Civil Technology: Civil Services Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupREQUIREMENTS:
- ANSWER BOOK
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable pocket calculator
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions: TWO questions are generic and FOUR questions are subject specific.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2.1, 3.6 and 6.1 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments where necessary.
- Write your NAME on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have answered the question or not.
- Owing to electronic transfer, drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale.
- Google images was used as the source of all photographs and pictures.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 Answer the following questions regarding the scaffolding in FIGURE 1.1.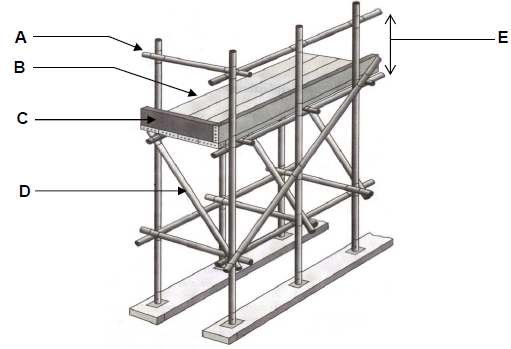
FIGURE 1.1
1.1.1 Name parts A to D. (4 x 1) (4)
1.1.2 What is the minimum width and thickness of part B? (2 x 1) (2)
1.1.3 What is the purpose of part D? (1)
1.1.4 What is the minimum and maximum measurements of E? (2 x 1) (2)
1.2 Describe the regulation that is applicable to the following facets when material is handled on a construction site:
1.2.1 Placing of building rubble (1)
1.2.2 When material is transported to higher surfaces (1)
1.3 Name THREE methods to ensure that a ladder is stable when it is used. (3 x 1) (3)
1.4 What are the horizontal parts of a ladder called? (1)
1.5 Explain the process of electroplating of a metal. (2)
1.6 Explain the purpose of electroplating of a metal. (1)
1.7 Name TWO advantages of galvanising. (2 x 1) (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 on ANSWER SHEET A shows a floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from the given ground level, by using the following information:
- The floor level height is 200 mm above the ground level
- Wall height is 2 600 mm from the floor level to the ceiling
- Window 1 is 1 200 x 900 mm
- Door 1 is 1 100 x 2 100 mm
- Doorknob
- Roof construction pitch is 30°
- Show construction lines to determine the roof height
- Gable end at the west elevation
- Hippen end at the east elevation
Use the marks table on ANSWER SHEET A as reference. (29)
2.2 Identify the type of nuts in FIGURES A to C.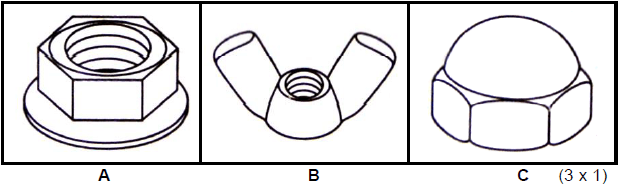
(3 x 1) (3)
2.3 Name TWO properties of rawl bolts. (2 x 1) (2)
2.4 Discuss how the height of the tripod should be set when a dumpy level is set up. (3)
2.5 Name THREE materials that can be detected in walls by a multi-detector. (3 x 1) (3)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: SAFETY, MATERIAL AND CONSTRUCTION (SPECIFIC)
Start the question on a NEW page.
3.1 FIGURE 3.1 show workers who must work in a manhole. Answer the following questions with related to the safety measures which must be applied.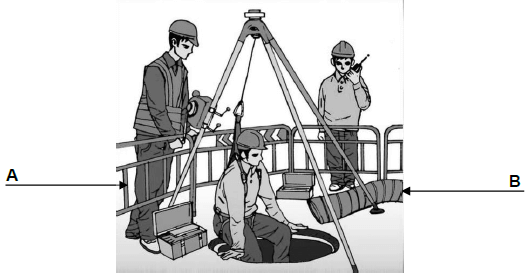
FIGURE 3.1
3.1.1 What is the purpose of structure A? (1)
3.1.2 What is the purpose of equipment B? (1)
3.1.3 Briefly describe in which circumstances equipment B will be used. (2)
3.1.4 Which personal protective equipment is lacking from the manhole worker, should there be dangerous fumes in the manhole? (1)
3.2 Which safety measure must be applied where falling objects can injure workers? (1)
3.3 Safety measures during construction work are very important. Identify TWO types of power tools which must be safeguarded. (2 x 1) (2)
