Civil Technology Construction Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: SAFETY, OHSA AND MATERIAL (GENERIC)
1.1 3 m (1)
1.2 (1) By means of a chute or (2) conveyor belt (2)
1.3 Similar answer:
- (1) Prevents unauthorised entry and (2) to protect the public. (2)
1.4
1.4.1
- 30°
- 50° (2)
1.4.2
- 760 x 560 mm
3,7 m (2)
1.5
- 1 : 4 = 2 m = 0,5 m (one meter horizontal to four metres vertical) (2)
4
1.6 (1) Not further than 2/3 (2) of the extension length (2)
1.7 (1) The coating of a metal by means of electrolysis (2) with a thin layer of another metal. (2)
1.8 Any THREE advantages of electroplating of metals:
- Protects against corrosion
- Improves the engineering and mechanical properties of metal
- Increases the thickness of metal
- Resistant against wear and tear (3 x 1) (3)
1.9 Any TWO advantages of galvanising metals:
- Adds strength to the metal
- Increases the thickness of metal
- Prevents staining
- Protects against corrosion (2 x 1) (2) [20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
2.1
2.1.1 False (1)
2.1.2 True (1)
2.1.3 True (1)
2.1.4 True (1)
2.1.5 False (1)
2.2 FIGURE 2.2 on ANSWER SHEET A:
2.2.1 Outside door at 2.2.A (2)
2.2.2 Window at 2.2.B (2)
2.2.3 Water closet at 2.2.C (2)
2.2.4 Washbasin at 2.2.D (2)
2.2.5 Single sink unit at 2.2.E (2)
2.2.6 One-way switch single pole at 2.2.F (2)
2.2.7 Fluorescent light at 2.2.G (2)
2.2.8 Socket outlet at 2.2.H (2)
2.2.9 Grease trap at 2.2.I (2)
2.2.10 Wall-mounted light at 2.2.J (2)
2.3
2.3.1 Trim hexagon
2.3.2 Hex flange
2.3.3 Square shoulder screws (3)
2.4
2.4.1 Dumpy level (1)
2.4.2 Any ONE use of this instrument:
- Determine the difference in levels
- Determine levels and slopes
- Setting out buildings
- Transferring levels and heights (1 x 1) (1)
2.4.3
- – Focussing knob
- – Eye piece
- – Foot piece
- – Objective (4 x 1) (4)
2.4.4 (1) To obtain a level / horizontal (2) sight line / reading (2)
2.5 (1) If the moisture inside the level freezes and later reaches normal operating temperature, the moisture can condense (2) inside the tool, where it may damage the circuit board (2)
2.6
- M08 = Thread diameter
- 25 = Thickness (2) [40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: ROOFS, STAIRCASES AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
3.1
3.1.1 Flat roof (1)
3.1.2 Mono-pitched roof (1)
3.1.3 1 400 mm / 1,4 m (1)
3.1.4 38 x 38 mm (1)
3.2 Any THREE requirements that roof trusses should meet:
- Sturdy enough to carry the roof covering safely
- Able to withstand wind and other forces that act on them
- Provide adequate height in rooms below the roof and ceiling assembly
- Should not allow the accumulation of rainwater upon the roof surface
- Neat and solid to enhance the appearance of the building (3)
3.3 Any THREE advantages with the use of roof underlays:
- Act as a secondary roof
- A weather shield during construction
- Waterproof and weatherproof
- Condensation barrier
- Dustproof
- Protects the building / structure
- Protects thermal insulation material
- Protects ceiling boards
- Superior wind uplifting strength prevents lifting of tiles
- Vapour resistant
- High tensile resistance
- Cost effective
- High heat resistance (3)
3.4
3.4.1 South African roof / Howe roof (1)
3.4.2 A – Rafter (1) B – Queen post (1) C – King post (1) D – Strut (1)
3.4.3 Span width more than 5 m (1)
3.4.4 114 (1) x 38 mm (1) (2)
3.5 Any TWO types of materials that staircases can be made from:
- Timber
- Concrete
- Bricks
- Metal (2)
3.6 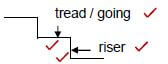 (4)
(4)
3.7 2 100 mm / 2,1 m (1)
3.8 100 mm (1)
3.9
3.9.1 Anchor / Galvanised steel straps / Hoop iron / Wires (1)
