AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAgricultural Sciences
Paper 2 (P2)
Grade 12
Nsc Past Papers And Memos
September 2016
QUESTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
1. This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
2. Answer ALL questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
3. Start EACH question on a NEW page.
4. Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
5. You may use a non-programmable calculator.
6. Show ALL your calculations, including formulae, where applicable. 7. Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 A breeder mated a good sire on a farm with a female of inferior quality to improve the quality of a poor herd. The breeding system used by the breeder is …
A species crossing.
B in-breeding.
C upgrading.
D out-crossing.
1.1.2 ... refers to a lack of response to price change. For example bread will be in demand even if the price rises.
A Price inelasticity
B Price elasticity
C Elasticity of supply
D Elasticity
1.1.3 To establish a successful business venture, you need to have the following:
(i) Commitment
(ii) Management skills
(iii) leadership
(iv) Academic degree
Choose the correct combination:
A (ii), (iii) and (iv)
B (i), (ii) and (iii)
C (i), (ii) and (iv)
D (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.4 One of the following descriptions constitutes a SWOT analysis of developing a business strategy:
A Strengths, wealth, opportunities and time
B Seriousness, weakness, opportunities and threats
C Strengths, weakness, opportunities and trust
D Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats
1.1.5 By the way of minimising or spreading risk, Grade 12 learners kept sheep, chicken and sheep and also cultivated vegetables on one farm. This is an example of …
A niche marketing.
B diversification.
C co-operative marketing.
D specialisation.
1.1.6 The type of credit required to purchase the illustration below is ... credit.
A medium term
B long term
C short term
D minimum term
1.1.7 The legislation which labour unions apply to fight against inappropriate working hours, leave, over time and how wages must be paid in the workplace.
A Employment Equity Act
B Labour Relations Act
C Basic Conditions of Employment Act
D Skills Development Act
1.1.8 The illustration below indicates one of the processes in which chromosomes may change. 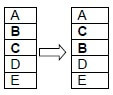
A Inversion
B Duplication
C Translocation
D Deletion
1.1.9 One of the following is NOT a reason for drawing up a business plan:
A Attracting investors or finding potential partners
B Obtaining financing
C Mapping out the direction of your business
D Employing a good entrepreneur
1.1.10 A … refers to a plant or grouping of plants selected for desirable characteristics.
A hybrid
B cultivar
C mutagen
D breed (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.2.1−1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.2.1 Contract A two equivalent genes 1.2.2 Business plan B DNA 1.2.3 Alleles C budget | A two equivalent genes B DNA |
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Write the agricultural term/phrase for each of the following descriptions next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 An apparatus that fires bullets into a piece of plant tissue
1.3.2 A sum of money provided for a specific purpose by a government that does not have to be repaid
1.3.3 Financial obligations such as the debts and loans that a company owes
1.3.4 Workers who are employed during peak periods, often for a specific task such as harvesting
1.3.5 The breeding system in which the offspring is always sterile or cannot reproduce (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD/S in the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the appropriate word(s) next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) on the attached ANSWER SHEET.
1.4.1 Cells are the units of inheritance.
1.4.2 There is a/an liquidity of products when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.
1.4.3 Capital is a production factor that does not depreciate, spoil, become old or get used up.
1.4.4 The approach that a company takes to marketing its products is called consumer index.
1.4.5 Negative external elements that could hamper the success of a business is creativity. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Study the illustration below and answer QUESTIONS 2.1.1 to 2.1.3 based on the illustration.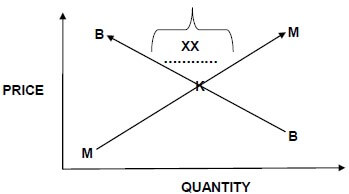
2.1.1 Identify the description marked XX in QUESTION 2.1. (1)
2.1.2 Explain your answer to QUESTION 2.1.1. (2)
2.1.3 Identify the letter K and the lines MM and BB in QUESTION 2.1. (3)
2.2
| You attended a seminar where one group of the participants were debating the difference between selling and marketing of processed goods. Another group was discussing eco-labelling and how it influences consumer behaviour. You were invited to draw TWO clear distinctions between marketing and selling. |
2.2.1 Tabulate the difference between marketing and selling. Provide TWO descriptions EACH for marketing and selling. (4)
2.2.2 State TWO main functions of agricultural marketing. (2)
2.2.3 Suggest TWO ways eco-labelling influence consumer behaviour. (2)
2.2.4 List TWO reasons why meat is processed. (2)
2.3 The illustration below is an example of a marketing chain showing the different components of supply chain and demand chain.
| MARKETING CHAIN | ||||||
SUPPLY CHAIN | DEMAND CHAIN | |||||
Purchasing | Manufacturing | Distribution | Marketing | Sales | Service | |
2.3.1 Define the underlined description in QUESTION 2.3. (2)
2.3.2 List TWO functions of post-harvest management in the marketing chain. (2)
2.3.3 Classify the following under either the supply chain or the demand chain.
(a) Value adding
(b) Packaging
(c) Cash flow and profitability (3)
2.4 You met a potential farmer standing next to the signboard below. The farmer asked you some questions about the signboard because the farmer wants to join the co-operative society.
