ECONOMICS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupECONOMICS PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MAY/JUNE 2021
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 B – Kitchin ✓✓
1.1.2 D – depreciation ✓✓
1.1.3 D – infant ✓✓
1.1.4 C – real flows ✓✓
1.1.5 A – local ✓✓
1.1.6 C – Expanded Public Works Programme ✓✓
1.1.7 B – social ✓✓
1.1.8 A – corridor ✓✓
(8 x 2) (16)
1.2
1.2.1 B – a complete ban imposed on the importing of goods from a particular country ✓
1.2.2 C – measured from peak to peak or trough to trough ✓
1.2.3 A – when a country engages in foreign trade and produces a given good at a lower input cost than other countries ✓
1.2.4 D – the proportion of income that households do not consume ✓
1.2.5 E – consumption by one person does not reduce the consumption by another person ✓
1.2.6 H – levied on properties according to their market value ✓
1.2.7 I – extensive increase in organized economic activity to manufacture, mine, farm and deliver services ✓
1.2.8 F – economic goods which do not take a tangible and storable form ✓
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3
1.3.1 Phillips ✓
1.3.2 Closed ✓
1.3.3 Integrated Manufacturing Strategy ✓
1.3.4 Spatial Development Initiatives ✓
1.3.5 Specific ✓
1.3.6 Endogenous/Keynesian✓
(6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MACROECONOMICS
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name any TWO examples of a strategic industry.
- energy (fuels)SASOL /Eskom✓
- iron and steel /Iscor✓
- agriculture (basic foodstuffs) ✓
- chemicals (fertilizers) ✓
- Mining✓
- Tele-communication✓
- Vaccine manufacturers✓
- Tourism
- Automobile
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 How does a progressive income tax system influence income redistribution?
Progressive income tax influences income redistribution by reducing the gap between the rich and the poor ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the table and answer the questions that follow.
2.2.1 Which year does the South African Reserve Bank currently use as the base year?
2010/2015 ✓ (1)
2.2.2 Identify the figure used to cater for errors and omissions when calculating the Gross Domestic Product at market prices.
R19 097 m ✓ (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term gross domestic expenditure.
Expenditure (spending) on all goods and services produced within the borders of a country within a specific period of time. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.4 What effect would an increase in imported clothing have on domestic textile manufacturers?
- Domestic textile manufacturers should face more competition that might force them to produce less ✓✓
- They might have less customers/market share/sales that will reduce profits ✓✓
- They might be forced to be more innovative due to high competition from foreign producers ✓✓
- Quality of their products should improve and they will become more competitive in global markets. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)(2)
2.2.5 How does gross capital formation impact the economy positively?
- The increased capital base of the country will increase production capacity✓✓
- Gross capital formation will contribute to the growth potential of the economy through value-adding process ✓✓
- Balance of Payments problems will decrease by an increase in export production ✓✓
- Households may benefit from employment opportunities thus reducing poverty/government will achieve its goal of full employment and collect more tax revenue✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2 x 2) (4)
2.3 Study the extract and answer the questions that follow.
2.3.1 Name the institution that promotes trade liberalisation.
World Trade Organisation / WTO ✓ (1)
2.3.2 Give ONE form of economic integration.
- Custom union ✓
- Common market ✓
- Economic union ✓
- Monetary union ✓
- Free trade area✓
(1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term free trade.
Free trade is when consumers and producers are free to buy goods and services anywhere in the world without restrictions ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.4 Why will import substitution have a negative effect on consumers in the long run?
- Consumers' choice will decrease as they will be limited to domestic products only ✓✓
- Consumers may pay higher prices on domestic products due to less competition ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.5 How could African countries benefit from a new free trade agreement?
- enjoying lower prices on goods and services ✓✓
- enjoying free movement and job opportunities across borders ✓✓
- specialising in the production of goods where they enjoy a comparative advantage ✓✓
- producing goods in large quantities that comes as a result of specialisation ✓✓
- producing better quality products due to improved innovation ✓✓
- improving relationships through mutual gains from the exchange of goods among themselves ✓✓
- improving consumer welfare as a result of more choice of goods and services ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2 x 2) (4)
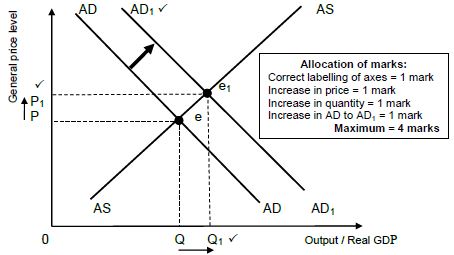
2.4 With the aid of a correctly labelled graph, explain the effects of demand-side policies to stimulate economic activity during a recession.
