TECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupTECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MEMORANDUM
MAY/JUNE 2021
QUESTION 1
1.1 D ✓✓(2)
1.2 A ✓✓ (2)
1.3 B ✓✓ (2)
1.4 C ✓✓ (2)
1.5 C ✓✓ (2)
1.6 A ✓✓ (2)
1.7 D ✓✓ (2)
1.8 B ✓✓ (2)
1.9 C✓✓(2)
1.10 B✓✓ (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 Is a series of (organic) compounds (molecules) that has the same general formula (and the same functional group), where each member differs from the previous member by a –CH2 group. (2)
2.2.1 C ✓ (1)
2.2.2 D ✓ (1)
2.2.3 A ✓ (1)
2.2.4 B ✓ (1)
2.2.5 E ✓ (1)
2.3 Propanal(1)
2.4 A OR ethyne/etyn
OR![]() (1)
(1)
2.5.1 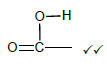
Marking criteria:
- If the bonds are missing 0/2
- If hydrogen atoms are added/missing 0/2
- If a structural formula of a compound is given and functional group is encircled 2/2 (2)
2.5.2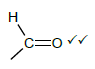
Marking criteria
- If the bonds are missing 0/2
- If hydrogen atoms are added/missing 0/2
- If a structural formula of a compound is given and functional group is encircled 2/2
2.6
- Chain isomers are organic compounds with the same molecular formula, but different types of chains/chain lengths.
- Positional isomers are organic compounds with the same molecular formula, but different positions of the side chain, substituents or functional groups on the parent chain. (4)
2.7.1 G & H
OR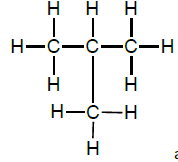
and butane (1)
2.7.2 I & J
OR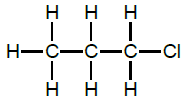
and 2-chloropropane (1)
2.8.1 Methylpropane
Accept/Aanvaar: 2-methylpropane (2)
2.8.2 1-chloropropane (2)
2.9 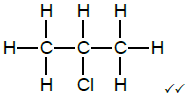
Marking criteria:
- Whole structure correct 2/2
- If a bond/hydrogen atom is missing 1/2
- Only correct functional group but not in correct place 1/2 (2)
[25]
QUESTION 3
3.1.1 London forces/induced dipole forces/dispersion forces(1)
3.1.2 London force/ dispersion forces /induced dipole forces and dipole dipole forces(2)
3.2 The stronger the intermolecular forces, the higher the boiling point.
OR
The weaker the intermolecular forces, the lower the boiling point. (1)
3.3.1 Ethanal (1)
Negative marking from 3.3.1 to 3.3.2
3.3.2
- The type of intermolecular forces are London forces and dipole-dipole forces.
- The chain length/ molecular mass/surface area increases from ethanal to pentanal.
- The longer the chain length/increase in molecular mass/larger surface area the stronger the intermolecular forces.
- More energy is required to overcome the stronger intermolecular forces in pentanal than in ethanal.
OR
Less energy is required to overcome the weaker intermolecular forces in ethanal than in pentanal.
OR
The stronger the intermolecular force the lower the vapour pressure.
OR
The weaker the intermolecular force the higher the vapour pressure.
OR
- The type of intermolecular forces are London forces and dipole-dipole forces.
- The chain length/ molecular mass/surface area decreases from pentanal to ethanal.
- The shorter the chain length/decrease in molecular mass/smaller surface area the weaker the intermolecular forces.
- Less energy is required to overcome the weaker intermolecular forces in ethanal than in pentanal. (4)
OR
More energy is required to overcome the stronger intermolecular forces in pentanal than in ethanal.
OR
The weaker the intermolecular force the higher the vapour pressure.
OR
The stronger the intermolecular force the lower the vapour pressure.