2.4.1 Explain briefly what an agricultural co-operative society is to the farmer. (2)
2.4.2 State TWO benefits of agricultural co-operative societies for a farmer. (2)
2.5
| When marketing to consumers, it is important to know the different types of buyers and their characteristics. A buyer can be an innovator, adopter or a traditionalist. Consumers have different reasons why they purchase goods. Sellers should try to promote what they sell and adopt different approaches to marketing in order to make maximum profit on sales. |
2.5.1 Predict TWO characteristics of a buyer who is a traditionalist. (2)
2.5.2 Identify TWO ways sellers could make a profit from the scenario. (2)
2.5.3 State TWO ways sellers could promote sales. (2)
2.6 Differentiate between niche marketing and stock sales. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Different types of farm labour are indicated in the illustration A, B, C and D below. 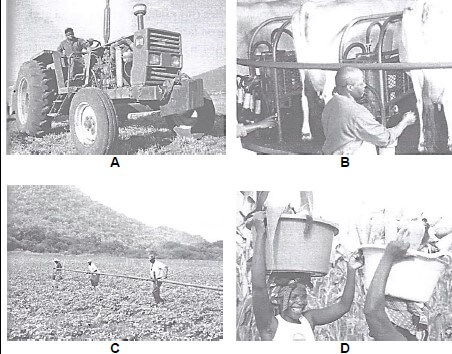
3.1.1 Indicate the type of farm labourer in illustrations A, B, C and D above that could be very scarce to commercial crop farmers. (1)
3.1.2 Justify your answer to QUESTION 3.1.1 with TWO reasons. (2)
3.1.3 Suggest TWO methods to improve the economic conditions of the workers in the illustrations (3.1). (2)
3.1.4 State a labour law that could apply in the following cases:
(a) The tractor operator could fall from the tractor which is in motion (1)
(b) The workers in D are no longer employed. (1)
3.2
| A farm manager is considering expanding a structure on the farm. The manager borrowed R15 000,00 from a friend. The manager took a bank loan of R28 000,00 and sold 5 000 birds to raise an additional R20 000,00. The gross income on the farm after two years was R73 000,00 |
3.2.1 Determine the net profit or loss of the farmer after two years. (3)
3.2.2 Identify TWO methods the manager used to raise capital from the scenario. (2)
3.2.3 Mention ONE other method the manager could use to create capital apart from the methods mentioned in QUESTION 3.2.2. (2)
3.2.4 Recommend the best record that could show all the expected income and expenditure over the period. (1)
3.3 A potential farmer wants to cultivate vegetables on commercial basis. A piece of land was sold to the farmer. When the farmer went to look at the land, the land looked like the picture below.
3.3.1 Suggest ONE economic characteristic of land as a production factor that can best describe the photograph in 3.3. (1)
3.3.2 Justify your answer in QUESTION 3.3.1 with TWO reasons. (2)
3.3.3 State THREE functions of land as a production factor in agriculture. (3)
3.3.4 Recommend TWO scientific methods to increase the productivity of land for agricultural purposes. (2)
3.4
| What sets farm management apart from other business management is the kind and number of daily duties involved, as well as the many management layers involved in farming. Even among farms, the process will vary depending on the type of farming business involved and the overall size of the business. Specific skills are therefore needed for different farming operations. |
3.4.1 Identify TWO reasons from the scenario to justify why managing poultry farm is different from managing a shop. (2)
3.4.2 Mention the specific management skills required in the following:
(a) Being able to keep the farm profitable and successful (1)
(b) Being able to deal with labour problems (1)
(c) Being able to deal with unforeseen issues or problems (1)
3.4.3 Outline TWO production risks that a farm manager may experience in crop production. (2)
3.5 The table below shows rice (in tons) exported by a commercial farmer for a period of seven years.
YEAR | QUANTITY EXPORTED |
2009 | 40 |
2010 | 25 |
2011 | 50 |
2012 | 55 |
2013 | 35 |
2014 | 60 |
2015 | 60 |
Translate the information into a line graph. (5)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1
| A breeder wants to increase the weaning weight of some animals. The average weaning weight of the animals on the farm is 22,5. The breeder selects a male animal with a weaning weight of 24,6 and a female with a weaning weight of 23,7. The heritability of weaning weight in the animals is 50%. |
4.1.1 Calculate the EBVs of the parents. (4)
4.1.2 Calculate the expected genetic gain of the off-spring. (2)
4.2 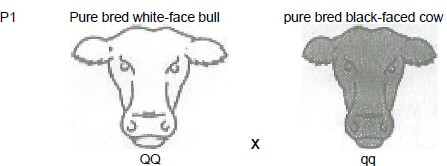
4.2.1 Draw a punnet square to complete the crosses illustrated in 4.2. (4)
4.2.2 State the possible percentage of white-faced offspring during the F2 generation. (3)
4.2.3 Give ONE appropriate genetic term to describe the differences in appearance of the two animals. (1)
4.2.4 Differentiate between phenotype and genotype. (2)
4.3
| For most organisms, sex is determined by chromosomal differences. During the formation of gametes by the process of meiosis and gametogenesis, two chromosomes of each homologous pair separate. Assume that a male gamete (29+X chromosomes) fuses with a female gamete (29+X chromosomes). |
4.3.1 Solve the chromosomes of the zygote. (2)
4.3.2 Predict the gender of the offspring. (1)
4.4 Define the following terminologies:
(a) Mutation (2)
(b) Out-crossing (2)
4.5
| Our ancestors had their traditional plant and animal improvement methods of selection and breeding such as mass selection and inbreeding respectively. A new method of plant and animal improvement has been developed, called genetic modification, which involves taking genes from one organism, the donor, and inserting them into another organism, the recipient. |
4.5.1 Deduce TWO aims of the genetic modification of plants. (2)
4.5.2 Provide TWO advantages of genetic modification over traditional methods. (2)
4.5.3 List TWO disadvantages of inbreeding. (2) 4.5.4 Distinguish between pedigree selection and progeny selection. (4)
4.6 State TWO environmental causes of variation in plants. (2) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150


