LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupLIFE SCIENCES PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MAY/JUNE 2021
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answer to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- Do ALL drawings in pencil and label them in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, tables or flow charts only when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You must use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass, where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A to D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 Which ONE of the following is a reproductive isolation mechanism?
- Breeding at the same time of the year
- Adaptation to the same pollinators
- Prevention of fertilisation
- Sharing the same habitat
1.1.2 The scientists who won the Nobel Prize for the discovery of the structure of DNA were …
- Watson and Franklin.
- Wilkins and Franklin.
- Crick and Wilkins.
- Watson and Crick.
1.1.3 In a dihybrid cross, an animal with long ears (E) and red fur (R) was crossed with an animal with short ears (e) and black fur (r).
Which ONE of the following could represent the genotypes of the parents?
- EERR x eerr
- EeRr x EeRr
- eeRR x eerr
- Eerr x EERr
1.1.4 Which ONE of the following reduces genetic variation in the offspring?
- Mutations
- Random mating
- Cloning
- Random fertilisation
1.1.5 Meiosis is best explained as a process that produces … daughter cells.
- two haploid
- two diploid
- four diploid
- four haploid
1.1.6 Colour-blindness is a disorder caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome. Which ONE of the following is the genotype of a colour-blind person?
- XDXD
- XDY
- XDXd
- XdY
1.1.7 The study of the inheritance of mutations in mitochondrial DNA is an example of …
- fossil evidence.
- genetic evidence.
- modification by descent.
- cultural evidence. (7 x 2)
(14)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.9) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The bonds that hold the two strands of a DNA molecule together
1.2.2 A genetic cross involving one gene and its alleles
1.2.3 Undifferentiated cells that may form any other cell in the human body
1.2.4 The structures in the cell that form the spindle fibres
1.2.5 The phase of meiosis when chromosomes are aligned at the equator of the cell
1.2.6 A genetic disorder where blood does not clot
1.2.7 The formation of new species
1.2.8 Evolution characterised by long periods of no change alternating with short periods of rapid change
1.2.9 The study of heredity and variation in organisms (9 x 1)
(9)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN I apply to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| COLUMN I | COLUMN II |
| 1.3.1 Found in the nucleus |
|
| 1.3.2 Random arrangement of chromosomes |
|
| 1.3.3 Site of meiosis in humans |
|
(3 x 2) (6)
1.4 The diagram below represents a pair of homologous chromosomes in a plant cell. The alleles for two characteristics, seed colour (G and g) and plant height (T and t), are indicated on the chromosomes.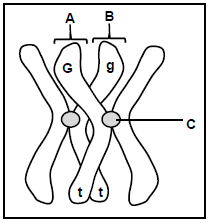
1.4.1 Give the term used to describe the position of an allele on a chromosome. (1)
1.4.2 Identify parts A and C. (2)
1.4.3 Name the process during which parts A and B exchange genetic material. (1)
1.4.4 During which phase of meiosis does the process named in QUESTION 1.4.3 take place? (1)
1.4.5 State the following for this plant:
- Genotype(2)
- The characteristic that is homozygous recessive(1)
(8)
1.5 The diagram below represents some nucleotides in a single strand of DNA.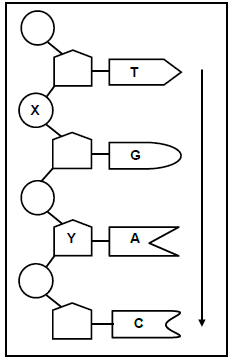
1.5.1 Give the LETTER of the part that represents a:
- Sugar molecule(1)
- Phosphate molecule(1)
1.5.2 How many nucleotides are represented in the diagram?(1)
1.5.3 Write down the nitrogenous bases (from top to bottom as indicated by the arrow) of the complementary DNA strand of this molecule.(1)
1.5.4 Name TWO processes that require the two strands of a DNA molecule to separate into single strands as shown in the diagram.(2)
(6)
1.6 The table below shows the blood groups of the members of a family. Two of the children are biological offspring of the parents and one child is adopted.
