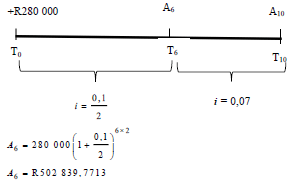ElimuZA Access to Education
Technical Mathematics P1 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMarking Codes | |
A | Accuracy |
CA | Consistent accuracy |
M | Method |
R | Rounding |
NPR | No penalty for rounding |
NPU | No penalty for units omitted |
S | Simplification |
SF | Substitution in the correct formula |
AO | Answer only |
NOTE:
- If a candidate answers a question TWICE, only mark the FIRST attempt.
- If a candidate has crossed out an attempt of a question and not redone the question, mark the crossed-out version.
- Consistent accuracy (CA) applies to ALL aspects of the marking guideline.
- Assuming answers/values to solve a problem is NOT acceptable.
| QUESTION 1 | ||||
| 1.1 | 1.1.1 | x(x - 5) = 6 x2 - 5x = 6 x2 - 5x - 6 = 0 (x - 6)(x + 1) = 0 x = 6 or x = -1 | √ Expansion √standard form √factors √x = 6 or x = -1 | (4) |
| OR | ||||
| x(x - 5) = 6 x2 - 5x = 6 x2 - 5x - 6 = 0 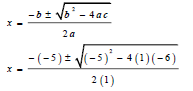 x = 6 or x = -1 | √expansion √standard form √substitution √x = 6 or x = -1 | |||
| 1.1.2 | -2x2 - 4x - 1 = 0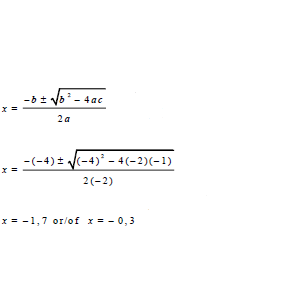 | √ formula √substitution √both values of x | (4) | |
| 1.1.3 | 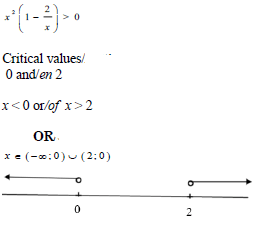 | √ critical values √ correct notation or √ number line | ||
| 1.2 | 1.2.1 | 20 seconds | √ 20 | (1) |
| 1.2.2 | 20 seconds = 20 hours 60 × 60 | √ 20 hours 60 × 60 | (1) | |
| 1.2.3 | 20 hours = 5,55 × 10-3 hours 60 × 60 | √Notation | (1) | |
| 1.3 | x/y = 2 ...............................(1) x2 + xy + y = 2 ..................(2) x = 2y ................................(3) Then (2y)2 + (2y)y + y = 2 4y2 + 2y2 + y - 2 = 0 6y2 + y - 2 = 0 (2y - 1)(3y + 2) = 0 | √ x- the subject √ substitution by √ simplification/std form √factors √ y-values √ x-values | (6) | |
| OR | ||||
| x/y = 2 ...............................(1) x2 + xy + y = 2 ..................(2) x/2 = y ................................(3) Then, x2 + x(x/2) + x/2 = 2 2x2 + x2 + x = 4 3x2 + x - 4 = 0 (3x + 4)(x - 1) = 0 x = -4/3 or x = 1 therefore: y = -2/3 or y = 1/2 | √ y-the subject √ substitute ; x/2 = y √ simplification / std form √factors √ x - values √ y- values | |||
| 1.4 | 1.4.1 | b = 2a = 2 × 2 = 4 | √ b = 4 √ c = 8 | (2) |
| 1.4.2 | b2 - 4ac = (4)2 - 4(2)(8) = 16 - 64 b2 - 4ac = -48 therefore; roots are non-real imaginary | √ Δ = -48 √ imaginary / non-real | (2) | |
| 1.5 | 41 = 1 × 25 + 0 × 24 + 1 × 23 + 0 × 22 + 0 ×21 + 1 × 20 -1 mark if base 2 is omitted | √ method √ 1010012 | (2) | |
| [26] | ||||
| 2.1 | 2.1.1 | 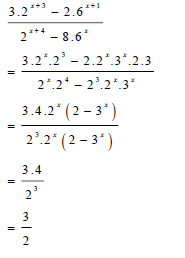 | √ Prime factors √ CF numerator √ CF denominator √ 3/2 | (4) |
| OR | ||||
