Technical Sciences Paper 2 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 C (2)
1.2 C (2)
1.3 D (2)
1.4 C (2)
1.5 D (2) [10]
QUESTION 2
2.1 Functional group (1)
2.2 Macromolecule (1)
2.3 Semiconductor (1)
2.4 Electrolysis (1) [4]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Doping is the process of adding impurities to an intrinsic semiconductor to improve its conductivity. (2)
3.2
- Silicon is a pure semiconductor, as impure atoms must be added to improve conductivity.
OR - A pure semiconductor which is undoped.(2)
3.3 3.3.1 P-type semiconductor/P-tipe halfgeleier (1)
3.3.2 A diode allows the current to flow in one direction only. (1)
[6]
QUESTION 4
4.1 4.1.1 C OR G (1)
4.1.2 A (1)
4.1.3 A AND E (2)
4.1.4 B (1)
4.1.5 E (1)
4.2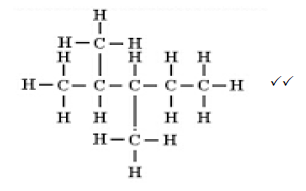 (2)
(2)
4.3 4.3.1 Addition(1)
4.3.2 HBr (1)
4.4 Pentanoic Acid and Ethanol (2)
[12]
QUESTION 5
5.1 A series of organic molecules that is defined by the same general formula and where each member differs from the next by a CH2 group. (2)
5.2
- An increase in the number of branched chains results in a decrease in the boiling point.
OR - Straight chain alkanes have a higher boiling point compared to their corresponding branched chains. (1)
5.3
- Straight-chained molecules can get closer to one another than branched molecules and have larger surface area in contact for intermolecular forces to form, therefore the Van der Waals forces/london forces are stronger. hence more energy is required to overcome intermolecular forces between the straight chain molecules compared to branched chains. therefore, straight-chained molecules have a higher boiling point.
OR - Branched chains form molecules that are more spherical with fewer points of contact for intermolecular forces. Therefore, the Van der Waals forces / London forces are weaker. Hence less energy is required to overcome intermolecular forces between the branched chains compared to straight chains, thus a lower boiling point. (4)
5.4 The learner should:
- Avoid direct heating with an open flame.
- Work in a well-ventilated area. Any one
- Use a fume hood.
Reason: Alkanes are fuels and are highly flammable (2)
[9]
QUESTION 6
6.1
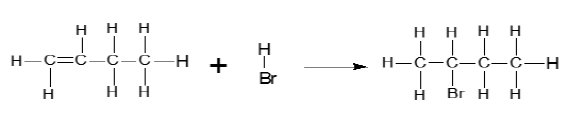 (4)
(4)
MARKING CRITERIA
- Correct structure of reactants. (2)
- Correct structure of the product(2)
6.2 Hydrohalogenation/addition. (1)
6.3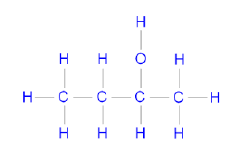
Butan-2-ol (2-butanol) (3)
6.4 Hydrolysis (1)
6.5
6.5.1 Water (1)
6.5.2 H2SO4 / HCℓ / H3PO4 (1)
6.5.3 Hydration (Accept: Addition) (1)
6.6
- Manufacturing of plastic bags (Any one )
- Synthesis of bullet proof vests
- Manufacturing of squeeze bottles
- Manufacturing of cling wrap (1)
[13]
QUESTION 7
7.1
- An electrolyte is a substance of which the aqueous solution contains ions.
OR - A substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that conducts electricity.
OR - A substance that forms free ions when melted. (2)
7.2 Electrolytic cell (1)
7.3
7.3.Cu2+ (aq) + 2e– → Cu (s) (1)
7.3.2 2Cl- (aq) → Cl2(g) + 2e- (1)
7.4 Chlorine (1)
7.5 Conversion of electrical energy to chemical energy. (1)
[7]
QUESTION 8
8.1
- Salt bridge. It maintains electrical neutrality.
OR - It separates the two compartments so that they do not mix. (2)
8.2 Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. (1)
8.3 It is a non-spontaneous reaction. (1)
8.4
8.4.1
- Eᶿcell = Eᶿcathode - EᶿAnode
= -0,74 – (-0,76)
= 0,02 V
OR - Cr3+ +3e- → Cr Eθ= -0,74
Zn →Zn2+ +2e- Eθ = +0,76
Eθcell = 0,02 V (3)
8.4.2 Decreases (1)
8.5 Measurements are not done under standard conditions of temperature at 25 °C and concentration of electrolytes of 1 mol·dm-3. (2)
8.6
8.6.1 Fuel cell/Brandstofsel (2)
8.6.2 It increases energy security, improves the quality of air and the environment. (ANY ONE ) (1)
8.6.3 More expensive than petroleum.
- Not suitable for use in low temperatures. (Any one)
- Could harm rubber hoses of some engines.
- Can contribute to food shortage. (1)
[14]
TOTAL: 75