3.4 Indicate if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question numbers (3.4.1–3.4.4) in the ANSWER BOOK.
3.4.1 Dezincification is a form of corrosion. (1)
3.4.2 Copper-zinc alloys containing more than 5% zinc, are susceptible to dezincification. (1)
3.4.3 Dezincification is an electrochemical reaction between zinc and water. (1)
3.4.4 Dezincification can cause leaks in pipe work. (1)
3.5 Fully explain what is meant by the electrolytic cleaning of a metal surface. (4)
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 on ANSWER SHEET B shows layer 1 of a T-junction in a one- brick wall in stretcher bond. Draw the alternate layer of the T-junction on scale 1 : 10 on ANSWER SHEET B. (7)
3.7 Which type of brick bond is illustrated in FIGURE 3.7?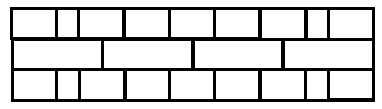
FIGURE 3.7 (1)
3.8 What is the purpose of a manhole in a drain system? (1)
3.9 Make a neat section sketch in good ratio to illustrate a manhole construction with benching. Show the following parts and indicate them with labels:
- Concrete base
- Brick walls
- Pipe channel
- Benching
- Cover frame and cover (5 x 1) (5)
[30]
QUESTION 4: COLD-WATER SUPPLY, HOT-WATER SUPPLY AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
4.1 Name THREE properties with which water for human use must comply. (3 x 1) (3)
4.2 What is the purpose of the packing gland inside the housing of a stopcock? (1)
4.3 Briefly motivate why the flow in the pipe of the ball valve releases the water at the bottom of the cistern. (1)
4.4 Answer the following questions with related to the valve in FIGURE 4.4.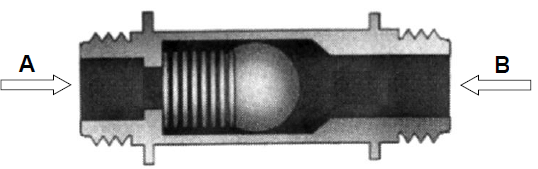
FIGURE 4.4
4.4.1 What is this valve called? (1)
4.4.2 Is A or B the correct flow direction for the valve? (1)
4.4.3 Is the valve open or closed? (1)
4.4.4 In which circumstances is this valve used? (1)
4.5 Answer the following questions regarding FIGURE 4.4. 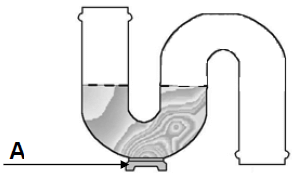
FIGURE 4.4
4.5.1 What is this structure called? (1)
4.5.2 Briefly describe the purpose of this structure. (2)
4.5.3 What is part A called? (1)
4.5.4 What is the purpose of part A? (1)
4.6 Briefly explain the difference between wastewater and soil water. (2)
4.7 Describe TWO advantages of electronic taps. (2 x 1) (2)
4.8 Motivate why muddy water must be pumped out of busted water supply pipes before they are repaired. (2)
4.9 Identify the following symbols and abbreviations for hot water systems.
4.9.1 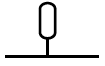 (1)
(1)
4.9.2 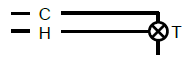 (1)
(1)
4.9.3 ![]() (1)
(1)
4.9.4 FV (1)
4.9.5 PVC (1)
4.10 Make neat sketches of the following symbols for hot-water systems:
4.10.1 Pressure-reducing valve (2)
4.10.2 Vacuum-relieve valve (2)
4.11 Explain how an airlock occurs and influences a water supply system. (4)
