Technical Sciences Paper 2 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 B (2)
1.2 A (2)
1.3 C (2)
1.4 A (2)
1.5 C (2)
1.6 C (2)
1.7 D (2)
1.8 D (2)
1.9 A (2)
1.10 B (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 A series of organic molecules that can be described by the same general formula and where each member differs from the next by a CH2 group. (2)
2.2 A group of atoms whose bonding is the same from molecule to molecule with similar physical and chemical properties. (2)
2.3
2.3.1 E (1)
2.3.2 C (1)
2.4
2.4.1 Butane/Butaan (2)
2.4.2 2-methylpropan-1-ol/ 2-metielpropan-1-ol OR 2-methylpropanol/2-metielpropanol (2)
2.5
2.5.1 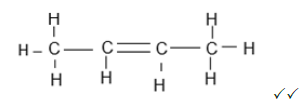 (2)
(2)
2.5.2 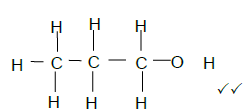 (2)
(2)
2.5.3 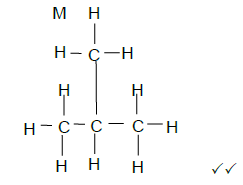 (2)
(2)
2.6 Positional isomers are organic molecules with the same molecular formula/ and same structural formula/ and same functional group, but differ from each other in the location (position) of the functional group in the carbon chain. (2)
2.7 Ketones/Ketoon (1)
2.8 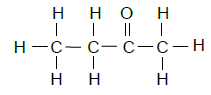 (2)
(2)
[21]
QUESTION 3
3.1 It is a long chain of monomers, covalently bonded together (in a repeating patterns). (2)
3.2 Unsaturated Not all C-C bonds are single bonds
OR
It contains C-C double bonds (3)
3.3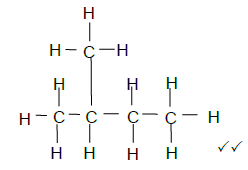 (2)
(2)
3.4
- Destruction of indigenous forests (leading to global warming)
- Rubber is not biodegradable – disposal impacts negatively on environment
- Burning of rubber releases toxic gases (Any 2) (2)
3.5
- Job creation
- Tyres for cars / gloves for medical industry / raincoats etc
- Protective devices – insulation (Any 2 x 2) (4)
[13]
QUESTION 4
4.1 D (2)
4.2
4.2.1 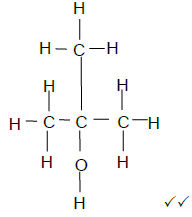 (2)
(2)
4.2.2 D (2)
4.3
4.3.1 C (propan-1-ol/1-propanol)
Longest flow time / flows the slowest / most resistance to flow. (2)
4.3.2
- Increase in chain length / molecular mass / molecular size / surface area from A to C.
- Increase in strength of intermolecular/ Van der Waals / Dispersion / London forces. (3)
4.3.3 C. Since it is having strong intermolecular forces and the longest chain length which contributes to its resistance to flow makes propan-1-ol a best lubricant. (3)
4.3.4 Vapour pressure is a measure of the tendency of a material to change into a gaseous state. (2)
4.4
- E (butan-2-ol or 2-butanol)
The more branched/more compact alcohol/E has a smaller surface area (over which the intermolecular forces act).
Decrease in strength of intermolecular forces/
reduced resistance to flow (and thus lower viscosity).
OR - The straight-chain alcohol/D has a larger surface area/less compact (over which intermolecular forces act).
Increase in strength in intermolecular forces.
Increased resistance to flow (and thus higher viscosity). (3)
[19]
QUESTION 5
5.1 Addition (reaction) (2)
5.2
- Add acidic reagent HBr
- At room temperatures OR 25ºC (2)
5.3 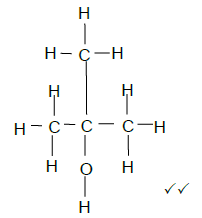 (2)
(2)
5.4 H2O OR Water (2)
5.5 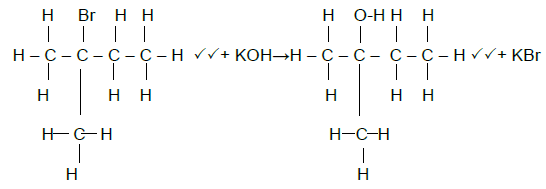 (4)
(4)
5.6 Addition (reaction) (2)
5.7
5.7.1 Water and Carbon Dioxide (2)
5.7.2 2 C6H14 + 19 O2 → 12 CO2 + 14 H2O
( balancing is 1 mark) (4)
[20]
QUESTION 6
6.1 Ethanol (2)
6.2 It acts as a catalyst(2)
6.3 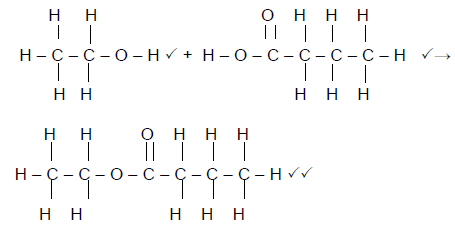 (4)
(4)
6.4 The contents of the mixture are flammable (2)
6.5 They are used to flavour foods and sweets (2)
7.1
- Transverse
- Waves are carried by the medium
OR
Waves travel through a medium - Wavelength (λ) per the period (T) of a wave (6)
7.2
7.2.1 Incident ray (1)
7.2.2 Refracted ray (1)
7.2.3 Normal (1)
7.2.4 Refracted angle(1)
7.3 Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one incident ray from one optical medium to another. (2)
[12]
QUESTION 8
8.1 Total internal reflection/Totale interne weerkaatsing (1)
8.2 It is when the incident ray completely reflects back to the optical denser medium. (2)
8.3
- Light must travel from a denser optical medium to a less dense optical medium.
- The incident angle must be greater than the critical angle (2)
8.4
- In medicine
- In submarines
- In telecommunications
- In cameras (Any 2) (2)
8.5 It is an angle of incidence in the denser medium such that the refracted ray just passes through the surface of separation of the two mediums. (2)
8.6 The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane and the angle of reflection Өr equals the angle of incidence Өi. (2)
8.7
8.7.1 Dispersion (1)
8.7.2 It is the spreading of the white light when entering an optical denser medium into its primary colours. (2)
8.8
8.8.1 Convex OR Converging(1)
8.8.2 It is the distance between the centre of a lens and its focus. (2)
8.8.3
- Virtual image
- Upright
- Enlarged (3)
[20]
QUESTION 9
9.1
- Radio waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared
- Visible light
- Ultraviolet rays
- X-rays
- Gamma rays (2)
9.2 Gamma rays (1)
9.3 It has the highest frequency; according to the formula E = hf, the higher the frequency, the higher the energy of a photon. (2)
9.4 It is a wave with a changing magnetic and electric field perpendicular to each other in the direction of propagation of the wave. (2)
9.5 Option 1
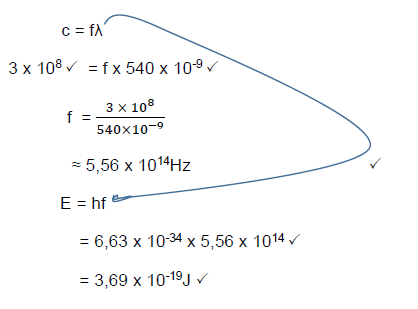
Option 2
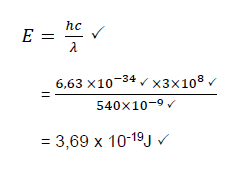 (5)
(5)
9.6 GREATER THAN (1)
[13]
TOTAL: 150