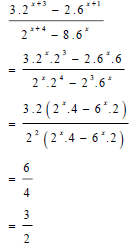 | √ same base √ CF numerator √ CF denominator √ 3/2 | |||
| 2.1.2 | 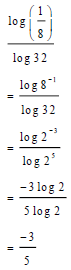 | √ log8-1 √ same base rule √ -3/5 | (3) | |
| OR | ||||
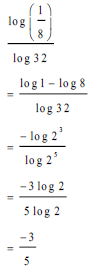 | √ log 1 - log 8 √ same base rule √ -3/5 | |||
| 2.2 | 2(x - y)(x - y) OR 2(x - y)(x + y) | √ substitution √ expansion √ simplification | ||
| 2.3 | 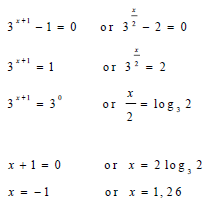 | √ 3x+1 = 1 √ 3x/2 = 2 √ 0 exponent rule √ log form 3x + 1 = 1 √ same base √ x = -1 3x/2 = 2 √ x = 2log32 √ x = 1,26 | ||
| OR | ||||
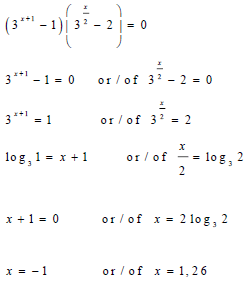 | √ 3x+1 = 1 √ 3x/2 = 2 √ log31 √ log32 √ x + 1 = 0 √ x = 2log32 √ x = -1 √ x = 1,26 | |||
| 2.4 | 3x = -3 and -5y = 0 x = -1 and y = 0 | √ equating parameters √ x = -1 √ y = 0 | ||
| 2.5 | 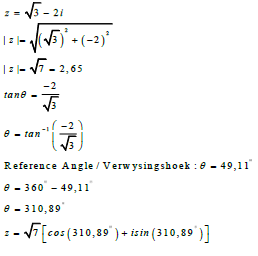 | √ finding r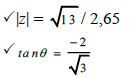 √ reference angle √ θ = 310,88º √ correct form | (6) | |
| [27] | ||||
| QUESTION 3 | ||||
| 3.1 | y = -4 | √ y = -4 | ||
| 3.2 | 3x - 4 = 0 3x = 4 x = log34 x = 1,26 | √ f(x) = 0 √ log form √ x = 1,26 | (3) | |
| 3.3 | f(x) = 3x - 4 f(0) = 3º - 4 y = -3 | √ subst. x = 0 √ y = -3 | (2) | |
| 3.4 | 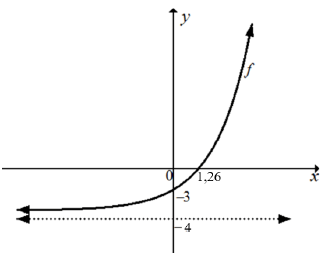 | √ shape √ both intercepts √ asymptote | (3) | |
| 3.5 | y > -4 or y∈(-4;∞) or -4<y<∞ | √ -4 | (1) | |
| [10] | ||||
| QUESTION 4 | ||||
| 4.1 | B(0;2) | √B(2;0) | (1) | |
| 4.2 | √ substitution √ g(x) = √4 - x2 | (2) | ||
| 4.3 | x∈[-2;2] OR -2 ≤ x ≤ 2 OR x ≥ -2 and x ≤ 2 | √ critical values from 4.1 √ notation | (2) | |
| 4.4 | x∈(-2;0) OR -2 < x < 0 | √ critical values from √ notation | (2) | |
| [7] | ||||
| QUESTION 5 | ||||
| 5.1 | h(0) = -(0)2 + 4(0) - 3 = -3 c(0;-3) | √ 0 √ -3 | (2) | |
| 5.2 | m(x) = p/x - 3 -1 = p/1 - 3 p = 2 | √ substitution √ p = 2 | (2) | |
| 5.3 | m(x) = 2/x - 3 | √ substitute 2 and -3 | (1) | |
| 5.4 | x = -b/2a = -4 2(-1) = 2 h(2) = -(2)2 + 4(2) - 3 = 1 D(2;1) | √ substitution √ x = 2 √ h(2) √ D(2;1) | (4) | |
| OR | ||||
| h'(x) = -2x + 4 = 0 therefore x = 2 h(2) = -(2)2 + 4(2) - 3 = 1 D(2;1) | √ h'(x) = -2x + 4 √ x = 2 √ h(2) √ D(2;1) | |||
| OR | ||||
| (-x + 1) (x - 3) = 0 x = 1 or x = 3 therefore axis of symmetry x = 1 + 3 = 2 2 h(2) = - (2)2 + 4(2) - 3 = 1 D(2;1) | √ x-intercepts √ x = 2 √ h(2) √ D(2;1) | |||
| 5.5 | DE = 1 + 3 = 4 units | √ OE + OD √ 4 | ||
| QUESTION 6 | ||||
| 6.1 | 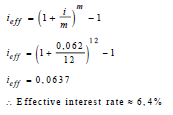 | √ formula √ substitution √ ieff ≈ 6.4% | ||
| 6.2 | A = P (1 - in) 40 000 = P(1 - 0,1 × 3) P = 40000 = R57 142,86 (1 - 0,1 × 3) | √ substitute i and n √ substitution √ P subject √ simplification | ||
| 6.3 |
A10 = R 352 839, 7713 (1 + 0,07)4 | √ values of i and n √ substitute P, i and n √ A6 √ P6 √substitution P6, i and n √ value of A10 | (6) | |
