Technical Sciences P1 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 B (2)
1.2 B (2)
1.3 B (2)
1.4 B (2)
1.5 A (2)
1.6 A (2)
1.7 B (2)
1.8 B (2)
1.9 D (2)
1.10 B (2) [20]
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 When a net force acts on an object, the object accelerates in the direction of the force. This acceleration is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. (2)
2.1.2
- Normal
- Force of gravity
- Tension (3)
2.1.3
- Fnet = ma
T = (10)(0,3)
T = 3 N (3)
2.1.4 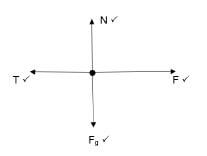 (4)
(4)
2.1.5
- Fnet = ma
F – T = ma
F – 3 = (20)(0,3)
F = 9 N (4)
2.1.6 Increases (1)
2.1.7 Increases (1)
2.2
2.2.1
- Pair 1 – Force exerted by the ring on the wall
Force exerted by the wall on the ring. - Pair 2 – Force exerted by the spring balance A on B
Force exerted by the spring balance B on A - Pair 3 – Force applied by learner on spring balance A
Force exerted by the spring balance A on the learner
(Any TWO sets)(Per set )(4)
2.2.2 3 N (2)
2.2.3
- Newton’s third law/Newton se derde wet.
When object A exerts a force on object B, object B simultaneously
exerts an oppositely directed force of equal magnitude on object A. (3) [27]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Impulse is defined as the product of the net force acting on an object and the time (the net force acts on the object.)(2)
3.1.2 (4)
| OPTION 1 Upward POSITIVE FnetΔt = Δp Fnet(0,01) = [0,06)(8 – (−14)] Fnet = 132 N | OPTION 2 Downward POSITIVE FnetΔt = Δp Fnet(0,01) = [0,06)(−8 – (14)] Fnet = −132 N Fnet = 132 N |
3.1.3 132 N (1)
3.1.4 Decreases (1)
3.2
- Air bags
- Crumple zones
- Arrestor beds (3)
3.3 3.3.1 An isolated system is one on which the net external force acting on the system is zero. (2)
3.3.2
- Σpi = pi(car) + pi(truck)
= 5 000 + 0
= 5 000 kg.m.s-1 (2)
3.3.3 5 000 kg.m.s-1 (1)
3.3.4 The total linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant (is conserved). (2)
3.3.5
- Σpi = Σpf
5000 = pfcar) + pf(truck)
5000 = (−500) + (1500)vf
vf = 3,67 m.s-1 due East (3)
3.3.6
- ΣEki = ½ mcvic 2 + ½ mTviT 2 mcvic = 5000 vic = 5 m.s-1
= ½(1 000)(5)2 + 0
= 12 500 J
ΣEkf = ½ mcvfc 2 + ½ mTvfT 2 mcvfc = −500 vfc = − 0,5 m.s-1
=½(1 000)(−0,5)2 + ½(1 500)(3,67)2
=10 226,68 J
ΣEki ≠ ΣEkf
∴ Collision is inelastic / (7) [28]
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1 The sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. (2)
4.1.2 B (1)
4.1.3 In an isolated system the total mechanical energy remains constant. (2)
4.1.4
- Mechanical energy at A = EP + EK
= 60 + ½mv2
= 60 + ½(0,2)(1,5)2
= 60,23 J
ME at/by A = ME at/by B
60,23 = mgh + ½mv2
60,23 = (0,2)(9,8)(4,5) + ½(0,2)v2
v2 = 514,05
v = 22,67 m.s-1 (6)
4.2
4.2.1
- F3 (1)
- Fgirl (1)
4.2.2(4)
| OPTION 1 Wnet = FnetΔx cosθ Wnet = (42 – 1,2)(3) cos 0° Wnet = 122,4 J |
| OPTION 2 Wnet = Wgirl + WF3 Wnet = Fgirl Δx cos θ + F3 Δx cosθ Wnet = (42)(3) cos 0° + (1,2)(3)(cos180°) Wnet = 122,4 J |
4.2.3 Power (1)
4.2.4
- Power = 400 W
Work done per second = 400 W
∴ Time taken = 1 s (2) [20]
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 A perfectly plastic body is a body which does not show a tendency to regain its original shape and size when the deforming force is removed. (2)
5.1.2 Modulus of elasticity / K (1)
5.1.3 B (1)
5.1.4 A (1)
5.1.5 C (1)
5.2
5.2.1 Pascal’s law states that in a continuous liquid at equilibrium, the pressure applied at a point is transmitted equally to the other parts of the liquid. (2)
5.2.2
- Area/Oppervlakte = πr2
= π (13 x10-2)2
= 0,053 m2
F1= F2
A1 A2
300 = 18 000
0,053 A2
A2 = 3,18 m2 (6) [14]
QUESTION 6
6.1 Capacitor is a device for storing electrical charge for a short time. (2)
6.2
- Filter circuits in power supplies.
- Separation of frequencies between the woofer (base) speaker.
- Power factor correction/improvement in electrical transmission systems. (ANY TWO )(2)
6.3
- Q = CV
Q = (10 x 10-6)(5)
Q = 50 x 10-6 C (3)
6.4
6.4.1 A semi-conductor is a material that has electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. (2)
6.4.2 Silicon and Germanium (2)
6.4.3 p-type (2) [13]
QUESTION 7
7.1 The potential difference across a conductor is directly proportional to the current in the conductor at constant temperature. (2)
7.2 1
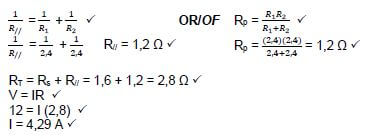 (6)
(6)
7.3
7.3.1 Decreases (1)
7.3.2 Current decreases RT increases when S1 is open (2) [11]
QUESTION 8
8.1
8.1.1 Faraday's law states that when the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes, an emf is induced in the coil. The magnitude of induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux. (2)
8.1.2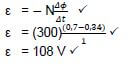 (3)
(3)
8.2
8.2.1
- A transformer that increases the voltage is called a step-up transformer.
A transformer that decreases the voltage is called a step-down transformer. (4)
8.2.2 Step-up transformer/Verhogingstransformator (2) [11]
QUESTION 9
9.1 DC generator. It has split ring commutator. (2)
9.2 Mechanical energy to electrical energy. (2)
9.3 Rectangular coil (1)
9.4 Principle of electromagnetic induction. (1) [6]
TOTAL: 150