ECONOMICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupECONOMICS PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MAY/JUNE 2021
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 D (implicit) ✓✓
1.1.2 A (perfect)/D(monopolistic competitive) ✓✓
1.1.3 A (leadership) ✓✓
1.1.4 D (limit) ✓✓
1.1.5 C (stagflation) ✓✓
1.1.6 B (Isimangaliso Wetland Park) ✓✓
1.1.7 B (depreciation of the currency) ✓✓
1.1.8 C (climate change) ✓✓ (8 x 2)
(16)
1.2 MATCH THE ITEMS
1.2.1 C (An instrument used by the government to evaluate public projects) ✓
1.2.2 F (Exists because of barriers to entry which are not economic in nature) ✓
1.2.3 G (A decrease in average cost of production per unit as output increases) ✓
1.2.4 B (Resources allocated in such a way that no one is made better off without making someone else worse off) ✓
1.2.5 A (People travelling through South Africa to another country) ✓
1.2.6 D (Dumping of harmful substances into the river streams) ✓
1.2.7 I (increase in output with the same factor inputs.) ✓
1.2.8 E (Occurs when aggregate demand for goods and services exceeds the aggregate supply of goods and services leading to price increases) ✓
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 GIVE THE TERM
1.3.1 Monopolistic competition ✓
1.3.2 Price floor/ minimum price ✓
1.3.3 Short-run ✓
1.3.4 Command and control ✓
1.3.5 Subsidy on production ✓
1.3.6 Property rights ✓
(6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name any TWO examples of a perfect market.
- Agricultural sector ✓
- Stock exchange ✓
- Foreign exchange market✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 How do oligopolists benefit from forming a cartel?
It enables them to fix prices✓ /restrict competition/supply✓✓/increase market power ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the graph and answer the questions that follow.
2.2.1 Which curve is used to determine supply of the firm?
MC ✓ (1)
2.2.2 Identify profit maximisation quantity.
60 ✓ (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term marginal revenue.
Marginal revenue refers to the extra amount of income gained by selling one more unit of production. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.4 When will a firm in a perfect market shut down its operations?
Firms would shut down when they can no longer cover their variable costs. / MC=AVC /when the price reaches R30/AR ˂AVC✓✓
(Accept any other relevant correct answer) (2)
2.2.5 Use the above graph to determine the type of profit made by this firm. Show all correct calculations.
TR - TC
= 50 x 60 – 50 x 60 ✓
= 3000 - 3000 ✓
= 0 ✓
Therefore, the firm is making normal profit. ✓
OR
(AR-AC) X Q ✓
=(R50- R50) X 60 ✓
=0 ✓
Therefore, the firm is making normal profit. ✓
(4)
2.3 Study the cartoon and answer the questions that follow.
2.3.1 Determine the nature of the product sold in this market structure.
Differentiated/heterogenous✓ (1)
2.3.2 What type of profit is made by monopolistic competitors in the long-run?
Normal profit ✓ (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term hybrid structure.
Hybrid structure describes the fact that the monopolistic competition is comprised of the characteristics of both the perfect competition and monopoly ✓✓
(Accept any other relevant correct answer) (2)
2.3.4 Why does a monopoly fail to achieve productive efficiency?
- The monopolist produces output that is less than the desired output/it fails to minimize average cost ✓✓
- Inefficiency may occur since there is no competition. ✓ ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (2)
2.3.5 How do oligopolists maintain their market share?
- Oligopolists extend shopping hours to encourage greater flexibility to households ✓✓
- Promoting online purchases, which makes it easier for customers to shop around without any additional cost/variety of goods available to make comparisons ✓✓
- Implementing product differentiation, products might slightly differ in terms of physical appearance, packaging etc. ✓✓
(Accept any other relevant correct answer) (2 x 2)
( A maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts) (4)
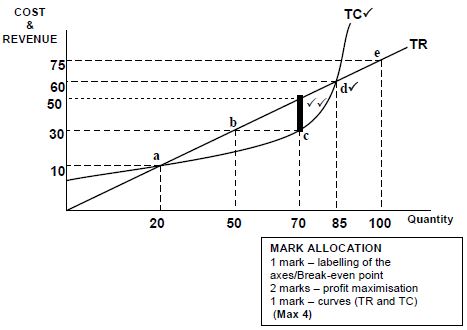
2.4 With the aid of a correctly labelled graph (using TR and TC curves), briefly explain how a firm in a perfect market maximises profit.