- Demand-side policies involve expansionary monetary such as a decrease in interest rates that encourage borrowing that would increase consumption an investment. ✓✓
- Expansionary fiscal policy that involves a decrease in tax and an increase in government spending will increase spending as well. ✓✓
- Both policies will result in a shift aggregate demand from AD to AD1 while aggregate supply remains at AS. ✓✓
- Real GDP will increase from Q to Q1 when aggregate demand increases✓✓
- The general price level will increase from P to P1 ✓✓
- The demand-side policies maybe used to stimulate economic growth although inflation may increase ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 4 marks will be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples)
(Max 4) (8)
2.5 How could an increase in investments contribute towards a higher national income in the economy?
- Investments will benefit national income by:
- increasing the capital base of the economy, to expand the production capacity ✓✓
- creating more job opportunities and increasing income levels of households, stimulating aggregate demand ✓✓
- increasing competition when new businesses are established, resulting in increased efficiency in production ✓✓
- encouraging the introduction of new production technologies resulting in higher productivity ✓✓
- expanding the tax base for the government, leading to higher tax revenue/ to finance infrastructure development projects ✓✓
- increasing the competitiveness of local businesses on global markets/ stimulating the demand for exports ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 2 marks will be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: ECONOMIC PURSUITS
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name any TWO examples of Industrial Development Zones in South Africa.
- Coega (steel and auto) ✓
- OR Tambo International Airport (high tech) ✓
- East London (vehicles) ✓
- Richards Bay (metals) ✓
- Mafikeng IDZ ✓
- Saldanha Bay (steel) ✓
- Dube Trade Port ✓
(2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 How can Public Private Partnerships contribute more to regional development?
- PPPs stimulate the development of infrastructure in underdeveloped areas ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Study the extract and answer the questions that follow.
3.2.1 Identify the institution that promotes small businesses.
Small Enterprise Development Agency / SEDA ✓
Small Enterprise Finance Agency / (SEFA) ✓ (1)
3.2.2 Which economic challenge is addressed by Small, Medium and Micro Enterprises in the economy?
- Unemployment /employment✓
- Poverty/distribution of income ✓
- Address economic and social inequalities✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term employment.
When people between 15 and 65, who are willing and able to work, find jobs and in return receive a wage or salary for services provided ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2)
3.2.4 How do Small Medium and Micro Enterprises benefit from the Small Business Support Programme?
- SMMEs receive a tax-free cash grant for investment in industries ✓✓
- New or expanding businesses will receive the grant for three years, after which the company is expected to be self-sustaining ✓✓
- Provision of business advise and related services✓✓
- They access platforms which provide the business infrastructure support and a regulatory environment that enable entrepreneurs to thrive. ✓✓
- They access platforms which provide the business infrastructure support and a regulatory environment that enable entrepreneurs to thrive. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.2.5 What are the challenges in implementing Broad-based Black Economic Empowerment?
BBBEE faces the following challenges:
- the majority of people do not have finances to buy shares to participate in the ownership / shareholding of companies ✓✓
- rural and local communities do not all have access to economic opportunities. ✓✓
- corruption in the awarding of contracts, resulted in few people benefitting from BBBEE ✓✓
- fronting resulted in many people failing to benefit from the policy ✓✓
- a lack of skills and necessary knowledge led to many black women and youth not being able to occupy top management strategic positions in companies ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2 x 2) (4)
3.3 Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
3.3.1 Which focus area provides economic infrastructure for industrial development?
Special Economic Zones / SEZs /Spatial Development Initiatives/SDIs✓ (1)
3.3.2 Name the Industrial Development Policy that sets out the government's broad approach to industrial development.
National Industrial Policy Framework / NIPF ✓ (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term innovation.