3.9.2 Bolted / Nailed / Galv. steel straps / Hoop iron / Wires (1)
3.9.3 Bolted / Welded / Glued (1)
3.9.4 Cast-in anchors / Bolted (1) [30]
QUESTION 4: MATERIAL, EXCAVATIONS, EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS (SPECIFIC)
4.1
4.1.1 F (tested on site) (1)
4.1.2 G (high volume of concrete) (1)
4.1.3 E (ferrous metals) (1)
4.1.4 C (tested in a laboratory) (1)
4.1.5 A (small volume of concrete) (1)
4.1.6 B (non-ferrous metals) (1)
4.2 Any FOUR types of apparatus for the slump test:
- Slump test cone / mould
- Base plate
- Tamping rod
- Ruler / Tape measure
- Spirit level / Rod (4)
4.3 Any TWO – Discuss the purposes of the cube test:
- Determine the maximum compressive strength of cured concrete with load
- Ensure concrete complies with requirements of project specifications
- Indicate compressive strength in MPa, thus its ability to resist loads (2)
4.4 Draw a neat sketch of a normal failure of a cube test: (3)
(3)
4.5 Any TWO – Discuss the purposes of cladding to external surfaces of buildings:
- Aesthetic purposes
- Functional purposes
- Help to control weather elements (rain / wind)
- Prevent runoff (water) from penetrating the building (3)
4.6 Any TWO methods of fixing cladding:
- Adhesive fixing
- Face fixing
- Proprietary fixing (2)
4.7 Any THREE safety factors and regulations that a site manager must have in place, before excavation commences:
- Ensure a competent person evaluates the stability of the ground
- Draw up safety plan and take steps to ensure safe working conditions
- Ensure that planned excavations / trenches be supported by a protective system (formwork / shoring) and are indicated on safety plan
- Eliminate as many risks / hazards as possible
- Erect fencing (at least one metre high) around perimeter of excavations
- All excavations done under qualified supervision
- Carry out inspections to determine position of services (cables, pipes etc.) (3)
4.8
4.8.1 Fencing / Warning signs / Warning lights / Covering (1)
4.8.2 All workers must wear protective clothing (1)
4.8.3 With a ladder / scaffolding (1)
4.8.4 Inspections must be done daily (1)
4.9
4.9.1 True (1)
4.9.2 True (1)
4.9.3 False (1)
4.9.4 False (1)
4.10
4.10.1 Firm ground / Hard ground (1)
4.10.2
- – Poling boards (1)
- – Strut (1)
- – Walling boards (1)
- – Folding wedges (1)
4.11
4.11.1 Plate compactor (1)
4.11.2 Any THREE ways to care and maintain the plate compactor:
- Maintain – lubricate and adjust to manufacturer’s instructions
- Clean after use and store in a safe, dry place
- Repair / replace damaged electrical cords
- Service regularly
- Remove loose dirt and soil after use
- Ensure that all parts are firmly attached (3) [40]
QUESTION 5: BRICKWORK, GRAPHICS, PLASTER AND SCREED (SPECIFIC)
5.1
5.1.1 Cavity wall (1)
5.1.2 270 mm (1)
5.1.3 Any THREE purposes of the gap in a cavity wall:
- Ensures that no water will penetrate the inner wall
- Provides insulation against heat
- Provides insulation against cold
- Provides insulation against sound (3)
5.2
5.2.1 Bedding sand (1)
5.2.2 Weep hole (1)
5.2.3 Pavements (1)
5.2.4 Air bricks (1)
5.2.5 Subgrade (1)
5.3
5.3.1 Butterfly pattern (1)
5.4 Any FOUR advantages of dry-laid paving:
- Very economical / Cheap
- Low initial installation cost
- Designed to accommodate lifting of individual pavers
- Can be easily repaired
- User-friendly installation materials
- Easy to repair underground utilities
- Can also be designed as a permeable pavement
- No off-gassing (harmful gasses) installation products are used (4)
5.5 Any TWO reasons for construction failure of paving:
- Concrete haunch is too thin to support itself and cracks / crumble under pressure