- The firm will earn maximum profit where the difference between TR and TC is the greatest (at 70 units) ✓✓
- This is at 70 units at a price of R50 ✓✓
- Any other quantity produced will result in lower profits (Q50) a loss (Q100) of break-even (Q20/85) ✓✓ (Max 4 marks) (8)
2.5 Outline the challenges in achieving the goals of the competition policy in South Africa.
Challenges experienced by the competition policy are that:
- fines charged are too lenient and do not cover the costs suffered by consumers. ✓✓
- fines are too lenient to act as a deterrent to other businesses colluding which is evident from the larger number of firms being investigated regularly.
- a lack of human resources results in some investigations or act of collusion sometimes goes undetected. ✓✓
- cases of restrictive practices take longer to investigate and lose merit in the process. ✓✓
- corruption and political interference/interests prevent some acts of collusion from being investigated properly ✓✓
- some mergers and acquisitions only protect workers in the short term. Eventually workers are retrenched. ✓✓
- artificial monopolies and other powerful businesses abuse their market power as the competition policy fails to create opportunities for new entrants to the market ✓✓
- the monitoring measures to identify collusion practices are compromised due to a lack of information as many investigations takes place after a long period of collusion. ✓✓
- the monitoring and enforcement of competition policies is difficult due to the vastness of areas ✓✓ (max 8)
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 2 marks will be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name any TWO examples of sites in South Africa that promotes cultural tourism.
- Robben Island ✓
- Table Mountain National Park ✓
- Apartheid museum ✓
- Richterveld Cultural and botanical Landscape ✓
- District Six ✓
- Bo Kaap ✓
- Constitutional Hill ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 1)
(2)
3.1.2 What is the negative impact of an increase in indirect taxes on goods and services?
It will lead to higher prices of goods and services which will decrease aggregate demand and slow down the economy ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2)
(2)
3.2 Study the graph and answer the questions that follow.
3.2.1 During which month in 2020 was the inflation rate outside the target range?
May/June ✓ (1)
3.2.2 Determine the increase in the inflation rate between June 2020 and July 2020.
1% ✓ (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term Production Price Index.
An index that measures the prices of domestically produced goods and shows domestic output. / Measures prices of goods that are produced domestically when they leave the factory yard.✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.2.4 Explain the reason for the exclusion of certain items from the CPI basket when calculating core inflation.
Government excludes certain items, such as frozen food because they have highly volatile prices ✓✓/Goods that are affected by government intervention or policies.eg subsidies on bread. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.2.5 How will an increase in social and unemployment grants influence inflation?
- Aggregate demand will increase for goods and services thereby raising prices ✓✓
- Income levels for the poor and unemployed will increase thereby increasing consumer spending ✓✓
- Creates an opportunity for producers to use the increase in social grants to increase their profit margins ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2 x 2) (4)
3.3 Study the extract and answer the questions that follow.
3.3.1 Identify the concept related to the removal of trees.
Deforestation ✓ (1)
3.3.2 Name ONE organization that campaigns for the sustainable use of the environment.
- World wildlife Fund ✓
- Green Trust ✓
- Collect a can ✓
- Keep South Africa Beautiful ✓
- Greenpeace✓
- Friends of the earth✓
- Rainforest alliance✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term hazardous waste.
Waste products that take time to decompose/dangerous or toxic to human and animal life ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2)
3.3.4 Explain the way in which the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) aims to reduce biodiversity loss.
- CITES bans commercial international trade on endangered species ✓✓
- CITES uses permits and quotas to regulate and monitor trade on other species that may become endangered ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.5 How can government address the extinction of animal species?