The incorporation of new ideas into production processes ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.4 How does industrial development promote entrepreneurship in the economy?
Industrial development:
- encourages entrepreneurs to exploit the world economy to trade and acquire knowledge ✓✓
- boosts improved innovation and technology ✓✓
- motivates entrepreneurs to establish large scale production ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.5 What are the challenges faced by the Industrial Policy Action Plan?
- A lack of policy coherence and programme alignment ✓✓
- The opening-up of the economy to a diversity of participants has not happened ✓✓
- Concentration and vertical integration within sectors has increased since 1994, reinforced by high barriers to entry. ✓✓
- High private sector input costs – steel, chemicals and products in the plastics value-chain - remains a continuing constraint on the competitiveness of SA manufacturing. ✓✓
- Continued escalation of electricity costs ✓✓
- High port charges and inefficiencies are a significant barrier and constraint on the export of value-added goods ✓✓
- Current structure of the SA economy is ill suited to the creation of large numbers of jobs at appropriate skill levels. ✓✓
- Inadequate state support for investment, upgrading, innovation and technology✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Discuss the general benchmark criteria for regional development.
- Good governance requires democratic decision-making, transparency, financial management and control ✓✓
- An integrated approach to ensure that the benefits of one region spill over to other industries and areas ✓✓
- Partnerships should be built between central government and the private sector ✓✓
- Provision of resources should be sufficiently provided in poorly resourced areas ✓✓
- Competitiveness requires that industries and businesses established as a result of regional policies should not need ongoing financial aid from the government ✓✓
- Development of people, for people, by people aims to serve people by training, education, improving productivity and providing essential goods and services to raise the standards of living in regions. ✓✓
- Development from below is necessary to concentrate on issues at grass roots level where most urgent human needs exist. It starts by dealing with poverty. ✓✓
- Total development as a multi-dimensional process: Treat development from a global perspective covering all human life, including the interaction of special forces in a community✓✓, e.g. education, health, nutrition✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 4 marks may be allocated for the mere listing of facts / examples)
(4 x 2) (8)
3.5 Evaluate the use of supply-side measures in solving the persistent low economic growth in South Africa.
Supply-side measures have been successful in solving low economic growth by:
- offering incentives, such as cash grants and subsidies to enhance export promotion / attract private sector investments and FDIs ✓✓
- lowering tax rates to motivate people to work harder to increase their income / increase production levels in the economy ✓✓
- lowering income tax rates may also encourage people to save more / improving availability of loanable funds for investment ✓
- increasing labour productivity through better education, training and healthcare services leads to higher production output ✓✓
- promoting (entrepreneurship), establishment of small businesses and new industries to increase competition / limit monopolies / oligopolies ✓✓
Supply-side measures still need to be improved in terms of:
- ensuring efficient and reliable supply of infrastructure services, such as transport and energy, to reduce the cost of doing business ✓✓
- reducing administrative cost, such as inspections and unnecessary regulations / by imposing simpler tax and operational regulations ✓✓
- privatising some of the state-owned assets to improve efficiency in service delivery ✓✓
- reducing government intervention by removing unnecessary rules and regulations / ensure free market operation / improve market efficiency ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 2 marks may be allocated for the mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MACROECONOMICS AND ECONOMIC PURSUITS
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name any TWO effects of international trade.
- specialisation ✓
- mass production /large scale production/economic growth✓
- efficiency/competition ✓
- globalisation ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How do consumers in the importing country benefit from dumping?
- Consumers will pay lower prices for imported goods ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Study the extract and answer the questions that follow.
4.2.1 Identify the account in the Balance of Payments that records exports and imports of goods and services.
Current account ✓ (1)
4.2.2 Which commodity is recorded as a separate export item in the South African Balance of Payments?
Gold ✓ (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term terms of trade.
Terms of trade expresses a country's ratio of export prices in terms of its import prices ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.4 Explain the impact of an increase in export prices on South Africa's trade balance.