3.4.1 Monomer is a small organic molecule that can be covalently bonded to each other in a repeating pattern.
Accept: Monomer is a basic structural unit from which a polymer (macromolecule) is made.(2)
3.4.2 Polythene(1)
[12]
QUESTION 4
4.1.1 Bromine (gas)/ Br2(g) (1)
4.1.2 Addition (reaction)(1)
4.1.3 Halogenation /Bromination (1)
4.1.4 1,2-dibromoethane (2)
4.2 B (1)
4.3.1 Hydrolysis (1)
4.3.2 Mild heat
OR
Dilute strong base/KOH/NaOH
OR
(Haloalkane is dissolved in) ethanol (1)
[8]
QUESTION 5
5.1 Cell/Battery/Power Source(1)
5.2 It is a source of electrical energy to run a non spontaneuos reaction
OR
The power source/battery/ cell provides the energy needed for the reaction to occur. (2)
5.3 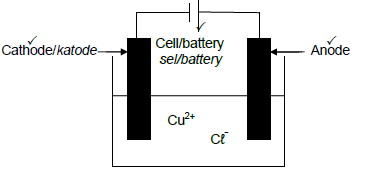
Marking criteria
- Correct symbol and position of the cell/battery/power source
- Anode labelled and connected to positive terminal of the cell/battery
OR - If power source is used credit the labelling of the anode.
- Cathode labelled and connected to negative terminal of the cell/battery.
OR - If power source is used credit the labelling of the cathode. (3)
5.4 CuCℓ2 (1)
5.5.1 Cathode: reduction (half reaction) Anode: oxidation (half reaction) (2)
5.5.2 Cathode is the negative (electrode)
Anode is the positive (electrode)
5.6 Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s)(2)
Marking criteria:
Cu ← Cu2+(aq) + 2e- ( 2/2) Cu2+(aq) + 2e- ⇌ Cu(s)0(½)
Cu ⇌ Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- (0/2) Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- ← Cu(s)(0/2)
NB: Don't penalise if phases are omitted
5.7 2Cℓ-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) → Cℓ2(g) + Cu(s) Balancing
Accept/Aanvaar: CuCℓ2(aq) → Cℓ2 (g) + Cu(s) (3)
[16]
QUESTION 6
6.1 Spontaneous (1)
6.2.1 (Electrochemical cell) that converts chemical to electrical energy. (2)
6.2.2 A substance of which the aqueous solution contains ions.
OR
A substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that conducts electricity. (2)
6.3 Chemical to electrical (2)
6.4 Ag /Silver (electrode)(1)
Positive marking from 6.4 to 6.7
6.5 Ag+ + e- → Ag (2)
Marking criteria:
Ag ← Ag+(aq) + e- (2/2) Ag+(aq) + e- ⇌ Ag(s)(½)
Ag ⇌ Ag+ (aq) + e- (0/2) Ag+ (aq) + e- ← Ag(s)(0/2)
6.6 OPTION 1
Eθcell = Eθcathode – Eθanode
Eθsel = Eθkatode – Eθanode
= 0,80 – (–0,27)
= 1,07 V
OPTION 2
Ag+ + e- → Ag +0,80
Ni → Ni2+ + 2e- – (–0,27)
2Ag+ + Ni → 2Ag + Ni2+ 1,07 V (4)
6.7 Ni(s)/Ni2+(aq)(1 mol·dm-3)//Ag+(aq)(1 mol·dm-3)/Ag(s)(298 K/25ºC)
NB: Don't penalise if phases and standard conditions are omitted (3)
6.8.1 Biodiesel
Fuel Cells
Wave (energy)
Wind (energy)
Nuclear (energy)
ANY ONE (1)
6.8.2 Pump water from underground
Light up at night
Activate switches
Charge batteries
Supply electric utility grid
ANY THREE(3)
[21]
QUESTION 7
7.1.1 Flat/plane mirror (1)
7.1.2 Reflection (of light)(1)
7.1.3
- Angle of incidence must be equal to angle of reflection.
- The normal, incident and reflected rays must lie in the same plane. (2)
7.1.4
- (The image) is always the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
- (The image) is upright.
- (The image) is virtual
- (The image) is laterally/parity inverted. (The image is left-right reversed).
- (The image) is the same size as the object.