- Community members should be educated on the dangers of killing animals ✓✓
- Encourage community members to report any activities related to illegal killing of animals by offering incentives ✓✓
- Grant property rights to private individuals and businesses to increase interest in preserving endangered animal species ✓✓
- Improve security in game reserves where most of endangered animal species are located ✓✓
- Prohibit hunting activities in areas where animals threatened by extinction are located ✓✓
- Impose huge fines to those who are illegally hunting. ✓ ✓
(2 x 2)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4)
3.4 Discuss the negative effects of soil erosion on the environment.
- Soil erosion occurs when the topsoil is removed through the action of wind and water at a greater rate than it is formed ✓✓
- It leads to increased pollution in streams and rivers ✓✓
- It is a major environmental threat to sustainability and productivity as it affects soil fertility and food security ✓✓
- Degrades land and often makes it less productive ✓✓
- Erosion may result in the destruction of water sources such as dams ✓✓
- Destroys the ecosystem (the grazing land for animals) ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2)
(A maximum of 4 marks will be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples)
(8)
3.5 How would low inflation expectations by the consumer keep inflation within the target range?
Low inflation expectations
- limit excessive wage demands by different labour unions because workers do not expect increases in cost of living in the future ✓✓
- allow consumers to postpone consumption expenditure thereby reducing pressure on price increases. ✓✓
- give households confidence that inflation rate will be low in future and encourage them to save more from the income, thereby controlling excess demand ✓✓
- reduce panic buying by consumers when they expect that prices will be stable in the future ✓✓
- boost real interest rates which will encourage savings. ✓✓
- increase the burden on debtors which discourages them from borrowing money, due to the real interest rate ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 2 marks will be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples)
(8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MICRO ECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name any TWO major international agreements on sustainable development.
- Rio de Janeiro ✓
- Johannesburg Summit ✓
- Kyoto Protocol ✓
- COP 17 ✓
(Accept any other relevant and correct response) (2 x 1)
(2)
4.1.2 Why do homogeneous products benefit consumers?
Consumers are guaranteed standardised products because it allows them to buy from any seller. ✓✓
(Accept any other relevant and correct response) (1 x 2)
(2)
4.2 Study the information and answer the questions that follow.
4.2.1 Which type of monopoly is discussed in the extract above?
Natural monopoly/ State owned monopoly ✓ (1)
4.2.2 What determines the quantity sold by a monopoly?
Market demand/revenue/cost ✓ (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term economic profit.
Economic profit is achieved when total revenue is greater than total cost/average revenue is greater than average cost/profit that is made above (in addition to) normal profit ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.4 Explain the relatively inelastic nature of the demand curve for the monopolist.
- Monopolists sell unique products with no close substitutes/consumers have no other alternative options of goods and services ✓✓
- Competition is limited due to the unique nature of the product or huge capital needed to start the business✓✓
(Accept any other relevant correct response)
(2)
4.2.5 Why is it difficult to enter into a monopoly market?
- Government set restrictions which make it difficult for new firms to enter the monopoly industry. ✓✓
- Strategic industries in the country need barriers to protect the market against penetration ✓✓
- High development cost (huge capital outlay) needed to enter such a market ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (2 x 2)
(Max 2 marks for mere listing of facts) (4)
4.3 Study the information and answer the questions that follow.
4.3.1 Which government department is responsible for granting marketable permits?
Department of Minerals resources and Energy✓ (1)
4.3.2 Name ONE market-related measure to protect the environment
- Recycling ✓
- Environmentally friendly products ✓
- Technology ✓
- Renewable energy ✓
- Tradeable emissions permits✓
- Congestion charges ✓
(Accept any other relevant correct answer)
(1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term marketable permits.
It is a license issued by the government to each business to pollute to a certain degree ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2)
4.3.4 Explain the effect of carbon emissions on agricultural production.
Carbon emissions may result in acid rains or a change in climatic conditions which will destroy agricultural products thereby decreasing production ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2)
4.3.5 How do green taxes contribute to promote a more sustainable environment?
- Production of harmful products to the environment are discouraged ✓✓
- The price of goods increase, which will force producers to be more environmentally friendly.✓✓
- Consumption (output) of environmentally unfriendly goods are reduced ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
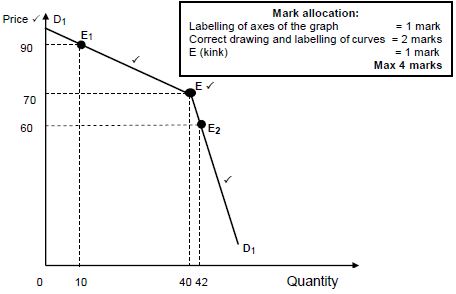
4.4 With the aid of a correctly labelled graph, briefly explain why it is advisable for oligopolies to sell at market price.