1.6.1 How many:
- Different phenotypes for blood group appear in this family(1)
- Possible genotypes are there for blood group AB(1)
1.6.2 Give the genotype of the father. (2)
1.6.3 Which member of the family:
- Has the genotype ii(1)
- Has co-dominant alleles(1)
- Is adopted(1)
(7)
| FAMILY MEMBER | BLOOD GROUP |
| Father | A |
| Mother | AB |
| Daughter | A |
| Son 1 | O |
| Son 2 | B |
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 Haemoglobin is a protein found in blood that carries oxygen to all the cells of the body. A portion of this protein is called a beta chain. If the sequence of amino acids in this chain changes, then a different form of haemoglobin, called haemoglobin S, is formed. Haemoglobin S cannot transport oxygen as efficiently as normal haemoglobin.
| Position of amino acids in the beta chain | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Normal haemoglobin | Val | His | Leu | Thr | Pro | Glu | Glu |
| Haemoglobin S | Val | His | Leu | Thr | Pro | Val | Glu |
The table below shows the DNA base triplets coding for some amino acids.
| DNA BASE TRIPLET | AMINO ACID |
| CAC | Val |
| GTG | His |
| GAC | Leu |
| TGA | Thr |
| GGA | Pro |
| CTC | Glu |
2.1.1
Give the:
- DNA base triplet for amino acid 3(1)
- mRNA codon for amino acid 4 (2)
2.1.2 What is a change in the sequence of DNA base triplets called?(1)
2.1.3 Use the information in the tables to explain how a change in the sequence of the DNA base triplets results in the formation of haemoglobin S, rather than normal haemoglobin.(4)
2.1.4 Describe how a person with haemoglobin S would be affected.(2)
(10)
2.2 Describe the process of translation during protein synthesis. (6)
2.3 The karyotype below represents the chromosomes of a person.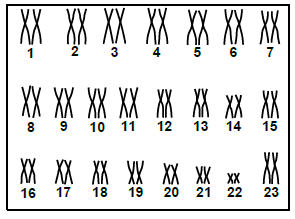
2.3.1 Give the collective term for the chromosomes numbered 1 to 22.(1)
2.3.2 State the gender of this person.(1)
2.3.3 Give ONE observable reason for your answer to QUESTION 2.3.2.(2)
2.3.4 State Mendel's principle of segregation.(2)
2.3.5 Describe how the karyotype of a person with Down syndrome would differ from the one above.(2)
(8)
2.4 In rabbits, fur colour may be black, white or grey. The inheritance of fur colour is controlled by two alleles namely:
Black fur (B) and White fur (W)
2.4.1 Explain why fur colour in rabbits is an example of inheritance with incomplete dominance.(2)
2.4.2 Use a genetic cross to show the expected genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring when a grey male mates with a black female.(6)
(8)
2.5 In humans, the ability to taste a certain substance is inherited and is controlled by the dominant allele T. People who are able to taste this substance are called tasters, while those who cannot, are called non-tasters.
The pedigree diagram below shows the inheritance of this trait in a family.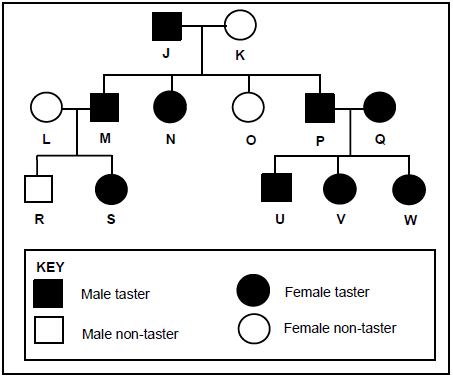
2.5.1 What does the term dominant allele mean?(2)
2.5.2 Give the:
- LETTER of a female in the F1-generation who is a taster(1)
- Genotype of individual J (1)
2.5.3 Use evidence from the diagram to support your answer to QUESTION 2.5.2(b). (4)
(8)
[40]
QUESTION 3
3.1 There are anatomical differences between African apes and humans. There are also characteristics that they share.
3.1.1 Name ONE characteristic of the hand that African apes share with humans.(1)
3.1.2 Tabulate THREE differences between the skulls of African apes and humans.(7)
3.1.3 Give TWO characteristics of the pelvis of a bipedal organism.(2)
(10)
3.2 The fat content of cow's milk may vary between 2,6% and 5%.
A farmer has found that there is a high demand for low-fat milk (milk with a fat content of 3% or less).
