Mechanical Technology: Welding and Metalwork Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupINSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your full name(s) on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational acceleration should be taken as 10 m/s2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- A formula sheet is attached to the question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME in minutes |
GENERICS | |||
1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 10 |
2 | Safety | 10 | 15 |
3 | Materials | 14 | 15 |
SPECIFIC | |||
4 | Multiple-choice questions | 14 | 13 |
5 | Terminology (Templates) | 23 | 18 |
6 | Tools and Equipment | 18 | 15 |
7 | Forces | 45 | 30 |
8 | Joining Methods (Inspection of Weld) | 23 | 18 |
9 | Joining Methods (Stresses and Distortion) | 18 | 18 |
10 | Maintenance | 8 | 10 |
11 | Development | 21 | 18 |
TOTAL | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: GENERIC
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE (GENERIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1–1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.7 D.
1.1 Which of the following safety measures is applicable to guillotines in terms of the Occupational Health and Safety Act?
- Clamp the workpiece securely to the table.
- Do not leave the chuck key on the machine.
- Machine must be fitted with fixed guards to prevent fingers from reaching through the point of operation.
- Use the table of the machine as an anvil. (1)
1.2 What is the purpose of cooling the blade of a band saw with cutting fluid?
- To cause friction
- To ensure clean cuts and remove metal waste
- To ensure straight cuts
- To move the blade forward and backwards (1)
1.3 Which ONE of the following safety procedures is applicable to the operation of a hydraulic press?
- Do not apply wrench to revolving work.
- Guards could be removed when pressing soft material.
- Pressure gauges must be tested regularly and adjusted or replaced if any malfunction occurs.
- Use the machine table as an anvil. (1)
1.4 Which ONE of the following tests is used to measure the ductility of a metal?
- Bend tests
- Sound tests
- Hardness tests
- Machining tests (1)
1.5 File tests are used as the simplest method of checking the ... of material.
- toughness
- hardness
- ductility
- softness (1)
1.6 Sound tests can be performed by tapping a material with a …
- hacksaw.
- spanner.
- hammer.
- file. (1)
[6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Name any TWO pieces of personal safety equipment that you need to wear when using gas welding equipment.(2)
2.2 Give TWO safety rules that must be followed while the surface grinder is in operation.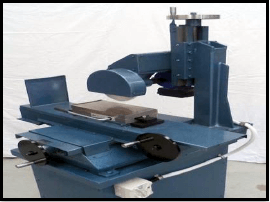 (2)
(2)
2.3 When completing a task on any machine, what safety aspect must be considered before leaving the machine? (1)
2.4 State TWO safety measures to observe before switching the angle grinder on. (2)
(2)
2.5 Why is it important to wear a welding helmet when using arc welding equipment? (1)
2.6 Name TWO types of workshop layouts. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 The following table shows the different types of tests and materials.
Copy and complete the table in your ANSWER BOOK by stating how these materials will react under the different tests.
| MATERIALS | DIFFERENT TYPES OF TESTS | ||
| Sound | Filing | Bend | |
| Cast iron | |||
| Mild steel | |||
(6)
3.2
Explain the purpose of heat-treatment processes. (1)
3.3 The hardness that can be achieved from a specific treatment depends upon THREE factors. Name any TWO factors. (2)
3.4 Explain the purpose of the following heat treatment processes:
3.4.1 Tempering (2)
3.4.2 Annealing (2)
3.5 What does the hardness of steel depend upon? (1)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1–1.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 4.15 A.
4.1 Which of the following best describes a template loft?
- It is the heart of the structural workshop.
- It is the welding workshop for roof trusses.
- It is the drawing workshop for roof trusses.
- It is where complicated steel structures are kept. (1)
4.2 What is the purpose of a supplementary symbol?
- To show you where to weld
- To indicate where to weld
- To indicate side weld in a welding joint
- To indicate additional information about the weld (1)
4.3 What is the maximum thickness of sheet metal that can be cut with a hand guillotine?
- 3,2 mm
- 1,6 mm
- 1,2 mm
- 2,1 mm (1)
4.4 Identify the following weld symbol.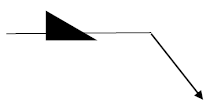
- Butt joint
- Lap joint
- Fillet weld symbol
- Square butt symbol (1)
4.5 Which property of material is tested using a Brinell tester?
- Tensile strength
- Elasticity
- Hardness
- Brittleness (1)
4.6 Which ONE of the following safety regulations applies to the MIG/MAGS welding process?
- Check the colour coding on cylinders.
- Hold the workpiece in your hand during the welding process.
- Turn the relief valve very slowly.
