Technical Sciences P2 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 A(2)
1.2 A(2)
1.3 B(2)
1.4 C(2)
1.5 A (2)
1.6 B(2)
1.7 A(2)
1.8 C(2)
1.9 A(2)
1.10 B(2) [20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 A series of organic molecules that can be described by the same general formula and where each member differs from the next by a CH2 group. (2)
2.2 2.2.1 Organic molecules with the same molecular formula, but different structural formula. (2)
2.2.2 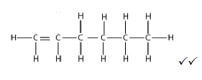 (2)
(2)
2.2.3 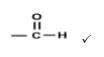 Aldehydes (2)
Aldehydes (2)
2.2.4 3-Chlorobut-1-ene (2)
2.2.5 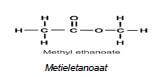
Methyl part | 1 mark |
|
Ethanoate part (functional group) | 1 mark |
|
(2)
2.3
2.3.1 Small organic molecules that can be covalently bonded to each other in a repeating pattern. (2)
2.3.2 2-Ethene (2)
2.3.3
- Manufacturing of plastic bags
- Synthesis of bullet proof vests
- Manufacturing of plastic bottles
- Manufacturing of cling wrap (Any 2) (2)[18]
QUESTION 3
3.1 CnH2n+2 (1)
3.2 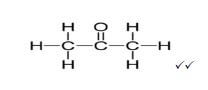 (2)
(2)
3.3 Propanal (2)
3.4
3.4.1 Hydrogen bonds and London forces (1)
3.4.2 Van der Waals forces (London forces) or Induced dipole force (Any one) (1)
3.5 As the strength of the intermolecular forces become stronger (increases) then the vapour pressure will become lower (decrease) OR As the strength of intermolecular forces become weaker, then the vapour pressure will become higher (increase). (2)
3.6 Ethanoic acid.
- Ethanoic acid has stronger intemolecular forces than Propan-1-ol hence a lower vapour pressure thus more energy will be required to overcome the intermolecular forces in ethanoic acid than in Propan-1-ol. The lower the vapour pressure, the higher the boiling point. (4) [13]
QUESTION 4
4.1 Addition (reaction) Hydation (1)
4.2
- Add sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide
- Heat the reaction mixture (2)
4.3 2-bromo butane (2)
4.4 
One mark for each reactant and product (3)
4.5 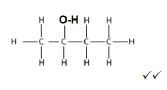
Butan-2-ol (3)
4.6 C4H8 + 6O2 → 4 CO2 + 4 H2O balance (3)
4.7 Hydrolysis (2) [16]
QUESTION 5
5.1
- An electrolyte is a substance of which the aqueous solution contains Ions.
OR
A substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that conducts electricity.
OR
A substance that forms free ions when melted. (2)
5.2 Temperature: 298 K or 25 °C
Concentration : 1 mol.dm-3 (2)
5.3
5.3.1 2 Cl- → Cl2 + 2e- (2)
5.3.2 Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu (2)
5.4 Electrolytic cell – Converts electrical energy to chemical energy. (2)
5.5 Q Reduction takes place (2)
5.6
5.6.1 Cu is a stronger reducing agent than Cl ions. Cu will be oxidised to Cu2+ ions resulting in the plate becoming eroded. (3)
5.6.2 Non-spontaneous (1) [16]
QUESTION 6
6.1 Galvanic Cell: Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy. (2)
6.2 External circuit or through the voltmeter. (2)
6.3 It maintains electrical neutrality OR It separates the two compartments so that they do not mix. (2)
6.4 Zn → Zn2+ + 2e- (2)
6.5 from Zn to Cu (1)
6.6 Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu (3)
6.7
- Eᶿcell = Eᶿcathode - Eᶿanode
= 0,34 – (-0,76)
= 1,1V (4)
6.8 It means they did not take the measurements at standard conditions where temperature is 298 K or 25 °C and concentration of 1 mol.dm-3. (3)
6.9
6.9.1 During solar construction, the following are identified as environmental threats:
- a release of greenhouse gases
- polution of drinking pure water (2)
6.9.2
- Lowers the electricity bill
- Increases home resale value
- Takes advantage of tax credits fom the goverment
- Net metering allows reselling of excess electricity to the utility company
(Any 2) (2) [23]
QUESTION 7
7.1 The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane and the angle of reflection ᶿr = angle of incidence ᶿi. (2)
7.2
7.2.1 Total internal reflection (1)
7.2.2 Refraction (1)
7.3
- In the medical field
- In telecommunications
- In submarines (Any 2) (2)
7.4
- Light must travel from a more dense optical medium to a less dense optical medium
- The incident angle must be greater than the critical angle(2)
7.5
7.5.1 It is an angle of incidence in the denser medium such that the refracted rays just passes through the surface of separation of the two medium. (2)
7.5.2 24° (2)
7.6 A
- Because of the phenomenon of total internal reflection, the cut will glow brighter than that of B (2)
7.7
7.7.1 Dispersion is when white light spreads into its component colours. (2)
7.7.2 Violet (blue region ) (1)
7.7.3 It has a higher frequency. The higher the frequency, the less the degree of refraction. (2) [19]
QUESTION 8
8.1 Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one optical medium to another. (2)
8.2
- Incident ray
- Refracted ray (2)
8.3
8.3.1 20° (1)
8.3.2 41° (2)
8.4
8.4.1
- Real Image
- Inverted
- Enlarged Image (3)
8.4.2
- Used in film projectors
- Used in microscopes
- Used in photographic zoom lens (Any 2) (2) [12]
QUESTION 9
9.1 It is a wave with a changing magnetic and electric field perpendicular to each other in the direction of propagation of the wave. (2)
9.2
- Lifting of heavy objects
- In music equipment (loudspeakers)
- In transmission of signals
- In communication systems
(Any 3) (3)
9.3 They have a penetrating ability into the skin that can cause skin cancer. (2)
9.4 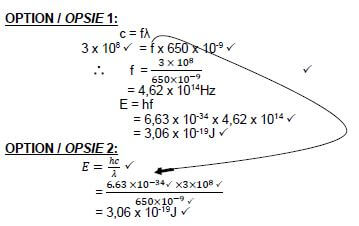 (5)
(5)
9.5 SMALLER THAN (1) [13]
TOTAL: 150