- Export earnings or the value of total exports would increase resulting in an increase in the value of the trade balance /
- Demand for exports would decrease, reducing the volume of export and the trade balance. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)(2)
4.2.5 How can import control be used in order to correct the Balance of Payments deficit?
- BoP deficit can be corrected by imposing import tariffs and import quotas ✓✓
- Import tariffs makes imported goods more expensive thereby discouraging local markets from buying them ✓✓
- Import quota limits the amount or quantity of imports allowed to the economy ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2)
(4)
4.3 Study the cartoon and answer the questions that follow.
4.3.1 Which government department is responsible for budgeting?
Department of Finance ✓ (1)
4.3.2 Name ONE factor that contributed to downgrading of the South African economy.
- Rising debt ✓
- Falling revenue ✓
- Widening deficit ✓
- Corruption ✓
- Low GDP growth ✓
- High unemployment ✓
- Power shortages✓
- Poor investor confidence✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)(1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term affirmative action.
A policy that seeks to redress past discrimination through active measures to ensure equal opportunity, as in education and employment ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.3.4 What impact will South Africa's credit rating to junk status have on the economy?
- Government would have to pay more in interest, which leaves less money for services (healthcare, education) and investment in infrastructure. ✓✓
- Government would need more money to cover its basic expenses. ✓✓
- Downgrading may lead to increased taxes ✓✓
- Disinvestment may occur which leads to low economic growth and increased levels of unemployment. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.3.5 How could state-owned enterprises contribute towards expanding the economy?
- Creating more job opportunities and appointing competent management. ✓✓
- Offering skills development programmes to improve productivity of existing workers ✓✓
- maintaining or servicing their machinery and equipment regularly to ensure quality service delivery ✓✓
- Dealing with corruption to reduce wastage of public funds ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Briefly discuss extrapolation and amplitude as features in the forecasting of business cycles.
Extrapolation:
- Forecasters use past data e.g. trends and by assuming that this trend will continue, they make predictions about the future ✓✓
- Something unknown is estimated from facts or information that are known ✓✓
- If it becomes clear that the business cycle has passes through a trough and has entered a boom phase, forecasters might predict that the economy will grow in the months that follow ✓✓
- It is also used to make economic predictions such as future share prices✓✓
(Max 4)
Amplitude:
- The difference between the total output between a peak and a trough ✓✓
- Measures the distance of the oscillation of a variable from the trend line ✓✓
- The intensity (height) of the upswing and downswing (contraction and expansion) in economic activity ✓✓
- A large amplitude during an upswing indicates strong underlying forces – which result in longer cycles ✓✓
- The larger the amplitude the more extreme the changes that may occur / extent of change ✓✓
- During the upswing inflation may increase from 5% to 10% (a 100% increase) ✓✓ (Max 4)
(8)
4.5 Evaluate the impact of the depreciating rand on the South African economy.
A depreciating rand will positively affect the South African economy in the following ways:
- exports will become relatively cheaper thus leading to increased demand for South African goods✓✓
- Demand for South African exports such as base metals and mineral products will increase as they become relatively cheaper. ✓✓
- Foreign tourist arrivals will increase because it will be cheaper for them to spend money in South Africa. ✓✓
- Improvement in the trade balance as exports will be greater than
imports. ✓✓
A depreciating rand will negatively affect the South African economy in the following ways:
- Imported production inputs such as crude oil and vehicle parts will become expensive, fuelling cost-push inflation. ✓✓
- Higher cost of imported production inputs will decrease domestic production and economic growth.✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 2 marks may be allocated for the mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS
- Discuss in detail the objectives of the public sector. (26 marks)
- How will public sector failure negatively influence economic stability in South Africa? (10 marks)
INTRODUCTION
- The government responds to market failure by establishing and maintaining state-owned enterprises to provide public goods and services ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 2)
BODY: MAIN PART
ECONOMIC GROWTH ✓
- An increase in the production of goods and services by the economy ✓✓
- It is measured in terms of an increase in the real gross domestic product ✓✓