(ANY 3 / ENIGE 3) (3)
7.2.1 Object (1)
7.2.2 Eye of the observer (1)
7.2.3 Image (1)
7.3.1 These distances are equal. (1)
7.3.2 Remains the same. (1)
[12]
QUESTION 8
8.2.1 The phenomenon whereby white light breaks up (spread out) into its component colours (2)
8.1.1 The ray moves along the surface between the two boundaries(1)
8.1.2 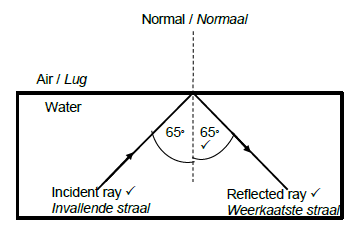
Marking criteria:
Correct label and direction of incident ray
Correct label and direction of reflected ray
Magnitude of incident angle and reflected angle correctly indicated on diagram, both equal to 65° (3)
Note: If direction is not indicated on both rays, penalise only once.
8.1.3 Total internal reflection (1)
8.2.2 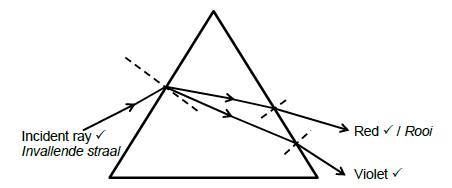
Marking criteria:
Violet light correctly labelled and positioned.
Red light correctly labelled and positioned
Incident ray correctly labelled and entering the prism.
Accept: white light, as the incident ray
All rays are refracted correctly at the normal. (4)
NB: Penalise ONCE if arrows are not included.
8.2.3 5 (five) (1)
8.2.5
- White light consists of colours of different wavelengths.
- The speed of waves decreases/changes when it enters the prism.
OR - The speed of waves increases/changes when it leaves the prism.
- The light waves with shorter wavelengths are refracted more than waves with longer wavelengths (so there will be a separation into different colours).(3)
8.2.4 The bending of light when it passes from one medium to another (of different optical density).(2)
[17]
QUESTION 9
9.1
| Convex (Converging lens) | Concave lens (Diverging lens) |
| The lens is thicker in the middle than at the edges. OR Surfaces bulge outwards in the centre. | The lens is thinner in the middle than at the edges. OR The outer surfaces curve inward. |
| Parallel light rays passing through it bend inward and meet (converge) at the focal point | Parallel light rays passing through it bend outwards or diverge. |
| Corrects farsightedness/hyperopia (hypermetropia) | Corrects shortsightedness/myopia. |
NB: Credit 2 marks if the comparison correlates with each other. (4)
9.2.1 Far-sightedness/hyperopia(hypermetropia)(1)
9.2.2 Convex lens (1)
9.3 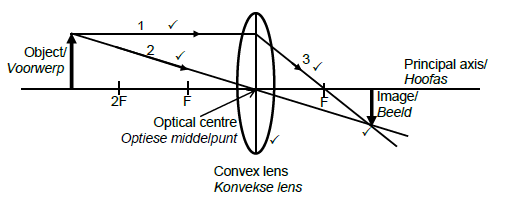
Marking criteria
Ray 1 starts at the head of the object and moves parallel to the principal axis.
Ray 2 starts at the head of the object and passes through the optical centre without changing direction.
Ray 3 deflects from ray 1 on the other side of the lens and passes through F.
Convex lens is used.
Both ray 2 and 3 intersect at the head of the inverted image. (5)
NB: Penalise ONCE if arrows are not included.
[11]
QUESTION 10
10.1 Electromagnetic waves are changing magnetic and electric fields mutually perpendicular to each other and the direction of propagation of the waves.(2)
10.2.1 Radio (waves)(1)
10.2.2 Gamma (rays) (1)
10.3 E = hf
= (6,63 × 10-34)(7,50 × 1014)
= 4,97 × 10-19J
Apply negative marking.
Therefore the energy of the photon is more than the energy of a photon of blue light.
Therefore it is a photon of indigo light.(4)
[8]
TOTAL: 150