Technical Sciences Paper 1 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 D (2)
1.2 D (2)
1.3 A (2)
1.4 B (2)
1.5 C (2)
1.6 A (2)
1.7 C (2)
1.8 A (2)
1.9 A (2)
1.10 C (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 F Net force
2.2 A Impulse
2.3 G Stress
2.4 B Thrust
2.5 C Optic axis
2.6 I Electric motor
2.7 E Tension
2.8 D Capacitor (8 x 1) [8]
QUESTION 3
3.1
Action force | Reaction force | |
3.1.1 | Weight of the boy | Force of boy on the earth ? |
3.1.2 | Normal force of ground on the trolley | Force of the trolley on the ground.? |
3.2 West (1)
3.3 When object A exerts a force on object B, object B simultaneously exerts an oppositely directed force of equal magnitude on object A. (2)
[5]
QUESTION 4
4.1 When a non-zero resultant force acts on an object, the object accelerates in the direction of the resultant force. This acceleration is directly proportional to the resultant force and inversely proportional to the mass of the
object. (2)
4.2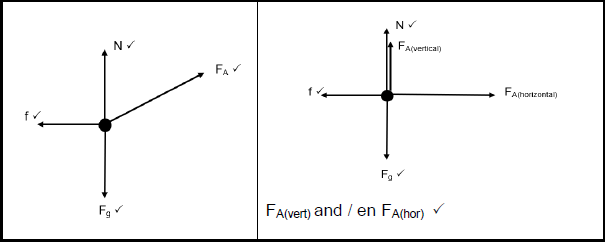 (4)
(4)
4.3
- fk = µkN
fk = (0,2)(473,28)
fk = 94,66 N Fg = N + Fv
(60)(9,8) = N + 200 sin 35°
N = 473,28 N (4)
4.4
- Fnet = ma
FA(hor) + fk = ma
(200 cos 350) + (- 94,66) = (60)(a)
a = 1,15 m.s-2 (3)
4.5 Decreases
Fhorizontal of 200 N and fk decrease as the angle increases.
Decrease in Fhorizontal is greater than decrease in fk.
∴ Fnet decreases.
Fnet α a (3)
[16]
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 Yes (1)
5.1.2
- pi = mv = 20 000 kg.m.s-1
K = ½mv2 = 200 000 J
½(mv)v = 200 000
½(20 000) v = 200 000
v = 20 m.s-1 due east (4)
5.1.3 Mark positive from Ques 5.1.2
OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 | OPTION 3 |
K = ½mv2\ | p = mv | ½mv2 = 200 000 … |
(2)
5.2
5.2.1 Total linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant. (2)
5.2.2 Right – Positive
- ∑ pi = ∑ pf Any one
∑ pi = (mP + mR)vf + mQvf 0 = (6)(2) +(3 + 2) (v)
v = 2,4 m.s-1 left / links (4)
[13]
QUESTION 6
6.1
6.1.1 Rate of transfer of energy / Rate at which work is done.(2)
6.1.2
- P = Fv
P = (300)(0,5)
P = 150 W (3)
6.1.3
OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
P = W | Δx = v Δt = (0,5)(50) = 25 m |
(3)
6.1.4
- 7500 J
Crate moves with constant velocity (2)
6.2
6.2.1 Total mechanical energy of an isolated system remains constant. (2)
6.2.2
- (ME)A = (ME)B
(U + K)A = (U+K)B Any one
(mgh + ½mv2)A = (mgh + ½mv2)B
(2)(9,8)(10) + 0 = 0 + ½(2)(v)2
v = 14 m.s-1 (4)
6.2.3
- (ME)A = (ME)C
(U + K)A = (U+K)B Any one
(mgh + ½mv2)A = (mgh + ½mv2)C
(2)(9,8)(10) + 0 = (2)(9,8)(h) + ½(2)(7)2
h = 7,5 m (4)
[20]
QUESTION 7
7.1 7.1.1 Hooke’s law states that, within the limit of elasticity, stress is directly proportional to the strain. (2)
7.1.2
- σ = F
A
? = 500
0,01
? = 50000 Pa (3)
7.1.3
- K = σ
ε
200× 109 = 50000
ε
ɛ = 2,5× 10-7
s = Δ?
?
2,5× 10-7 = Δ?
0,9
Δl = 2,25× 10-7 m (6)
7.1.4 Decreases (1)
7.2 As the temperature increases the viscosity decreases. (2)
7.3
7.3.1
- F1 = F2
A1 A 2
?1 = 1200×9,8
0,04 0,7
F1 = 672 N (4)
7.3.2 Hydraulic brakes / car lifts / hydraulic jacks / forklifts / dentist chairs (ANY TWO) (2)
[20]
QUESTION 8
8.1
8.1.1 Same as the object (1)
8.1.2 50 + 50 = 100 cm (2)
8.2
8.2.1 48,8° (1)
8.2.2 The ray will be totally reflected on the water. (2)
8.2.3 Total internal reflection/Totale interne weerkaatsing (1)
8.3
8.3.1 24 cm away on the other side of the lens (1)
8.3.2 20 mm (1)
8.3.3 Real (1)
8.3.4 Cameras / projectors / spectacles / lighthouse / telescope / microscope (ANY ONE) (1)
[11]
QUESTION 9
9.1 9.1.1 Gamma rays (1)
9.1.2 To sterilise medical equipment/treatment of cancer/Detection of radioactive tracers (ANY ONE) (1)
9.2 9.2.1 Wave packets/quantum packets are called photons. (2)
9.2.2
OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
c = fλ | E= hc |
(5) [9]
QUESTION 10
10.1
10.1.1 A capacitor is a device for storing electrical charge. (2)
10.1.2
- C = εo A
d
480 × 10-9 = 8,85×10−12×A
0,012×10-3
A = 0,65 m2 (3)
10.1.3 Decreases (1)
10.2
10.2.1
 (3)
(3)
10.2.2
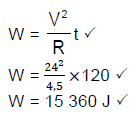 (3)
(3)
[12]
QUESTION 11
11.1 1
1.1.1 The process of generating electricity from motion. (2)
11.1.2 Galvanometer needle deflects. (1)
11.1.3 No deflection
- A current is induced only when there is a relative motion. (2)
11.2
- ε = − NΔɸ
Δ?
ε = (2)(50−38)
0,42
ε = 57,14 V (3)
[8]
QUESTION 12
12.1
12.1.1
- V? = ??
?? ??
9 = ??
230 400
Ns = 15,65 ≈ 16 (3)
12.1.2 Step down (1)
12.2
12.2.1 Electromagnetic induction / Faradays law (1)
12.2.2 Brush (1)
12.2.3 Slip rings (1)
12.2.4 Replace slip rings with a split ring commutator. (1)
[8]
TOTAL: 150