- Real GDP is the value of goods produced in the country after the effects of inflation have been taken into account ✓✓
- For economic development to occur, the economic growth rate must be higher than the population growth rate ✓✓
- A high economic growth rate also means there will be fewer people who are dependent on the state to satisfy their basic needs ✓✓
- The state tries to ensure that there is continual growth in this capacity because it leads to an improvement in the standard of living ✓✓
FULL EMPLOYMENT ✓
- Attaining high levels of employment is one of the most important economic objectives for all governments ✓✓
- Full employment means that all persons who would like to work and who are looking for work, should be able to find work or create work for themselves ✓✓
- The unemployment rate increased over the past few years and above 30% after Covid-19 pandemic. ✓✓
- Informal sector activities must be promoted because it is an area where employment increases✓✓
- In the short-run, the state accelerates employment creation through direct employment schemes, targeted subsidies and expansionary macroeconomic packages ✓✓
- Over the medium term the state support labour-intensive activities in the agricultural and light manufacturing sectors ✓✓
- Over the longer run, as full employment is achieved, the state supports knowledge-intensive and capital-intensive sectors to remain competitive ✓✓
EXCHANGE RATE STABILITY / BALANCE OF PAYMENTS (BoP) EQUILIBRIUM ✓
- Depreciation and appreciation of a currency create uncertainty for producers and traders and should therefore be limited ✓✓
- Government uses its monetary and fiscal policies to ensure that the exchange rate remains relatively stable for as long as possible ✓✓
- BoP equilibrium influences the flow of goods, services and capital in a country ✓✓
- Exchange rate stability has a strong impact on the inflation rate and other macroeconomic variables ✓✓
- The choice and management of an exchange rate system forms a critical aspect of economic management to protect and encourage competitiveness, macroeconomic stability and growth ✓✓
- More money inflows into a country results in a surplus on the Balance of Payments account ✓✓
- The SARB changed the Exchange rate from a Managed floating to a Free- floating exchange rate. ✓✓
- Promoting domestic production will increase exports ✓✓
PRICE STABILITY ✓
- Market economies produce better results in terms of economic growth and employment when prices are relatively stable ✓✓
- In South Africa relative price stability means that the inflation rate remains within the inflation target of 3–6% ✓✓
- Interest Rates, based on the Repo Rate are the main instruments used to achieve price stability. ✓✓
- The benefit of the inflation target is a greater degree of transparency in monetary policy ✓✓
- If inflation exceeds the upper limit of the range, the Reserve Bank must consider increasing the interest rate to cool down the heated economy ✓✓
ECONOMIC EQUITY ✓
- A redistribution of income and wealth is essential in market economies ✓✓
- There are sections of society that earn a large amount of money while others earn very little ✓✓
- Progressive income tax and tax on profits, wealth and expenditure are used to finance free social services ✓✓
- Basic education, primary healthcare, basic economic services and cash grants to poor and other vulnerable people, will enhance economic equity ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 26)
ADDITIONAL PART
The public sector failure impacts negatively on economic stability by:
- causing price instability which depress consumer spending ✓✓
- causing policy uncertainty which may reduce investors' confidence ✓✓
- increasing unemployment as the economy fails to create new job opportunities ✓✓
- discouraging exporters due to exchange rate instability ✓✓
- reducing the volume of exports which may increase the balance of payments (BOP) deficit ✓✓
- exposing the economy to a recession due to lack of real GDP growth ✓✓
- increasing the fiscal burden due to wastage of resources especially by parastatals ✓✓
- decreasing production of goods and services as parastatals/state-owned enterprises fail to supply key input services. ✓✓ e.g. energy and transport ✓
- increasing the cost of doing business in the economy as a result of inefficiencies ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant higher order response) (Max 10)
CONCLUSION
The state plays a significant role in achieving the macroeconomic objectives by guiding the economy through the national budget ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant higher order conclusion) (Max 2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- Discuss the various economic indicators in detail. (26 marks)
- How did the COVID-19 pandemic negatively influence the South African economy? (10 marks)
INTRODUCTION
Governments use different statistical data to predict economic trends and formulate suitable developmental strategies toward influencing the direction that the economy should take / Economic indicators are used to establish the performance of an economy in terms of the basic economic objectives ✓✓
