AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2020
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
NOVEMBER 2020
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read the questions carefully and answer only what has been asked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The section in a worker's contract which indicates the position occupied by the worker:
- Job description
- Job title
- Workplace
- Starting date
1.1.2 The employee's information required in a worker's contract:
- Name and ID number
- Meal breaks
- Annual leave
Date of employment
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
1.1.3 A type of leave a permanent farm worker is entitled to:
- Bonus leave
- Family responsibility leave
- Resting leave
- Funeral leave
1.1.4 A loss of soil quality and productivity:
- Erosion
- Pollution
- Degradation
- Conservation
1.1.5 A type of farmer who uses most of the farm produce for household consumption:
- Cash crop farmer
- Subsistence farmer
- Commercial farmer
- Irrigation farmer
1.1.6 A resource in the primary sector of the farming business that needs both physical and mental inputs to produce goods and services:
- Physical resource
- Natural resource
- Financial resource
- Human resource
1.1.7 An incentive given to workers to improve their level of performance:
- Exploitation
- Disciplinary action
- Good living conditions
- Corrective measures
1.1.8 The type of agritourism where people visit farms with the aim of trophy hunting:
- Game farm stays and trips
- Product routes
- Cultural tourists
- Adventure tourists
1.1.9 A person who transforms commodities using value-adding methods:
- Retailer
- Processor
- Wholesaler
- Producer
1.1.10 The marketing organisation established by the government to provide international trade information:
- Outspan and Unifruco
- Product export control board
- South African Foreign Trade Organisation
- Capespan Group Ltd (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term/phrase in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–L) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.11 M. Use each description in COLUMN B only ONCE.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.2.1 Inventory 1.2.2 Product colour 1.2.3 Record keeping 1.2.4 Straight line 1.2.5 Planters 1.2.6 Drying 1.2.7 Free marketing 1.2.8 Marketing of Agricultural Products Act, 1996 (Act 47 of 1996) 1.2.9 Business survival strategy 1.2.10 Business threat |
|
(10 x 2) (20)
1.3 Give the CORRECT agricultural term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.3.6 Recording.
1.3.1 A financial document indicating all possible income and expenditure of a farming enterprise for a year
1.3.2 The process used to select products for different markets
1.3.3 The Labour Act addressing procedures on the termination of employment
1.3.4 An excessive quantity of products or goods available in the market
1.3.5 Business expenses that must be met within a short period of time (5 x 1) (5)
1.4 The following statements are INCORRECT. Change the UNDERLINED word(s) to make the statements CORRECT. Write the answers next to the question numbers (1.4.1 to 1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.4.6 Fixed Capital.
1.4.1 Monoculture ensures better utilisation of land, labour and capital.
1.4.2 Credit can only be created if the necessary funds are available.
1.4.3 Flexibility of the market should be maintained in respect of supply and demand.
1.4.4 Plains is a characteristic of natural pastures consisting of mountains, plateaus and slopes.
1.4.5 Free marketing is when farmers supply their produce to large chain stores or food suppliers based on a written agreement. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: PHYSICAL AND FINANCIAL PLANNING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Describe how strong winds can influence crop production negatively. (3)
2.2 Farm workers have the right to work in a safe environment.
2.2.1 Name the Act that provides for a safe workplace. (1)
2.2.2 Name FOUR protective measures that workers must consider when working with dangerous substances. (4)
2.3 Redraw the table below in the ANSWER BOOK and complete it by indicating the type of capital needed for each item with a tick () in the appropriate block.
