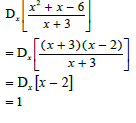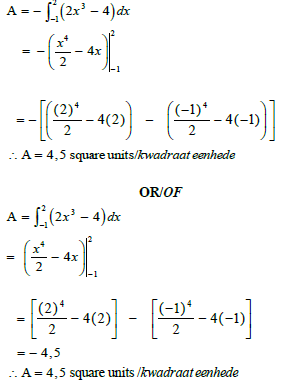TECHNICAL MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupTECHNICAL MATHEMATICS PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MEMORANDUM
MAY/JUNE 2021
QUESTION 1 | ||
1.1.1 | (3 - x)(x +1) = 0 | x = 3 OR x = 3 |
1.1.2 | 2x2 = 3x + 7 | standard form |
| 1.1.3 | x ( x - 5 ) ≤ 0 | both critical values A |
| 1.2 | y + x = 3 and x2 + y2 = 89 OR | y subject of formula A OR |
| 1.3.1 | F = K Q1 Q2 | transposing r 2 A |
| 1.3.2 | r = K Q1Q2 OR r = √(9 x 109 )(0,5 x 10-6 )(0,2 x 10-6 ) | SF CA value of r CA
OR |
| 1.4 | 11012 +1112 OR | 101002 A OR |
QUESTION 2 | ||
2.1 | x = - 3 or x = 0 | roots or discriminant A |
2.2 | x2 + p x - 2 p 2 = 0 | F A [6] |
QUESTION 3 | ||
3.1.1 | √16a6 | 4 A |
3.1.2 | √log 2 32 + log100 + 9 | 5log 2 2 A |
3.1.3 | (4√5 + 2)( 2 - 4√5) OR | product A OR |
3.2 # | log3x = 3 - log3(x + 6) OR | log property A OR |
| 3.3.1 | z = 2(½ + 3i) - 7i = 1 + 6i - 7i | substitution w |
| 3.3.2 # | z = r = √x2 + y2 = √(1)2 + (-1)2 = √2 | modulus CA from |
| 3.4 | a +b + ia - bi = 5 -3i OR OR | equation OR |
QUESTION 4 | ||
4.1.1 | x ∈ x ≠ 0 OR x ∈ (-∞; 0) ∪ (0;∞) | domain A |
4.1.2 | P (-4 ; 0) | coordinates of P A (1) |
4.1.3(a) # | P( - 4 ; 0) , S( 2 ; 0) and U(1 ; 10) OR | subst. roots A OR |
4.1.3(b) | h ( x ) = k/x + q | F (asymptote) |
| 4.1.4 | At / by R: y = - 2(-1)2 - 4(-1) + 16 = 18 OR | y valueCA from Q 4.1.3(a) OR |
| 4.1.5 | x = - 4 | x = - 4 |
4.2.1 (a) | y = (1,495)0 - 5 = - 4 OR | -4 A |
4.2.1 (b) | 0 = (1, 495) x - 5 | y = 0 |
| 4.2.2 | 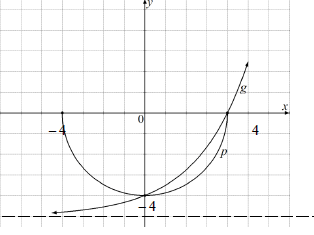 | g: |
| 4.2.3 (a) | - 4 ≤ y ≤ 0 | both endpoints |
4.2.3 (b) | m = 0 - 4 = 1 OR | gradient CA OR |
4.2.3 (c) | 0 < x < 4 OR OR | both endpoints CA |
| 4.2.3 (d) | - 4 < x ≤ 0 | both endpoints |
QUESTION 5 | ||
5.1 |
| formula CA OR |
5.2 | A = P (1 - i)n | ? SF A |
| 5.3.1 | AMartin = P (1 + in) OR | ?SF A OR |
| 5.3.2 # | ANosizwe = P (1 + i) n OR | ?(1 +0,0764)24 OR |
| If a candidate indicate only conclusion without calculation: 0 marks (5) [13] | ||
QUESTION 6 | ||||
Penalty (1 mark) for incorrect notation only in QUESTION 6.1 | ||||
6.1 | f (x) = 2x + 3 | definition | ||
6.2.1 | y = - x -5 + 3x 4 | 5x -6 A | ||
6.2.2 | f ( x ) = 3 - x OR | 3x-4 A (4) | ||
6.2.3 |
| factors | ||
6.3 | mave = f (x2) - f x1) OR | SF A OR |
6.4.1 | g ( x ) = 1 - x2
| derivative A |
6.4.2 | g ( - 3)= 1 - (- 3) 2 = - 8 | y-value A [22] |
QUESTION 7 | |||
7.1.1 | B(0 ; - 5) | Coordinates of B A (1) | |
7.1.2 | h ( x ) = x3 - 3x2 - 9x - 5 | SF A | |
7.1.3 | By inspection OR OR | quadratic factor A OR OR | |
7.1.4 | h/ ( x ) = 3x2 - 6x - 9 OR | derivative M | |
7.2 | x < - 1 or x > 3 OR | both crit. values CA OR [13] | |
| QUESTION 8 | ||
| 8.1 | 30- 6t = 0 30 = 6t t = 5 s | 30 - 6t A |
| 8.2.1 | s = 30t - 3t 2 ds = 30 - 6t dt = 30 - 6( 0) m/s = 30 x 3600 km/h 1000 = 108 km/h NO Penalty if correct unit omitted. | t = 0 x 3600 1000 S |
| 8.2.2 | s = 30(5) - 3(5)2 m | substitution A |
| 8.3 | 75 m > 70 m | reason CA |
QUESTION 9 | ||||||||
9.1.1 | = -x-1 + In x + C OR = -1/x + in x + C | - x -1 or -1/x | ||||||
9.1.2 | 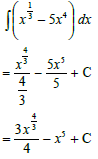 | (2) | ||||||
9.2 |
| Area notation using intergrals M OR | ||||||
TOTAL: 150 | ||||||||