Life Sciences P1 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupINSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in your ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answer to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- Do ALL drawings in pencil and label them in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, tables or flow charts only when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 Which ONE of the following forms part of the placenta?
- Chorion
- Amnion
- Umbilical cord
- Uterus
1.1.2 The list below represents some reproductive strategies in animals:
- Amniotic egg
- External fertilisation
- Oviparous development
- Altricial development
Which of the strategies above are applicable to chickens?- (i) and (ii) only
- (i) and (iii) only
- (i), (ii) and (iii) only
- (i), (ii) and (iv) only
1.1.3 The diagram below represents a process that takes place during meiosis.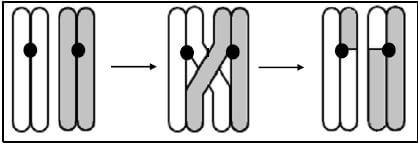
Which ONE of the following statements correctly describes the process?
- The process is crossing over and it results in genetically identical gametes
- The process is nondisjunction and it results in gametes with the same number of chromosomes
- The process is crossing over and it results in genetically different gametes
- The process is nondisjunction and it results in gametes with an abnormal number of chromosomes
1.1.4 The table below shows the average lengths of human foetuses.
TIME (weeks) | FOETAL LENGTH (cm) | |
Female | Male | |
8 | 1 | 1 |
16 | 13 | 14 |
24 | 31 | 33 |
36 | 43 | 46 |
40 | 49 | 51 |
Which of the following statements about the information in the table is correct?
- The female foetuses grow at the same rate as the male foetuses.
- The female foetuses grow faster than the male foetuses.
- The male foetuses grow faster than the female foetuses in the beginning and then the female foetuses will grow faster than the males at the end.
- The male foetuses grow faster than the female foetuses.
1.1.5 The diagram below shows two eyes focused on objects at different distances from the eye.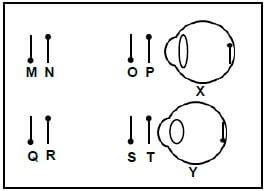
The objects on which eye X and Y are focused are …
- N and R respectively.
- M and T respectively.
- O and S respectively.
- M and R respectively.
1.1.6 The diagram below shows the development of a zygote in humans.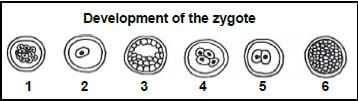
The correct sequence of the structures is:
- 1, 4, 2, 3, 5, 6
- 6, 4, 2, 5, 3, 1
- 2, 4, 5, 1, 6, 3
- 2, 5, 4, 1, 6, 3
1.1.7 Which part of the brain interprets the information from the cristae?
- Cerebellum
- Cerebrum
- Medulla oblongata
- Corpus callosum
1.1.8 The onset of the reproductive age is called …
- menstruation.
- puberty.
- menarche.
- menopause.
1.1.9 Which combination of structures below indicates the correct sequence in which the sperm travels to meet the ovum in a human female?
- Vagina → cervix → uterus → fallopian tube
- Vagina → fallopian tube → cervix → uterus
- Vagina → uterus → cervix → fallopian tube
- Vagina → fallopian tube → uterus → cervix
1.1.10 The list below shows the characteristics of a sperm cell:
- Head with nucleus
- Enzyme-rich structure in the head
- Many mitochondria
- Movable tail
Which of the above characteristics enables the sperm cell to move?- (i), (iii) and (iv) only
- (ii), (iii) and (iv) only
- (ii) and (iii) only
- (iii) and (iv) only
(10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The use of resources in such a way that they are available for future generations
1.2.2 The hormone that regulates the amount of salt in the blood
1.2.3 The structure that provides nutrients to the developing embryo in oviparous organisms
1.2.4 A diagram showing the number and appearance of chromosomes in a cell
1.2.5 The division of cytoplasm during cell division
1.2.6 The type of fertilisation where the ovum is fertilised inside the female reproductive organs
1.2.7 The organ in human females where meiosis takes place
1.2.8 Chemical substances used to eliminate pests
1.2.9 Points on homologous pairs of chromosomes where crossing over takes place
1.2.10 The structure in the head of the sperm that contains enzymes (10 x 1) (10)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN І applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE of the items in COLUMN ІІ. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN І | COLUMN ІІ |
1.3.1 Inhibits the growth of lateral branches |
|
