MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE SEPTEMBER 2016
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
MEMORANDUM
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
SEPTEMBER 2016
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1 D ✓ Make certain the dipstick is in the hole. (1)
1.2 D ✓ All the abovementioned. (1)
1.3 B ✓ Guards should be removed when cutting metals. (1)
1.4 C ✓ Multimeter (1)
1.5 C ✓ deflection (1)
1.6 C ✓ iron carbide (1)
1.7 B ✓ 480 °C - 520 °C (1)
1.8 D ✓ 25 mm (1)
1.9 B ✓ Cylinder head (1)
1.10 A ✓ To determine the percentage of elongation of the weld metal. (1)
1.11 B ✓ To check for size of the weld (1)
1.12 D ✓ Resultant (1)
1.13 A ✓ 25 MPa (1)
1.14 B ✓ It must increase the engine speed. (1)
1.15 B ✓ ‘Winter grades’ (1)
1.16 C ✓ 16 : 1 (1)
1.17 C ✓ Block and tackle (1)
1.18 D ✓ ABS braking system (1)
1.19 C ✓ mechanical drive. (1)
1.20 C ✓ Kaplan (1)
[20]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY
2.1
- Make sure all the guards are in place. ✓
- Do not use or come close to its moving parts while wearing loose clothing. ✓
- Keep any cleaning material such as waste and rags away from rotating parts.
- Check that there are no oil or grease on the floor around the machine.
- Do not leave spanners or keys on rotary parts. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2
- The welding operator should know how to operate the oxy-acetylene welding plant safely. ✓
- The work place should be partitioned off effectively. ✓
- The operator should wear protective equipment.
- Never use damaged equipment.
- Never use oil or grease near oxygen equipment. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3
- Ensure that the beam is clamped parallel to the back board. ✓
- Do not leave plastic beams loaded for any length of time. ✓
- Gently drop the weights onto the hanger. ✓ (3)
2.4
- The operator should be instructed to use the machine safely. ✓
- The work place should be effectively partitioned off. ✓
- An operator uses protective equipment while using the equipment. ✓
- The operator should ensure that the insulation of electric leads are satisfactory. (Any 3 x 1) (3)
[10]
QUESTION 3: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
3.1
- It involves the indenting of the test material with a diamond cone or hardened steel-ball indenter.✓
- The indenter is forced into the test material under a preliminary minor load (FO), usually 10 kgf.✓
- The permanent increase in depth of penetration, resulting from the application and removal of the additional major load, ✓ is used to calculate the Rockwell Hardness Number.✓ (4)
3.2
- To test the system for leaks. ✓
- To pump compressed air into the cooling system of a motor car to determine whether there are any leaks in the system. ✓
- To test if the pressure cap on the cooling system operates according to the prescribed pressure of the system. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.3
3.3.1
- To determine the fuel operating pressure in the system. ✓
- To test the pressure of the fuel in the fuel line that runs to the direct injection system. ✓ (2)
3.3.2
- To test different electrical components and concepts. ✓
- To test current, voltage, resistance, continuity, transistors and diodes. ✓ (2)
3.4 1 mm + 0,5 mm + 0,25 mm = 1,75 mm ✓✓ (2)
[12]
QUESTION 4: MATERIALS
4.1