(Accept any other relevant response) (Max. 2)
BODY: MAIN PART
PRODUCTION INDICATORS ✓
Nominal GDP (at current / market prices) ✓
- Nominal GDP cannot be used because the amount tends to be overestimated (inflation) ✓✓
Real GDP (at constant prices) ✓
- The growth performance of an economy is measured in terms of real GDP figures ✓✓
- Real GDP is obtained when the effect of inflation is removed from the data ✓✓
- When nominal growth is 8% and inflation is 3% then real growth is 5% ✓✓
Per capita real GDP ✓
- Per capita real GDP is calculated by dividing the real GDP figure by the total population ✓✓
- The purpose of per capita real GDP is to indicate economic development / indicate living standards / compare living standards between countries ✓✓
PRODUCTIVITY INDICATORS ✓
Labour productivity ✓
- Watched most closely, particularly in relation to real wage increases ✓✓
- In South Africa productivity increased less than labour remuneration ✓✓
- Labour productivity is measured by dividing the real GDP by the number of workers employed ✓✓
Remuneration per worker ✓
- If productivity increases are lower than the real wage increases, inflationary pressures will occur ✓✓
- The relationship between productivity and wages is crucial for employers survive in vigorous markets and workers to survive on their salaries. ✓✓
(Accept analysis of other kind of productivity)
FOREIGN TRADE INDICATORS ✓
The terms of trade ✓
- Changes in terms of trade serve as indicator of changes that may spill over into the balance of payments and may lead to a deficit ✓✓
- Terms of trade will deteriorate, if a greater volume of exports must be produced to keep export earnings constant ✓✓
The exchange rate ✓
- Changes in an exchange rate affect the prices for imports and prices of exports ✓✓
- A depreciation of the rand against the dollar will result in US goods and services becoming more expensive domestically and earnings from exports to the US increasing ✓✓
THE INFLATION RATE ✓
Inflation can be described as an increase in the general level of prices in an economy that is sustained over a period of time ✓✓
SARB aims to keep the inflation rate stable between 3 and 6% ✓✓
The following instruments measure inflation:
Consumer prices/CPI ✓
- This is the weighted average of the prices of a general basket of goods and services likely to be bought by consumers ✓✓
Production prices /PPI✓
- Measures prices of locally produced goods when they leave the factory and imported goods when they enter the country ✓✓
Serves as an indicator to predict consumer inflation (CPI) ✓✓
EMPLOYMENT ✓
The economically active population (EAP / labour force) ✓
- The official employment ages in South Africa are between 15 and 65 who are willing to work and it includes workers in the formal sector, informal sector, employers, self-employed persons and unemployed persons ✓✓
Employment rate ✓
- The number of employed persons expressed as percentage of the EAP gives the employment rate ✓✓
- The South African employment rate was 70,9% during 2019 and is not accompanied by a similar growth in employment numbers ✓✓
Unemployment rate ✓
- The unemployment rate is expressed as the percentage of unemployed persons out of the total number of people willing and able to work ✓✓
- In South Africa the official unemployment rate was 29,1 % in 2019 and is the most important cause of poverty ✓✓
MONEY SUPPLY ✓
- Money supply is of critical importance to give early warning of likely changes in inflation ✓✓
- South African Reserve Bank defines money in different categories: M1 - coins and notes; M2 - equal to M1 plus all short- and medium-term deposits; M3 - equal to M2 plus all long-term deposits of domestic private sector with monetary institutions ✓✓
INTEREST RATES ✓
Repo rate ✓
- Repo rate: the rate at which South African Reserve Bank lends money to commercial banks ✓✓
- Interest rate is based on the repo rate; when repo rate changes interest rate also change ✓✓ (Max 26)
ADDITIONAL PART
The COVID-19 pandemic negatively influenced the South African economy by:
- shutting down industrial and business sectors, resulted in the reduction of production of non-essential goods and service ✓✓
- slowing down economic growth that increased unemployment / loss of income ✓✓
- restricting global trade, reduced the demand for South African products ✓✓
- contributing to more balance of payments problems as exports decreased ✓✓
- reducing mining and manufacturing productivity due to operational restrictions or scale-down. ✓✓
- restricting movement of people that reduced tourism activities domestically and internationally ✓✓
- reducing tax revenue for the government led to trade restrictions on non-essential products such as alcohol and tobacco. ✓✓
- decreasing real GDP growth with a possible recession in the economy as a result of the negative impact on production of goods and services. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 10)
CONCLUSION
The use of economic indicators is important, because analysts use the data to interpret
current or future investment possibilities ✓✓ (Max 2) [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150