 x 18 x 42 x 1440
36 x 46 x 80
= 164,35 r/min
60
= 2,74 r/sec
OR
NB x TB = NA x TA
NB x 36 = 1440 x 20
NB =1440 x 20
36
NB = 800 r/min
NB = NC
ND x TD= NC x TC
ND x 46 = 800 x 18
ND = 800 x 18
46
ND = 313,04r/min
ND = NE
NF x 80 = 313,04 x 42
NF = 313,04 x 42
80
NF = 164,35r/min
60
NF = 2,74r/sec (4)
[28]
TOTAL: 200