1.3.2 A structure involved in gaseous exchange in the amniotic egg |
|
1.3.3 Components of the autonomic nervous system |
|
(3 x 2) (6)
1.4 The diagram below represents the structure of the male reproductive system.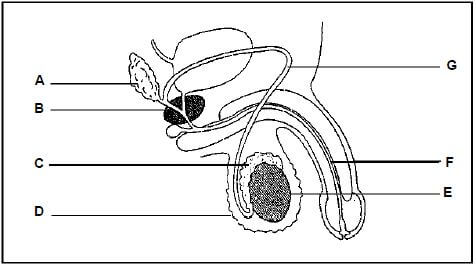
1.4.1 Label part:
- G (1)
- F (1)
1.4.2 Supply the LETTER and the NAME of the structures with the following functions:
- The part where the sperm cells mature (2)
- The structure that controls the temperature for sperm production (2)
1.4.3 Describe the common function of parts A and B. (2)
1.5 The diagrams below show different phases of the process of meiosis.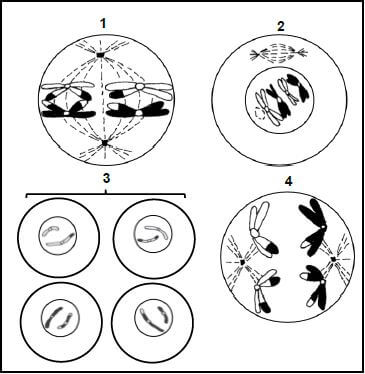
Give the NUMBER of the phase where:
1.5.1 The chromosomes are haploid (1)
1.5.2 Spindle fibres pull chromosomes to opposite poles (1)
1.5.3 Crossing over takes place (1)
1.5.4 A new nuclear membrane forms around unreplicated chromosomes (1)
1.5.5 The spindle fibres start to form (1)
1.5.6 Random arrangement of chromosome pairs take place (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 A factory was built on a hill next to a dam as shown in the diagram below. The dam is a source of water for an informal settlement built next to the factory. As a result of the activities of the factory, hot water is pumped from the factory into the dam next to it.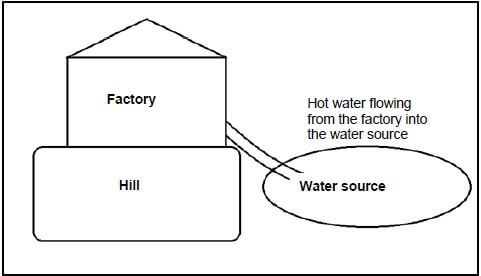
2.1.1 Define the term thermal pollution. (2)
2.1.2 Explain ONE advantage of the dam to the community. (2)
2.1.3 The management of the factory made a statement saying that the hot water pumped into the dam has no effect on the water and the living organisms in the water. Explain TWO reasons why this statement is false. (4)
2.2 The diagram below shows the process of the greenhouse effect. 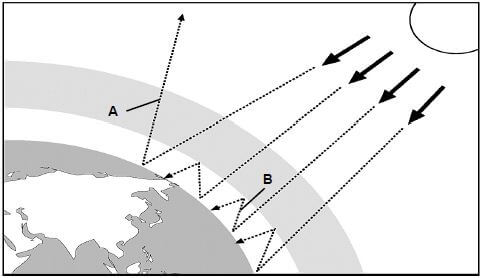
[Adapted from www.blogs.ntu.edu.sg]
2.2.1 The process at B is caused by an increased concentration of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide. Name TWO human activities that cause an increase in the carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere. (2)
2.2.2 Describe what happens at the following points on the diagram:
- A (1)
- B (1)
2.2.3 An increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere leads to enhanced greenhouse effect which may result in increased average temperature of the surface of the earth known as global warming. Explain TWO effects of increased average temperatures on earth. (4)
2.3 Gonadotropin-releasing hormone is a hormone released by the hypothalamus in females. It starts a chain of events during the menstrual cycle. The following diagram is a representation of the steps during the menstrual cycle in females.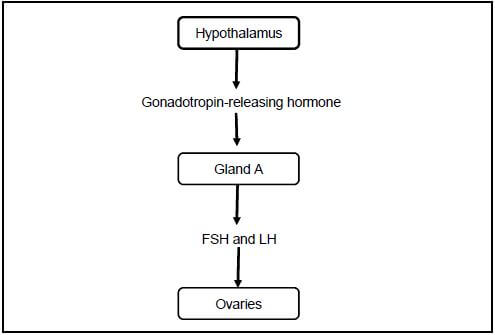
[Adapted from www.open.edu]
2.3.1 Name gland A. (1)
2.3.2 According to the diagram, what is the function of gonadotropin-releasing hormone? (2)
2.3.3 Describe the effect of FSH on the ovaries. (2)
2.3.4 An ovulation indicator test can be used to predict the time of ovulation in a woman. It measures the amount of LH in blood or urine. Explain why a woman who wants to fall pregnant would use an ovulation indicator test. (2)
2.3.5 In some females too little progesterone is secreted. Explain ONE problem this could cause in a female who is trying to fall pregnant. (2)
2.4 Read the following extract about motor neuron disease.
Motor neuron diseases (MNDs) refers to a group of conditions that cause the motor neurons in the nerves of the spinal cord and brain to progressively lose function. MNDs are rare but serious and incurable forms of progressive neurodegeneration. Motor neurons are nerve cells that send impulses to the muscles. [Adapted from www.medicalnewstoday.com] |
2.4.1 According to the extract, what is the definition of motor neuron disease? (1)
2.4.2 From the extract, list TWO factors that can cause motor neuron disease. (2)
2.4.3 Explain the possible effect that this disease will have on the reflex action if a person was to step on a thorn. (3)
2.4.4 Draw a labelled diagram of a motor neuron. (4)
2.5 One of the defects of the eye is astigmatism.
2.5.1 Describe how astigmatism is caused. (2)
2.5.2 Describe how astigmatism can be treated. (1)
2.5.3 Name TWO defects of the eye that are associated with the lens. (2) [40]
QUESTION 3
3.1 An investigation was conducted by scientists to determine the effect of a low GI breakfast and a high GI breakfast on the average blood glucose concentration of women.