- Ensure that the welding area is well-ventilated. (1)
4.7 What is the purpose of cooling the blade of a power saw with cutting fluid?
- To cause friction
- To ensure small cuts with no wastage
- To ensure a straight cut
- To prevent the blade from overheating and binding or breaking (1)
4.8 Calculate Young’s modulus of elasticity for a metal with a strain value of 2 x 10-3 caused by stress of 6 MPa.
- 12 MPa
- 3 MPa
- 12 GPa
- 3 GPa (1)
4.9 Stress can be defined as an internal force in a material resisting a/an …
- internal load.
- spin load.
- moving load.
- external load. (1)
4.10 When does overloading occur in a pedestal drill ?
- When the drill bit is forced into the material
- When the chuck is forced into the material
- When excessive force is applied on the ma chine
- When the machine is moving fast (1)
4.11 Which ONE of the following is an inspection during arc welding?
- Rate of rod burning and the progress of th e weld
- Correct flame for the work on hand
- Correct angle of the blow pipe
- Depth of fusion (1)
4.12 Which ONE of the following is a cause for undercutting during arc welding?
- Clean bead
- Travel speed too high
- Slag inclusion
- Distortion (1)
4.13 A destructive test is a method of testing a weld …
- without destroying the finished product.
- by destroying the finished product.
- by weld defects.
- without weld defects. (1)
4.14 Which ONE of the following factors influences the rate of cooling of the weld metal during the welding process?
- Weld metal thickness
- Amount of oxygen used in process
- Current setting of the welding machine
- Electrode thickness (1)
[14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (TEMPLATES) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Define a template loft. (2)
5.2 Describe THREE qualities of a good template loft. (3)
5.3 State the function of a web template. (2)
5.4 A steel ring with an outside diameter of 500 mm must be manufactured from a 30 x 30 mm square bar.
5.4.1 Calculate the dimensions of the required materials. (6)
5.4.2 Make a neat sketch of the steel ring indicating all the dimensions of the material. (4)
5.5 Make a neat sketch of a weld symbol indicating the following information of a site weld on a T-joint done with arc welding.
- The intermitted square butt weld on both sides is 10 mm in size
- The lengths of the weld beads are 60 mm each
- The pitch of the weld is 100 mm (6)
[23]
QUESTION 6: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
6.1 State TWO uses of each of the following machines:
6.1.1 Guillotine (2)
6.1.2 Bench grinder (2)
6.1.3 Press machine (2)
6.2 FIGURE 6.2 below shows a joining equipment.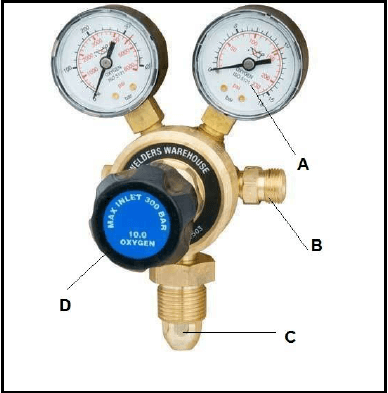
FIGURE 6.2 (4)
6.2.1 Label A–D.
6.2.2 Identify the joining equipment shown in FIGURE 6.2 above. (1)
6.3 What is the function of stock and dies? (1)
(1)
6.4 What is the primary function of the regulator fitted to the gas cylinder of the oxy-acetylene equipment? (2)
6.5 Explain the operating principle of plasma cutting machine that is used in a welding workshop. (4)
[18]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Define the following terms:
7.1.1 Force (2)
7.1.2 Hooke’s Law (2)
7.2 A machinist is performing a tensile test using a mild steel bar with a diameter of 24 mm. An applied load of 60 kN cause an extension of 0,22 mm and the original length was 212 mm.
Calculate the following:
7.2.1 Stress in the mild steel bar (2)
7.2.2 Strain in the mild steel bar (2)
7.2.3 Young’s modulus of elasticity (4)
7.3 FIGURE 7.3 below is diagram of a beam with a UDL resting on the beam. The beam is supported at two ends.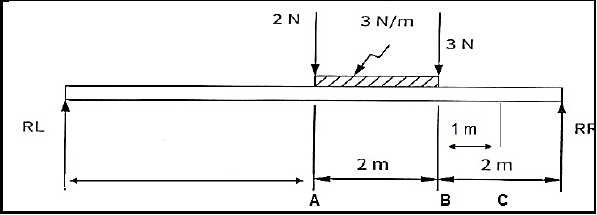
FIGURE 7.3
Calculate the following for FIGURE 7.3:
7.3.1 The magnitudes of RL and RR (6)
7.3.2 The bending moments at points A, B and C (3)
7.3.3 Shear forces at points, A, B and C (3)
7.3.4 Draw a shear force diagram (5)
7.3.5 The bending moment diagram
NOTE:
- Space diagram scale 1 : 100
- Shear force diagram scale 2 mm =1 N
- Bending moment diagram scale 2 mm = 1 N.m. (5)
7.4 Construct the space and force diagram of the following steel frame structure in order to determine the magnitude and nature of the forces in each member of the framework.