4.1.1 Pearlite is a type of crystal formed before hardening when the steel contains 0,83% carbon. ✓✓ (2)
4.1.2 Carbon Content is the mixture that is added to steel to change the property of the metal. ✓✓ (2)
4.1.3 Martensite is the structure obtained when austenite is quenched suddenly. ✓✓ (2)
4.2
- Alloying ✓
- Heat treatment ✓ (2)
4.3 To increase service life of a product or to prepare the material for improved manufacturability.✓ (2)
4.4 A map of the temperature at which different phase changes occur ✓ on very slow heating and cooling in relation to carbon. ✓ (2)
4.5 Iron carbide (which is a component of Iron carbon (Fe2C) found in steel and cast iron. ✓ (1)
[13]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY
5.1
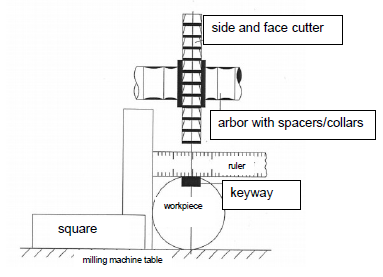
5.2
5.2.1 Conventional milling also regarded as up-cut milling is the process whereby the cutter turns against the direction of feed ✓as the work piece moves toward it from the side where the teeth are moving upwards. ✓ (2)
5.2.2 Climb milling also regarded as down-cut milling is the process where all looseness in the table-feed screw must be eliminated, ✓ where the motion of the cutter tends to pull the work piece into the cutter. ✓ (2)
5.3 Indexing required:
Number of turns = 40 = 40
N 43
There will be no turns but 40 holes in a 43 hole plate. ✓✓ (4)
5.4 Class 1: ✓ for screw thread work in which shake or play is not objectionable ✓
Class 2: ✓ for threaded parts that can be put together with the fingers(hand tight) ✓
Class 3: ✓ for higher grade of threaded parts, requiring greater accuracy ✓
Class 4: ✓ for the finest threaded work ✓ (8)
5.5 Identify: Milling process ✓
Name: Gear cutting ✓ (2)
5.6
- Anvil✓
- Screw thread✓
- Barrel✓
- Thimble✓
- Spindle✓
- Frame✓ (6)
[30]
QUESTION 6: JOINING METHODS
6.1
| DEFECT | PREVENTION | |
| 6.1.1 | Porosity✓ |
|
| 6.1.2 | Incomplete penetration✓ |
|
| 6.1.3 | Slag inclusion ✓ |
|
6.2
- Nick-break test ✓
- Nick-bend test ✓
- Machinability test✓ (3)
6.3
- Continuous wire reel ✓
- Wire feed unit ✓
- Power cable ✓
- Gun conduit ✓
- Welding gun ✓
- Shielding gas cylinder ✓
- Regulator
- Flow meter
- Gas hose (Any 6 x 1) (6)
6.4
- Use a hacksaw and cut both edges through the centre of the weld approximately 6,5 mm deep. ✓
- Place the saw-nicked specimen on two steel supports ✓ and use a sledge hammer to break the specimen by striking it in the zone where you made the saw cuts. ✓
- The weld metal exposed in the break should be completely fused, ✓ free from slag inclusion and contain no gas pockets greater than 1,6 mm. ✓
- There should not be more than one pore or gas pocket per square centimetre visible. ✓ (6)
6.5
- Motor ✓
- Tension roller ✓
- Consumable wire reel ✓
- Wire liner ✓ (4)
[25]
QUESTION 7: FORCES
7.1
7.1.1
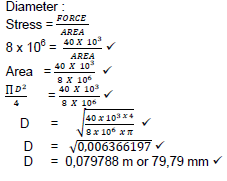
(6)
7.1.2 Young’s Modulus = Stress
Strain

(3)
7.1.3 Change in Length:
Strain = Change in length
Original Length
Change in Length = Strain x Original Length ✓
= 0,0001333 x 275 ✓
= 0,0366575 mm ✓ (3)
7.2
7.2.1 AP = π x0,0342
4
AP = 0,00090792 m2 ✓
P = FP
AP
P = 320
0,00090792
P = 352453,8532 kN ✓ (3)
7.2.2 Diameter of the Ram:
AR = FR
P
= 35 x 103
352453,8532
= 0,09930378
BUT: Area =πD2
4
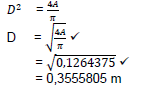
Diameter of Ram = 35,5 mm ✓ (4)
7.3 L :(R x 8 = (8 x 2) + (50 x 4) + (30 x 10) ✓
= 16 + 200 + 300
R = 516
8
R = 64,5 N ✓