| FARM ITEM | LONG-TERM CAPITAL (FIXED CAPITAL) | MEDIUM-TERM CAPITAL (MOVABLE CAPITAL) | SHORT-TERM CAPITAL (WORKING CAPITAL) |
| E.g. Fertilisers | |||
| Livestock | |||
| Implements | |||
| Fences | |||
| Wages |
(4)
2.4 Identify EACH of the types of farm labourers described below:
2.4.1 Labourers that harvest fruit during a specific time of the year(1)
2.4.2 Labourers milking cows in the morning and the afternoon(1)
2.4.3 A bricklayer hired to build a concrete reservoir on the farm(1)
2.5 Discuss FIVE ways of protecting soil fertility against erosion and loss of nutrients.(5)
2.6 Distinguish between commercial farming and subsistence farming with regard to the following aspects:
2.6.1 Use of technology(2)
2.6.2 Volume of output (2)
2.7 The sketches below illustrate camp systems designed for rotational grazing.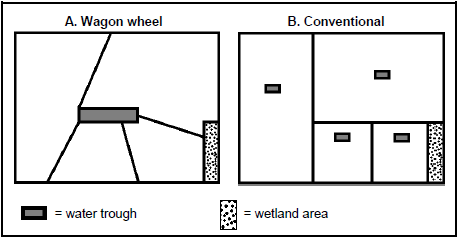
2.7.1 Give an explanation of why some camps are bigger than others. (2)
2.7.2 Discuss the advantages of the wagon wheel layout (A). (3)
2.7.3 Explain how the farmer can solve the problem of grazing camps of different sizes. (2)
2.7.4 Give THREE reasons why it is necessary to give camps a resting period in a rotational grazing system. (3)
2.8 Soil data collected during sampling describes the nature of the soils by referring to their properties.
Discuss the influence of the following TWO properties on the production capability of the soil:
2.8.1 Soil colour(4)
2.8.2 Soil texture (6)
2.9 Discuss the effect of soil pollution that occurs due to the incorrect application of pesticides, under the following headings:
2.9.1 Soil degradation(2)
2.9.2 Water pollution (2)
2.10 Give TWO examples of where animal traction could be used on a farm. (2)
[50]
QUESTION 3: ENTREPRENEURSHIP, RECORDING, MARKETING, BUSINESS PLANNING AND ORGANISED AGRICULTURE
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Give FOUR important aspects that a farmer should consider when a market survey is analysed before starting a new business. (4)
3.2 The list below shows the different types of businesses found in the agriculture sector.
- Agritourism
- Vegetable production
- Feed companies
- Irrigation equipment supplier
- Dairy
- Abattoirs
Deduce from the list above which TWO businesses can be categorised into EACH of the following:
3.2.1 The primary agricultural sector (2)
3.2.2 The secondary agricultural sector (2)
3.2.3 The tertiary agricultural sector (2)
3.3 Compare the features of free marketing and cooperative marketing of agricultural products. Write only the answers next to the question numbers (3.3.1 to 3.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| FEATURES | FREE MARKETING | COOPERATIVE MARKETING |
| Bargaining power | 3.3.1 | 3.3.4 |
| Marketing costs | 3.3.2 | 3.3.5 |
| Consumer protection | 3.3.3 | 3.3.6 |
(6)
3.4 Give TWO reasons why a farmer needs finance when selling the produce. (2)
3.5 The prices of goods in any market depend on the interaction of three factors. Name the THREE factors and describe how each will determine the price. (6)
3.6 Advise a farmer about the best time to take produce to the market in order to make the greatest possible profit from the sale of produce. (4)
3.7 CROP PRODUCTION BUDGET
| EXPECTED EXPENDITURE | |||
| ITEM | QUANTITY | VALUE | TOTAL |
| Seed | 2 kg | R40/kg | (a) |
| Fertilisers | 850 kg | R280/50 kg | R4 760 |
| Transport of fertilisers | 17 bags | R5/bag | (b) |
| Pesticides | 500 g | R187/500 g | R187 |
| Wages per week | 4 workers | R400/worker | (c) |
| Packaging materials | 1 500 units | R1/unit | R1 500 |
| Transport to markets | 6 trips | R300/trip | R1 800 |
| TOTAL EXPECTED EXPENSES | (d) | ||
| EXPECTED INCOME | ITEM | QUANTITY | VALUE |
| Harvested crops | 1 500 bags | R15/bag | (e) |
| TOTAL EXPECTED INCOME | |||
3.7.1 Define a budget. (2)
3.7.2 Calculate the missing amounts (a) to (e). (5)
3.7.3 Calculate the profit or loss. Motivate your answer. Show ALL the calculations and the formula for calculations. (4)
3.7.4 Name TWO basic elements of a budget. (2)
3.8 Complete the table below in the ANSWER BOOK. Use the table to classify the following records as production, physical or financial records.