4.12 Indicate if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question numbers (4.12.1–4.12.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
4.12.1 A heat pump is energy efficient. (1)
4.12.2 A solar geyser reduces greenhouse gases. (1)
4.12.3 Poor hot-water pressure is caused by faulty valves. (1)
4.13 Why must loose clothing be avoided when working with the pipe-thread cutting machine? (1)
4.14 Name TWO tools which are used for cleaning blockages in drains. (2 x 1) (2)
4.15 Which machine is used for the pressure testing of water systems? (1)
[40]
QUESTION 5: DRAINAGE AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Describe the following requirements for an efficient drainage system:
5.1.1 The finishing of the inside of the pipes (1)
5.1.2 Minimum diameter of the pipes (1)
5.1.3 Placing of manholes (3)
5.2 Explain the circumstances where cast iron must be used. (2)
5.3 Name TWO properties of earthenware drainpipes. (2 x 1) (2)
5.4 Make a neat section sketch of a coupling socket joint for drainpipes. (3)
5.5 Name TWO positions in a drainage system where gullies must be installed. (2 x 1) (2)
5.6 Choose the correct description regarding the septic tank.
5.6.1 Sewerage / Soil water flows from the tap / water closet into the first chamber. (2)
5.6.2 Heavier particles are retained in the benching. / sink to the bottom of the chamber. (1)
5.6.3 Viruses / Bacteria digest the solid waste and turn it into a gas / liquid. (2)
5.6.4 The sludge / liquid must be cleaned regularly. (1)
5.7 Give the colour coding for the following drainage fittings:
5.7.1 Soil pipes (1)
5.7.2 Waste vents (1)
5.7.3 Existing drains (1)
5.8 Identify the following abbreviations for drainage fittings:
5.8.1 IR (1)
5.8.2 ST (1)
5.8.3 CE (1)
5.9 What is the purpose of the compressed air test for drains? (1)
5.10 The side of a cubic water supply tank is 1 800 mm. Determine the following volumes of the tank: (Show all calculations and formulas.)
5.10.1 The volume of the tank (3)
5.10.2 The volume of the water in the tank (2)
5.11 FIGURE 5.11 shows the pictorial view of a part of the layout for a drainage system. Answer the following questions regarding the system.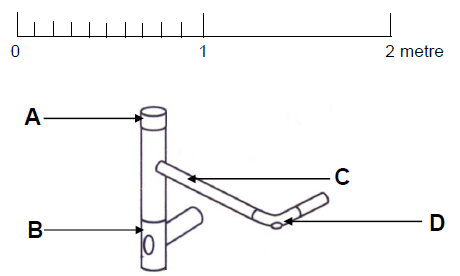
FIGURE 5.11
5.11.1 Name the sanitary fittings A to D. (4)
5.11.2 What is die section size of part B? (1)
5.11.3 What is the section size of part D? (1)
5.11.4 Of which type of material is the fitting manufactured? (1)
5.11.5 Use the graphic scale in FIGURE 5.11 and calculate the length of part C. (1)
[40]
QUESTION 6:
GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION, ROOF WORK, STORMWATER AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
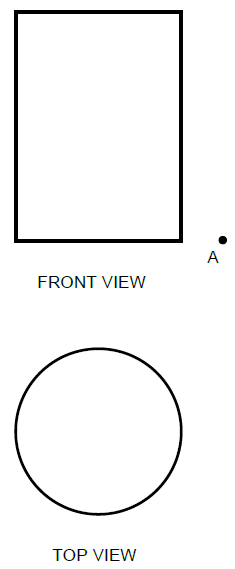
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 on ANSWER SHEET C shows the top and front view of a cylindrical pipe.