- Space diagram 1 : 100
- Force diagram 1 mm = 1 kN
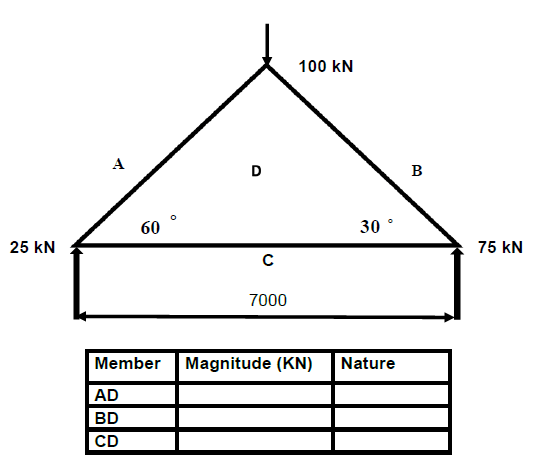
(11)
[45]
QUESTION 8: JOINING METHODS (INSPECTION WELD) (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Name TWO things to be observed during oxy-acetylene or arc welding to ensure that weld defects are not formed. (2)
8.2 Describe TWO types of cracks in welded joints. (4)
8.3 Label the diagram in FIGURE 8.3. (5)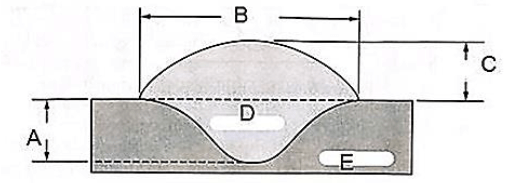
FIGURE 8.3
8.4 State TWO elements that should be inspected during the visual inspection process. (2)
8.5 State TWO causes of each of the following arc-welding defects:
8.5.1 Spatter / welding spatter (2)
8.5.2 Incomplete penetration (2)
8.6 Name TWO factors that should be observed to ensure a good welded joint during the arc-welding process. (2)
8.7 Give ONE reason for performing the following destructive tests:
8.7.1 Nick-break test (2)
(2)
8.7.2 Machinability test (2)
(2)
[23]
QUESTION 9: JOINING METHODS (STRESSES) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Define the following terms:
9.1.1 Weld distortion (2)
9.1.2 Residual stress (2)
9.2 Give any TWO main factors affecting grain size of steel when being cold worked. (2)
9.3 State any TWO types of steel groups and name the percentage carbon content in each. (4)
9.4 Name TWO types of quenching mediums. (2)
9.5 Discuss any TWO factors that affect shrinkage in welding. (2)
9.6 Describe with the aid of a sketch/diagram the following terms:
9.6.1 Transverse shrinkage (2)
9.6.2 Longitudinal shrinkage (2)
[18]
QUESTION 10: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
10.1 What is the purpose of keeping service records of maintenance of machines in the workshop? (1)
10.2 Give TWO reasons of locking out large machines before maintenance. (2)
10.3 How can friction be reduced when drilling holes? (1)
10.4 Explain how the following machines can be overloaded:
10.4.1 Guillotine (2)
10.4.2 Horizontal band saw (2)
[8]
QUESTION 11: TERMINOLOGY (DEVELOPMENT) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 FIGURE 11.1 below shows a conical hopper.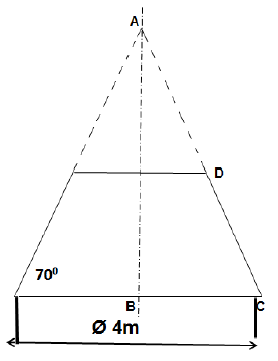
FIGURE 11.1
Calculate the following:
11.1.1 The true length DC (5)
11.1.2 The true length AD (4)
11.1.3 The base circumference of the hopper (3)
11.2 FIGURE 11.2 below shows a square-to-round transition piece. In order to develop the transition, the true lengths must be calculated: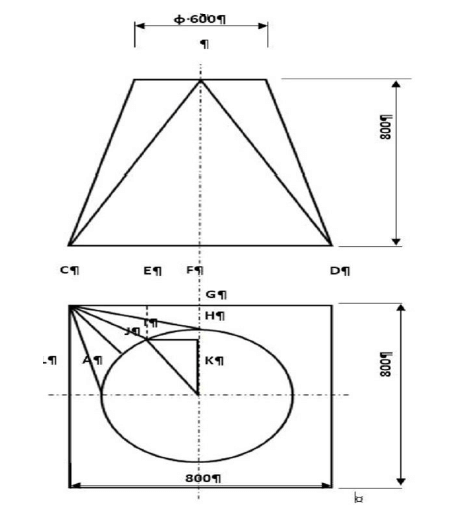
FIGURE 11.2
Determine the following true lengths with the help of calculations:
11.2.1 True length FG (5)
11.2.2 True length CI (4)
[21]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: WELDING AND METALWORK