LIST OF RECORDS
- Cash flow
- Workshop tools inventory
- Stock of seeds for next planting season
- Crop yield per ton of fertiliser used
- Number and condition of young animals born
| PRODUCTION RECORD | PHYSICAL RECORD | FINANCIAL RECORD |
(5)
3.9.1 Identify an asset that increased in value. Give a reason for your answer. (2)
3.9.2 Identify an increase in liability. (1)
3.9.3 Give a reason for the lower value of the machinery and equipment in March 2020. (1)
3.9
| BALANCE SHEET FOR THE YEAR ENDING 20 MARCH 2020 | ||
| 31 MARCH 2019 | 20 MARCH 2020 | |
| ASSETS: | R | R |
| Fixed assets | ||
| Land and buildings | 600 000 | 650 000 |
| Medium term | ||
| Vehicles | 100 000 | 100 000 |
| Machinery and equipment | 200 000 | 180 000 |
| Current assets | ||
| Cash in bank | 15 000 | 20 000 |
| Livestock on hand | 200 000 | 210 000 |
| Accounts receivable | 50 000 | 30 000 |
| Total assets | ||
| LIABILITIES: | R | R |
| Long-term loan | 400 000 | 350 000 |
| Accounts payable | 140 000 | 150 000 |
| Total liabilities | 540 000 | 500 000 |
| Owners' equity | 625 000 | 690 000 |
[50]
QUESTION 4:HARVESTING, PROCESSING, MANAGEMENT AND AGRITOURISM
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Planning is a management task where a plan of action is created.
4.1.1 Give and discuss THREE reasons for planning.
4.1.2 Rearrange, in the correct sequence (order), the following steps in the planning process: (6)
- Develop alternatives
- Analyse information
- Formulate objectives and goals
- Implementation and evaluation
- Choose between alternatives
- Collect information (6)
4.2 A part of labour management is to ensure that the correct legal documents are available.
Give FIVE reasons why a contract between an employer and an employee (worker) is so important. (5)
4.3 Explain the storage of agricultural products in terms of the following:
4.3.1 Temperature(1)
4.3.2 Ventilation (1)
4.4 The farmer can process agricultural products to stop decay.
4.4.1 State the main aim of processing agricultural products.(2)
4.4.2 Briefly discuss THREE disadvantages of processing.(3)
4.4.3 Name THREE ideal requirements of suitable packaging material.(3)
4.4.4 Name TWO types of packaging material.(2)
4.5 The Department of Health considers the routine medical examination of food handlers as unreliable in the prevention of food-borne disease.
4.5.1 Name ONE food-handling strategy that can prevent food-borne diseases.(1)
4.5.2 State TWO principles of a healthy food-handling strategy.(2)
4.6 Match the list of products provided (4.6.1 to 4.6.3) with the list of value-added methods below. The value-added methods should be in the correct order for each product, e.g. Fruit – graded, dried, packed.
- Cuts
- Dried
- Graded
- Sheared
- Milled
- Butter
- Packed
- Baked
4.6.1 Meat(4)
4.6.2 Wool(3)
4.6.3 Grains(4)
4.7 Agritourism is experiencing a phase of growth and development.
4.7.1 Discuss the reasons behind this positive growth in the demand for agritourism.(4)
4.7.2 Describe how agritourism can positively contribute to the economic objectives of a country.(3)
[50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 150
GRAND TOTAL: 200