Draw the development of the cylindrical pipe on ANSWER SHEET C. Show all construction lines. (12)
6.2 Indicate if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question number in the ANSWER BOOK.
6.2.1 GMS-gutters have a pitch of 25 mm for each 4,8 m. (1)
6.2.2 The gutter brackets are fixed onto the facia board. (1)
6.2.3 A ripsaw is used to cut GMS-gutters to measurement. (1)
6.2.4 The seams of GMS-gutters are soldered with 50/50 solder. (1)
6.3 What is the purpose of a union clip when PVC-gutters are installed? (1)
6.4 Where, in a gutter system, is a downpipe shoe installed? (1)
6.5 Discuss the following regulations which are applicable to stormwater disposal.
6.5.1 Rainwater accumulates around buildings (2)
6.5.2 Soakaways (2)
6.6 Name THREE negative consequences of stormwater constructions that do not comply to the requirements. (3 x 1) (3)
6.7 Discuss the purpose of the flux when soldering work is done. (2)
6.8 Which type of soldering flux is manufactured from pine-tree bark? (1)
6.9 Identify the type of joining methods in FIGURES 6.9.1 and 6.9.2.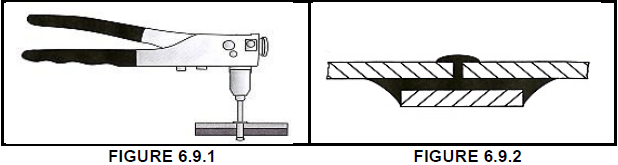 (2)
(2)
[30]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 on ANSWER SHEET A shows the floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from the given ground level. (29)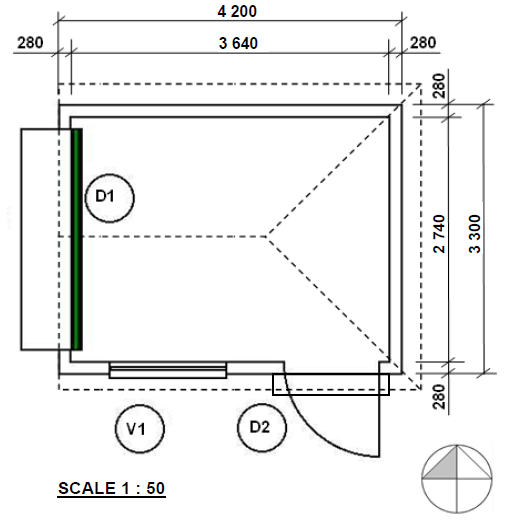
Floor level | 2 | |
Wall | 3 | |
Window | 3 | |
Windowsill | 1 | |
Door | 4 | |
Stair | 1 | |
Ramp | 1 | |
Fascia board | 2 | |
Gutter | 1 | |
Down pipe | 1 | |
Gable end | 4 | |
Hipped end | 3 | |
Roof height | 3 | |
TOTAL: | 29 |
![]()
ANSWER SHEET B
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 on ANSWER SHEET B shows layer 1 of a T-junction in a one- brick wall in stretcher bond. Draw the alternate layer of the T-junction on
scale 1 : 10 on ANSWER SHEET B. (7)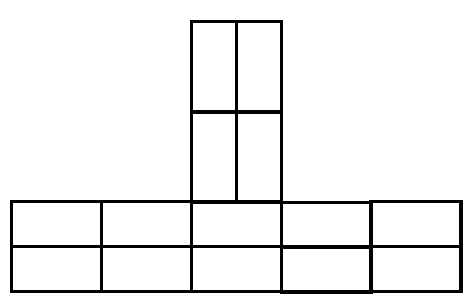
Brickwork | 6 | |
Application of scale | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 7 |
ANSWER SHEET C
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 on ANSWER SHEET C shows the top and front view of a cylindrical pipe. Draw the development of the cylindrical pipe on ANSWER SHEET C. Show all construction lines. (12)
Dividing lines 0–12 on top view | 6 | |
Base line A–B | 1 | |
Dividing lines AE | 2 | |
Vertical construction lines 0–12 | 2 | |
Seam lines A–C and B–D | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 12 |