R : (L x 8) + (30 x 2) = (50 x 4 ) + (8 x 6) ✓
(L x 8) + 60 = 200 + 48
RL = 188
8
RL = 23,5 N ✓
To check if the beam is in equilibrium:
Downward forces = Up ward forces
8 + 50 N + 30 N = 64,5 N + 23,5 N
88 N = 88 N (6)
7.4 Solution:
The horizontal component of the resultant is:
H = 15 Cos 30° + 20 Cos 60° – 10 Cos 10°
AND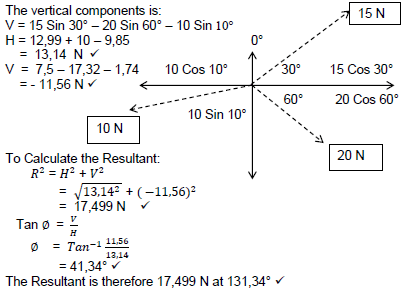
(5)
[30]
QUESTION 8: MAINTENANCE
8.1
- Gear lever ✓
- Selector for gear changes ✓
- Splined input shaft ✓
- Lay shaft ✓ (4)
8.2 Because it gives of vapours which ignite✓ and therefore a high flashpoint is required. ✓(2)
8.3 It is used in the turning process on a lathe✓ as illustrated by the drawing, cutting a thread on a shaft. ✓ (3)
8.4
- Flywheel ✓
- Diaphragm ✓
- Crankshaft ✓
- Clutch plate ✓
- Throw-out release lever ✓
- Pressure plate ✓ (6)
[15]
QUESTION 9: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL
9.1
9.1.1 Rotational Frequency of the output shaft:
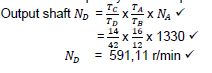
(3)
9.1.2 Velocity Ratio:
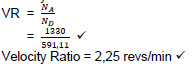
(2)
9.2
9.2.1 Fluid Pressure:
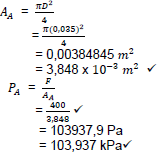
(3)
9.2.2 Load that can be lifted:
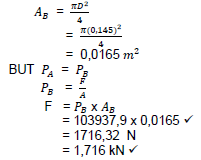
(2)
9.3
9.3.1 Rotational Frequency of the driven pulley.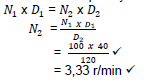 (2)
(2)
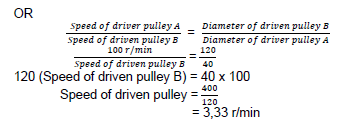
9.3.2 Power transmitted: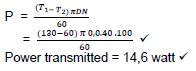 (2)
(2)
9.3.3 Belt speed:
V = πDN
60
= π.0,04.100
60
= 0,209 m/sec ✓ (2)
9.4 New Pressure:
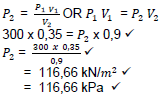
(4)
9.5 Purpose of airbags:
- It provides protection for the head and upper body of the driver and passengers of a motor vehicle during a collision. ✓
- In head on collisions, drivers and passengers are thrown forward inside the vehicles and when the airbags is activated, it inflates instantly and creates a firm barrier which counters the forward motion of the driver or front seat passenger. ✓
- It is designed to prevent the occupants from hitting the windscreen or dashboard of the vehicle. ✓
- It is also designed to work in conjunction with seat belts. ✓ (5)
[25]
QUESTION 10: TURBINES
10.1
- Wicket gate ✓
- Blades ✓
- Water flow ✓
- Rotor ✓
- Stator ✓
- Shaft ✓ (6)
10.2
- Reaction turbines ✓
- Impulse turbines ✓ (2)
10.3 Air is compressed isentropically, ✓ combustion occurs at constant pressure ✓ and expansion over the turbine occurs isentropically ✓ back to the starting pressure. ✓ (4)
10.4 Advantages of steam turbines:
- It has greater thermal efficiency and higher power-to-weight ratio. ✓
- It is suited to drive an electrical generator. ✓
- It does not require a linkage mechanism to convert reciprocating motion to rotary motion. ✓
- It uses multiple stages in the expansion of the steam, which results in greater efficiency. ✓
- It is compact.
- No lubrication is required.
- Can be more accurately regulated.
- A variety of fuels can be used to obtain steam.
- It converts heat energy into mechanical energy (Any 4 x 1) (4)
10.5 Advantages of gas turbines:
- It has smooth vibration ✓
- It is easy to start ✓
- It has no rubbing parts such as pistons ✓
- No internal friction and wear ✓
- Higher power output from a given weight of engine
- Can use a wide range of fuels
- No water cooling system needed
- Require little routine maintenance
- Very little trouble with pollution (Any 4 x 1) (4)
[20]
TOTAL: 200