| OR | ||||
| A6 = R502 839, 7713 A6(1) = R 502 839, 7713 (1 + 0,07)4 A6(1) = R 659 120,3659 A7(1) = R 150 000(1 +0,07)4 A7(1) = R 196 619, 4015 A10 = R 659 120, 3659 - R 196 619, 4015 A10 = R 462 500, 96 | √values of i and n √ substitute P, i and n √ A6 √ P6 √ A6 √ P6 √ A 2(1) √ A6 √ P6 √ value of A10 | |||
| [13] | ||||
| QUESTIONS 7 | ||||
| 7.1 | 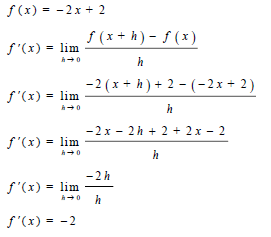 | √ definition √ substitution √ simplification √ simplification √ f'(x) = -2 | (5) | |
| 7.2 | 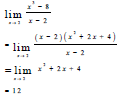 | √ (x - 2)(x2 + 2x + 4) √ simplification √ 12 | (3) | |
| 7.3 | 7.3.1 | y = - 3 - 2x2 + 2x 5x2 y = 3x-2 - 2x2 + 2x 5 dy = 6x-3 - 4x + 2 dx 5 | √ - 3 5x2 √ 6x-3 5 √ - 4x √ 2 | (4) |
| 7.3.2 | 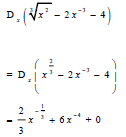 | √ x 2/3 √ 2/3x-1/3 √ 6x-4 | (3) | |
| [15] | ||||
| QUESTION 8 | ||||
| 8.1 | 8.1.1 | y = -4 | √ y = -4 | (1) |
| 8.1.2 | f(x) = (1 - 2x)(x2 - 4) 0 = (1 - 2x) (x2 - 4) x = ½ or x = 2 or x = -2 | √ f(x) = 0 √ x = ½ √ x = ± 2 | (3) | |
| 8.1.3 | f(x) = -2x3 + x2 + 8x - 4 | √ f(x) = -2x3 + x2 + 8x - 4 | (1) | |
| 8.1.4 | f(x) = -2x3 + x2 + 8x - 4 f'(x) = -6x2 + 2x + 8 0 = -6x2 + 2x + 8 0 = 3x2 - x - 4 0 = (x + 1) (3x - 4) x = 4/3 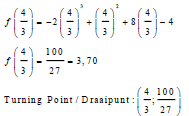 | √ f(x) CA from 8.3 √ f'(x) = 0 √ factors √ x = 4/3 √ [100] [ 27 ] | (5) | |
| 8.1.5 | 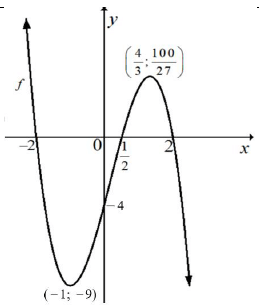 | √ x-intercept √ y-intercept √ turning points √ shape | (4) | |
| 8.2 | Average gradient = g(a) - g(4) = 9 a - 4 (2a2 - a - 3) - 25 = 9 a - 4 2a2 - a - 28 = 9a - 36 2a2 - 10a + 8 = 0 a2 - 5a + 4 = 0 (a - 4) (a - 1) = 0 a = 1 | √ g(a) - g(4) a - 4 √ = 9 √ STD form √ factors √ a = 1 | (5) | |
| [19] | ||||
| QUESTION 9 | ||||
| 9 | 9.1 | V(t) = t2 - 9t + 35 V(0) = (0)2 - 9(0) + 35 = 35L | √ substitution √ V(0) = 35L | (2) |
| 9.2 | V(t) = t2 - 9t + 35 V(1) = (1)2 - 9(1) + 35 = 27L | √ substitution √ V(1) = 27L | (2) | |
| 9.3 | V(t) = t2 - 9t + 35 V'(t) = 2t - 9 V'(t) = 2t - 9 = 0 t = 9/2 | √ V'(t) √ V'(t) = 0 √ t = 9/2 | (2) | |
| 9.4 | maximum amount of fuel leaked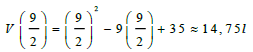 | √ substitution √ V ≈ 14,75L | ||
| QUESTION 10 | ||||
| 10.1 | √ x3 3 √ 3inx √ x √ c | |||
| 10.2 | 10.2.1 | 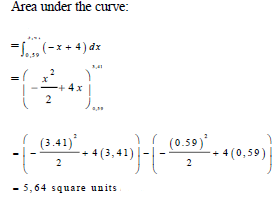 | √ integral function √ correct lower and upper bounds √ simplification √ substitute 3,41 √ substitute 0,59 √ 5,64 | (6) |
| 10.2.2 | Striped A = A under f (x) – A under g(x) Striped area =5,64−3,5 Striped area =2,13 square units | √ difference √ substitution √ 2,13 square units | (3) | |
| [13] | ||||
| TOTAL | 150 | |||
Published in Grade 12 September 2019 Preparatory Examinations