- When oligopolists sell at market price, they yield more income. ✓✓
- Suppose an oligopolist is selling at a market price of R70 and 40 units of outputs are sold. Total revenue is R70 x 40 = R2800 ✓✓
- When a firm wants to increase profits by increasing the price to R90, quantity demanded will fall to 10 units and total revenue would decrease to R90 x 10 = R900/If a firm wants to increase profits by reducing the price to R60, the quantity demanded will increase to 42 units, total revenue would be R 2520
Graph: 4 marks
Explanation: 4 marks
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 4 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples) (8)
4.5 How does the government encourage producers to combat inflation?
The government may encourage producers to combat inflation by:
- Paying cash grants to producers to encourage them to produce more goods and services to cater for excess demand. ✓✓
- Providing subsidies on production to reduce cost of production and enable producers to charge lower prices. ✓✓
- Encouraging competition to promote establishment of small businesses thereby increasing aggregate supply. ✓✓
- Improve efficiency of parastatals that provide input services to reduce the cost of doing business✓✓, e.g., Eskom. ✓✓
- Removing unnecessary laws and regulations to encourage producer efficiency. ✓✓
- Maintaining exchange rate stability to ensure that producers import productions inputs at a lower cost. ✓✓ e.g., oil and vehicle parts. ✓
- Reduction in corporate tax which will reduce cost, thereby encouraging production.
- Negotiating with countries for reduced tariffs on imported inputs which will reduce the cost of production.
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 2 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples) (8)
[40]
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS
- Discuss the causes of market failure in detail. (26 marks)
- How effective has government spending been, in addressing market failure?
(10 marks)
[40]
INTRODUCTION
Market failure occurs when market forces of demand and supply do not ensure the correct quantity of goods and services are produced to meet demand at the right price. ✓✓ (Max 2)
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
BODY/MAIN PART
Externalities ✓
- These are known as spill-over effects to third party which is not directly involved in the production process. ✓✓
- As externalities in production and consumption often exist and output is usually based on private costs and benefits, this is a significant cause of market failure. ✓✓
Negative externalities✓
- Negative externalities are costs to third parties that are not included in the market price ✓✓e.g. pollution, ✓
- The costs of negative externalities such as ill health are not paid by the producers. ✓✓
- Harmful these good are often over produced in the economy which is not socially desirable. ✓✓
Positive Externalities✓
- A positive externality occurs when a benefit to a third party from the action or decision of another party. ✓✓e.g., Education ✓
- These goods are often under-produced by the market and government steps in to provide for the short fall. ✓✓
( A maximum of 4 marks will be allocated for graphical illustration)
Public goods/Missing markets ✓
- can only form under certain conditions and when these conditions are absent, markets struggle to exist. ✓✓
- Public goods are not provided for by market mechanism because producers cannot withhold the goods for non-payment and since there is often no way of measuring how much a person consumes, there is no basis to establish a market price. ✓✓
- Markets measuring how much a person consumes, there is no basis for establishing a market price
- lightning, flood control, storm water drainage and lighthouses.✓✓
- Collective goods: these are goods and services such as parks, beaches and beach facilities, streets, pavements, roads, bridges, public transport, sewerages systems, waste removals, water reticulation and refuse removals.✓✓
- Community goods: these are goods such as defence, police services, prison services, streetlights: these are goods and services such as parks, beaches and beach facilities, streets, pavements, roads, bridges, public transport, sewerages systems, waste removals, water reticulation and refuse removals. ✓✓
Merit goods and demerit goods: ✓✓
- Merit goods: Some goods are highly desirable for the general welfare of the people of the country and are often not highly rated by the market. ✓✓
- If people have to pay market prices for them, relatively little would be
consumed. ✓✓ - Demerit goods: Items such as cigarettes, alcohol, and non-prescriptive drugs are example of demerit goods. ✓
- In a free market economy, these goods are over-consumed. ✓✓
- Government can ban their consumption or reduce it by means of taxation such as excise duties✓✓ and by providing information about their harmful side effects. ✓✓
Imperfect competition ✓