NOTE:
- High GI food is quickly digested and absorbed.
- Low GI food is slowly digested and absorbed.
- GI is the Glycaemic Index of a person. Glycaemic Index is a figure representing the relative ability of a carbohydrate food to increase the level of glucose in the blood.
The following steps were followed during the investigation:
- Ten women who were between the ages of 28 and 30 volunteered to participate.
- The blood glucose concentration of each female was measured before eating breakfast.
- After eating breakfast, the blood glucose concentration was measured at 15-minute intervals over a period of 120 minutes.
The results of this investigation are shown in the graph below.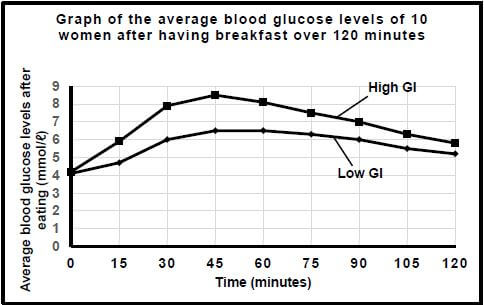
[Adapted from www.ncbi.nih.gov]
3.1.1 Explain ONE possible reason why blood samples were taken before breakfast was eaten. (2)
3.1.2 Give the independent variable for this investigation. (1)
3.1.3 Give the blood glucose concentration at 45 minutes after eating a high GI breakfast in mmol/ℓ . (1)
3.1.4 With reference to the graph, describe the difference between the effect of eating low GI food compared to eating high GI food on the blood glucose levels of the women. (2)
3.1.5 Name the hormone secreted by the pancreas that will cause the effects on blood glucose levels as seen in the graph from 45 to 120 minutes. (1)
3.1.6 Explain the effect of a high GI breakfast on the secretion of the hormone named in QUESTION 3.1.5. (2)
3.1.7 Six months later the scientists decided to repeat the investigation. Five additional women joined the investigation and were not given breakfast at all as a control group.
- Give ONE reason why the scientists decided to repeat the investigation. (1)
- Explain the significance of having a control group for this investigation. (2)
3.1.8 Give TWO ways in which the scientists ensured the validity of the original investigation. (2)
3.2 A group of Grade 12 learners set up the following apparatus in their classroom. Two plants were used. One was placed on a clinostat that rotated (Diagram A) and the other was placed in a stationary position (Diagram B). They left the apparatus in these positions inside a dark cupboard for two weeks before making the observations as indicated in the diagram below.
NOTE: A clinostat is an apparatus that is able to rotate.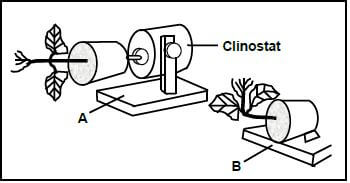
3.2.1 What type of plant growth movement was observed? (1)
3.2.2 Briefly explain the results observed in:
- A (3)
- B (4)
3.2.3 State ONE reason why the apparatus was placed in a dark cupboard for the duration of the investigation. (1)
3.3 Alien plant invasions may lead to loss of biodiversity.
3.3.1 List THREE ways in which alien plant invaders can be controlled. (3)
3.3.2 Explain how alien plant invaders can lead to loss of biodiversity. (2)
3.3.3 Apart from alien plant invasions, name TWO other causes of loss of biodiversity. (2)
3.4 The diagram below shows the structure of a human ear.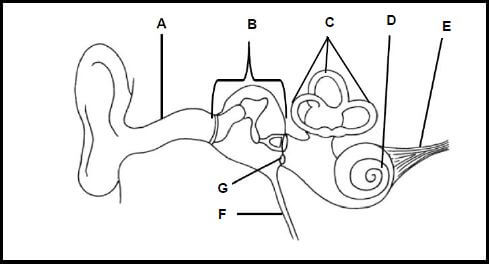
3.4.1 Label parts:
- A (1)
- C (1)
- D (1)
3.4.2 Identify the LETTER representing the auditory nerve. (1)
3.4.3 Name the type of neuron that can be found in the auditory nerve. (1)
3.4.4 Explain the significance of the structures labelled C being arranged in different planes. (2)
3.4.5 When a person is close to a bomb explosion, a significant amount of pressure is exerted on the ear. Explain the effect this will have on the process of hearing. (3) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
A marathon runner participated in a race that started before sunrise.
Describe how her body temperature and water balance was regulated during the race. Also describe the changes that took place in her eyes as the sun rose in front of her.
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
NOTE: No marks will be awarded for answers in the form of charts or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150