He determined the fat content in the milk produced by the cows on his farm.
The results of his survey are given in the table below.
| FAT CONTENT (%) | NUMBER OF COWS |
| 2,6–3,0 | 11 |
| 3,1–3,5 | 66 |
| 3,6–4,0 | 93 |
| 4,1–4,5 | 61 |
| 4,6–5,0 | 15 |
3.2.1 Draw a histogram to represent the results of the survey.(6)
3.2.2 Calculate the percentage of the farmer's cows that produce low-fat milk. Show ALL your working.(3)
3.2.3 State the type of variation that occurs in the cows, based on the evidence in the table.(1)
3.2.4 Give an explanation for your answer to QUESTION 3.2.3.(1)
(11)
3.3 The diagram below represents the evolution of the flightless birds and the continents on which they exist at present.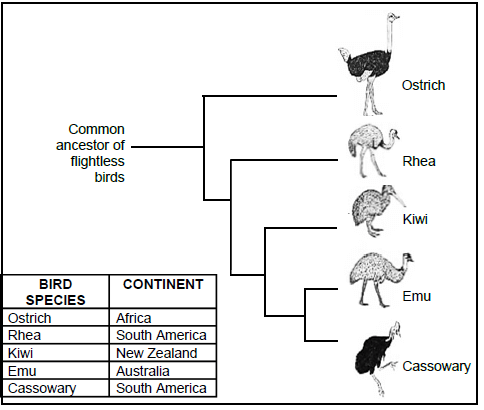
3.3.1 Identify the type of diagram shown above.(1)
3.3.2 Name the TWO species that share the most recent common ancestor.(2)
3.3.3 Use information in the diagram to describe how biogeography supports the theory of evolution. (4)
3.3.4 Describe how it can be proven that ostriches and rheas are different species. (2)
(9)
3.4 There is variation in tawny owls. Some are white and others are brown in colour.
Scientists studied these owls over a period of 30 years, from 1980 to 2010, to determine the effect of climate change on the survival of the owls. During this time, climate change caused increasing global temperatures with less snow falling each year.
The scientists:
- Conducted the investigation over the same four months of winter each year
- Observed the same population of tawny owls each year
- Determined the number of tawny owls of each colour that survived every year
The results are shown in the graph below: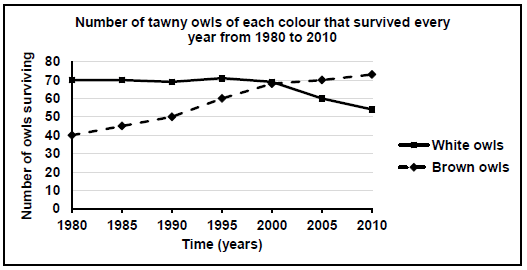
3.4.1 Identify the dependent variable in this investigation. (1)
3.4.2 What conclusion can be made about the suitability of each colour owl to survive in more snow? (2)
3.4.3 Explain the results obtained from 2000 to 2010 for the white owls. (3)
3.4.4 Describe how the scientists determined the number of owls that survived each year. (3)
3.4.5 Name ONE variable that was kept the same. (1)
(10)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Modern spider monkeys live high up in trees. They have very long tails which they use to hold on to branches. This reduces their risk of falling to the ground where they could be attacked by predators. The ancestor of spider monkeys had a much shorter tail.
Use Lamarck and Darwin's theories to explain why all spider monkeys have long tails and how artificial selection could have produced the same result.
Content:(17)
Synthesis:(3)
(20)
NOTE: NO marks will be awarded for answers in the form of a table, flow charts or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C:20
GRAND TOTAL:150