- In market economies, competition is often impaired by power. ✓✓
- Power often lies to a greater extent with producers than with consumers. ✓✓
- Most businesses operate under conditions of imperfect competition that allow producers to restrict output, raise prices and produce where price exceeds marginal cost. ✓✓
Lack of information ✓
- Consumers, workers and entrepreneurs do not always have the necessary information at their disposal to make rational decisions. ✓✓
- Consumers: Although advances in technology increase the amount of information to which people have access, they obviously do not have perfect information. ✓✓
- Workers: They may be unaware of job opportunities outside their current employment. ✓✓
- Entrepreneurs: They may lack information about the costs, availability and productivity of some factors of production, and may be operating on the basis of incorrect information. ✓✓
Immobility of the factors of production: ✓
- Most markets do not adjust rapidly to changes in supply and demand. ✓✓
- Labour: may take time to move into new occupations and geographically to meet the changes in consumer demand. ✓✓
- Physical capital: Factory buildings and infrastructure such as telephone lines, bridges, rail links and airports are not moveable at will. ✓✓
- This capital last for many years but cannot be moved to fit change in demand. ✓✓
- Technological applications change production methods: Technology used in the production may change such as the use of robots rather than labour in mines. ✓✓
- It takes time for most industries to adapt - with greater technological changes✓✓
- Workers need to be flexible, upskilled and be able to change employment, as well as work patterns. ✓✓
Imperfect distribution of income and wealth: ✓
- The most important shortcoming of market systems is that it is neutral in the issue of income distribution. ✓✓
- If the initial distribution is unequal, the final distribution will be too. ✓✓For this reason, it is often argued that the market fails. ✓✓ (max 26)
- (Accept any other correct relevant response)
ADDITIONAL PART
How effective has government spending been in addressing market failure?
Government spending is effective in addressing market failure by:
- transferring income directly to the poor such as child support grants, unemployment benefits and thereby reducing income inequalities. ✓✓
- providing goods free of charge e.g. community goods, education etc. ✓ and allowing access to basic needs to all citizens. ✓✓
- implementing employment creation programmes, which will create jobs and improve skills for all types of labour ✓✓ e.g. public works programme, subsidising producers to encourage production of merit goods as they are beneficial to the society.✓
- spending on campaigns that will inform public about policies and legislation that protects them against exploitation. ✓✓
- investing on infrastructure development such as roads, railways and communication networks as private sector find these unprofitable or difficult to finance. ✓✓ (Max 10)
(Accept the negative evaluation of government spending)
CONCLUSION
Market failures can have devastating effects on the economy which requires government to intervene to reduce their consequences. ✓✓ (Max 2)
(Accept any other correct relevant higher order response)
[40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
- Discuss in detail the benefits of tourism. (26 marks)
- Evaluate the impact of the Covid-19 on the tourism sector. (10 marks)
[40]
INTRODUCTION
Tourism refers to activities of people travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year and for different reasons. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant introduction) (Max. 2)
BODY: MAIN PART
Households ✓
- Households may benefit from an increase in income and opportunities for employment and entrepreneurship.✓✓
- Individuals receive training through programmes established to promote tourism.✓✓
- Households are indirectly involved in tourism as employees in hotel industry, financial institutions etc.✓✓
- They benefit from improved infrastructure created for tourists though local people can use.✓✓
- They acquire skills from that are required by the tourism industry.✓✓
- Income earned is spent in their communities and they can contribute to the local economy.✓✓
- Entrepreneurs from households operate as tour guides ✓
Businesses ✓
- Formal sector activities are promoted through tourism ✓✓ e.g. companies are tasked with building infrastructure such as hotels or roads ✓
- Tourism benefits local businesses and companies through an increase in expenditure on the goods and services offered by local businesses ✓✓
- The informal sector benefits because of trading in traditional products such as crafts and arts ✓✓
- Banks employ more tellers, and this leads to higher employment ✓✓
- The business environment is stimulated in rural and urban areas promoting entrepreneurial opportunities and assisting with BEE ✓✓
