AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1 (P1)
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C √√
1.1.2 B √√
1.1.3 A √√
1.1.4 A √√
1.1.5 D √√
1.1.6 A √√
1.1.7 C √√
1.1.8 B √√
1.1.9 A √√
1.1.10 D √√ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 None √√
1.2.2 B only √√
1.2.3 A only √√
1.2.4 B only √√
1.2.5 Both A and B √√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Pancreas √√
1.3.2 Stock density √√
1.3.3 Virus √√
1.3.4 Impotence √√
1.3.5 Concentration √√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Urea √
1.4.2 Conduction √
1.4.3 Mesoderm √
1.4.4 Posture √
1.4.5 Bulbo-urethral/Cowpers gland √ (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
2.1
2.1.1 Non-ruminant/monogastric √ (1)
2.1.2 Single/Simple stomach/Monogastric √ (1)
2.2
2.2.1 C √ (1)
2.2.2 D √ (1)
2.2.3 F √ (1)
2.2.4 I √ (1)
2.2.5 E √ (1)
2.3
2.3.1 It is highly soluble than biuret. √ (1)
2.3.2 Avoid keeping the lick in rain. √ (1)
2.3.3 ∙ A mixture of 2 kg urea and 20 kg molasses be sprayed on grazing √ ∙ Use of premixed fodders/mixtures/stock licks √ (2)
2.4
2.4.1
- Only abomasum is functioning √
- Rumen/reticulum/omasum still underdeveloped √
- Oesophogal groove transport milk to the abomasum √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4.2 When the calf starts eating solid food/starts grazing √ (1)
2.4.3
- Enable to digest cellulose √
- Hydrolyse protein √
- Synthesis of vitamins √
- Synthesis of amino acids √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5
2.5.1 DE of 5 kg DM intake = Gross Energy – energy lost in faeces
= 92,5 J – 42,5 J√
= 50 J √ (2)
2.5.2 Nett energy = Metabolic energy – Energy lost as heat
Metabolic energy = 50 J – 18,5 J = 31,5 J √
Nett energy = Metabolic energy – Energy lost as heat
= 31,5 J – 9 J √
= 22,5 J √
NB: Learners may use different ways/formula to arrive at 22,5 J, e.g. OR NE = DE – energy lost in urine + gases – heat loss |
(3)
2.6
Percentage of feed mixture
Ratio of Maize meal : peanut oilcake meal = 22 : 7,5
22 + 7,5 = 29,5 √
% of peanut oilcake meal = (7,5 / 29, 5) × 100 √
= 25, 42% √ (3)
2.7
2.7.1
Concentrate requirement = kg/day
= 42 kg/cow/day √
= 42 kg × 30 days × 100 cows √
= 126 000 kg (126 tons) √ (3)
2.7.2
Feed supply = 650 kg × 30 × 6 = 117 000 kg √
Feed required = 100 × 60 kg × 30 = 180 000 kg p/month × 6
= 1 080 000 kg √
= Feed supply – Feed required
= 117 000 kg –1 080 000 kg
= -963 000/1 000 √
= -963 tons √ (4)
2.7.3 Not enough √ - pasture has a shortage of 963 tons √ (2)
2.8
2.8.1 Tranquillisers √ (1)
2.8.2 Antibiotics √ (1)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
3.1
3.1.1
A Feeding shed √
B Holding pen √ (2)
3.1.2
(a) Holding pen / B √ (1)
(b) Feeding shed / A √ (1)
3.1.3
- Give cows time to pick up their calves before moving √
- Cows and calved should be moved slowly √
- Avoid trying to work cows and calves with dogs √ (3)
3.2
3.2.1 To warn animals of your presence √ (1)
3.2.2 Makes them feel insecure √ (1)
3.2.3 Allow animals to establish social groups √ (1)
3.3
3.3.1 D √ (1)
3.3.2 C √ (1)
3.3.3 A √ (1)
3.3.4 B √ (1)
3.4
Subsistence | Commercial | |
| 3.4.1 Purpose (2) | Produce only enough to feed the family √ | Produce to sell for a profit √ |
| 3.4.2 Management (2) | Limited as only few animals and crops produced √ | Intensive to ensure increased production √ |
3.5
3.5.1
A Chronic √
B Very sudden/develops within an hour/weeks √
C Acute √
D Deadly √ (4)
3.5.2 Anthrax √ (1)
3.5.3
- Burn the carcass √
- Do not cut open the animal carcass √
- Burry carcass deep in the ground √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.6
3.6.1 Nasal worm √ (1)
3.6.2
(a) C √ (1)
(b) A/B √ (1)
3.6.3 Summer √ (1)
3.6.4
- Sneezing and nasal irritation √
- Yellow nasal discharge √
- Shaking of head to get rid of the parasite √ (3)
3.7
3.7.1 Proper hygiene standards in abattoirs √ (1)
3.7.2 Quarantine of imported animals at ports of entry √ (1)
3.7.3
- Reporting any suspicion of the disease √
- Eradication programs √
- Immunisation campaigns √ (Any 1) (1)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
4.1
4.1.1 Embryo transfer √ (1)
4.1.2
- Prostglandin injection √
- Gonadotropin - release hormone √ (2)
4.1.3 A Donor √ (1)
4.1.4 37 °C √ (1)
4.1.5
(a) Their reproductive cycle is extended to produce more progeny √ (1)
(b) More profit from selling superior animals √ (1)
4.2
4.2.1
A Oestrus √
B Di-oestrus √
C Met-oestrus √
D Pro-oestrus √ (4)
4.2.2
(a) A √ (1)
(b) C √ (1)
4.3
4.3.1
B vas deference √
D scrotum√
F seminal vesicle √ (3)
4.3.2
- Hypoplasia √
- Cryptochidism √
- Sperm defects √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.4
4.4.1 Exhaustion/Fatigue √ (1)
4.4.2 Malnutrition √ (1)
4.4.3 Lack of experience √ (1)
4.4.4 Temperament √ (1)
4.5
4.5.1 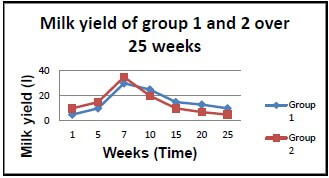
Marking graph with the following checklist:
Criteria | Yes: 1 mark | No: 0 mark |
1 Line graph | 1 | 0 |
2 Y-axis labelled | 1 | 0 |
3 X-axis labelled | 1 | 0 |
4 Points correctly labelled in group 1 and group 2 | 1 | 0 |
5 Correct heading | 1 | 0 |
6 Units (and time) | 1 | 0 |
(6)
4.5.2 Milk yield increases drastically in week 7 and drops from week 15 to week 20. √
OR
For both groups milk yield increases from week 1 to week 7 and then it decreases after week 7 until week 25. (1)
4.6
4.6.1 C √ allantois √ (2)
4.6.2 F √ placenta √ (2)
4.6.3 B √ chorion/embryonic sac √ (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150