- Tourist destinations are developed through the public and private partnerships (PPPs) ✓✓
Government ✓
- Government benefits because of income it receives from tourists ✓✓
- Tourism enables the government to advertise a country tourism potential ✓✓
- Direct and indirect contributions to the government revenue is made through levies on tourists ✓✓—these are made for two purposes
- To recover external costs ✓ –this assists the host community for providing infrastructure ✓✓
- To raise revenue ✓ –with the growth of tourism many countries levy tourist tax which are used as a source of revenue ✓✓
- income earned can be used to promote tourism in the country ✓✓
- Through this the government is enabled to achieve its socio-economic objectives, informal sector growth, BEE and SMME development.✓✓
Infrastructure development ✓
- For any country to be regarded as a tourist destination, physical infrastructure has to be adequate and well maintained.✓✓
- The needs of a large number of tourists in any country for accommodation and infrastructure leads to the construction of hotels en improvement in the existing infrastructure ✓✓
- Together with the private sector the government has to develop and upgrade infrastructure to meet the demands and expectations of tourists ✓✓
- Locals and tourists benefit from the infrastructure ✓✓
- Tourists require social infrastructure e.g. clinics and ambulances.✓✓
The following positive effects of tourism should also be considered:
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) ✓
- Travel and Tourism contributes both directly and indirectly to the GDP. ✓✓
- The direct contribution of travel and tourism reflects the internal spending of travel and tourism by residents and non-residents for business and leisure purposes✓✓, e.g. spending on accommodation, food, retail, transport and destination services, and the public sector’s spending directly linked to visitors. ✓✓
- The indirect contribution includes purchases from suppliers of goods and services by the sectors dealing directly with tourists✓ ✓ – including purchases of cleaning services by hotels, or fuel and catering services by airlines and IT services by travel agents. ✓✓
Employment✓
Tourism sector is a large generator of jobs for the following reasons:
- Tourism is labour intensive. It has the lowest rate of investment to employment creation. ✓✓
- Tourism employs many skills. There is room for almost any skill in the tourist industries such as accountants, hairdressers, tour guides etc. ✓✓
- Tourism can provide immediate employment. If it is properly organised and focused the tourism sector can create many jobs within a short period of time. ✓✓
- Tourism provides entrepreneurial opportunities. The tourism industry accommodates informal sector enterprises, form craft and fruit vendors to pavement vendors, chair rentals and others. ✓✓
Poverty Alleviation✓
- Tourism brings development to the poor in rural areas. ✓✓
- Tourism offers opportunities to diversify sources of income for poor people:
- Allowing them a stake: for example, to start and operate small-scale tourism businesses around community assets and to establish SMMEs to provide services. ✓✓
- Empowering them: for example, to exploit opportunities of on-the-job and other training. ✓✓
- Creating partnerships: linking up with mainstream tourism businesses supplying goods and services. ✓ ✓
- Consider inputs that relate to the benefits to international tourists
(Max 26)
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
ADDITIONAL PART
Assess the impact of the COVID-19 on the tourism sector.
- Impacted negatively on the demand for tourism services, due to lockdown rules ✓✓
- Most businesses in the sector became bankrupt and led to closure and unemployment prevailed ✓✓
- There was a sharp decline of the contribution of this sector towards GDP as the borders of the country were closed and no travelling was allowed. ✓✓
- Large scale travel restrictions led to a sharp fall in consumer and business expenditure which could create economic recession. ✓✓
- Most tourism infrastructure was underutilized, yet fixed costs for these structures had to be paid.✓✓
- Poor communities are largely dependent on tourism sector for income generation and Covid-19 deprived them such income and left them more vulnerable.✓✓
- Promotion of local tourism and the call by the president to the tourism sector to reduce prices ✓✓
- As soon as the lockdown-levels were lowered, local tourism increased between provinces ✓✓
- The opening of the economy led to an increase of business tourism ✓✓
(A maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 10)
(Acept the positive evaluation of COVID-19 on tourism)
CONCLUSION
Although globalization has increased tourism between countries, COVID-19 has significantly reduced the growth of tourism which has created major challenges to the economy✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant higher order conclusion) (Max 2)
TOTAL SECTION C: (40)
GRAND TOTAL: [150]