- Too little weight to retain the structure and keep paving in place
- Bond between the haunch and edge units is weak and crumbles easily
- Sub-base is not contained and will be washed out by groundwater (2)
5.6 Draw a neat partial sketch of the herringbone paving pattern: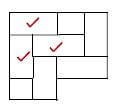 (3)
(3)
5.7 Any THREE advantages of beam filling:
- Prevents wind from penetrating the building
- Provides good insulation
- Prevents the perching / breeding of birds (open eave)
- Prevents insects from entering the roof and infesting the roof timber
- Prevents dust from entering the building
- Prevents small animals from entering the roof and ceiling (3)
5.8
5.8.1 True (1)
5.8.2 False (1)
5.8.3 True (1)
5.9
5.9.1 Semi-circular gauged arch (1)
5.9.2
- – Intrados (1)
- – Extrados (1)
- – Span (1)
5.10 Sand (1) and cement (1) (2)
5.11 Any ONE purpose of builder’s lime in a plaster mixture:
- Improves / enhances the workability of the mixture
- Improves the plasticity of the mixture
- Reduces cracking / crazing in the plaster (1)
5.12 Any TWO uses / purposes of interior plasterwork:
- Covers uneven, rough walls
- Improves sound insulation
- Improves fire resistance
- Prevents damage to the walls
- Provides a neat, hygienic finish to a house (2)
5.13 Any ONE purpose of a screed layer:
- To ensure a fine, smooth surface (paint)
- To ensure a flat, level surface (tiles) (1)
5.14
5.14.1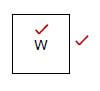 (2)
(2)
5.14.2 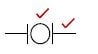 (2)
(2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: FORMWORK, REINFORCEMENT, FOUNDATIONS, CONCRETE FLOORS AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Any ONE material that can be used to line the formwork, to obtain a smoother finish:
- Plastic
- Metal sheeting
- Hardboard
- Fibre-glass (1)
6.2
6.2.1
- – Bearer / head tree (1)
- – Brace / strut (1)
- – Prop / strut (1)
- – Soleplate (1)
6.3
6.3.1 Soft / mild steel (1)
6.3.2 200 mm (1)
6.3.3 10 mm (1)
6.4
6.4.1 Compressive forces (Anchor bars) (1)
6.4.2 Shear forces (Stirrups) (1)
6.5 Any ONE method of joining steel bars with wire:
- Crosswise method
- Hair knot method
- Crown method (1)
6.6 Any TWO purposes of the cover depth at the reinforcing of concrete work:
- To protect steel against corrosion
- To ensure adequate bonding between the steel and concrete
- To ensure adequate protection of steel in event of a fire (2)
6.7 Any TWO types of pile foundations:
- Precast concrete piles / prefabricated piles
- Steel tube caisson piles
- In-situ (driven) foundation piles
- Short-bored (auger) piles (2)
6.8 Any THREE reasons for using pile foundations:
- Ground conditions not stable / solid enough
- Distribute the load to more stable ground (underground / water supports)
- Provides stability when raft / floating foundation is used
- When structures are subjected to horizontal forces, resist pile foundations
- Pending stress while still lending vertical support
- Soils prone to swelling and shrinking (clay soil)
- Superstructure is exposed to uplifting forces (offshore platforms)
- Where soil erosion is possible (bridges) (3)
6.9
6.9.1 A Hollow-core blocks / Concrete floor block (1) B Rib / Reinforced ribs / Pre-stressed ribs (1)
6.9.2 Any ONE disadvantage of the rib-and-block floor construction:
- Mechanical handling for the ribs requires on site
- Manual labour required to place blocks between ribs (1)
6.10 Foundation strip - outside room is 5 500 x 3 250 (outside measurements). The foundation is 700 mm wide and 200 mm thick.
6.10.1 Calculate the centre-line of the foundation:
- 2 / 5 500 = 11 000
2 / 3 250 = 6 500
17 500
Min corners:
4 / 700 = 2 800
14 700 (5)
6.10.2 Calculate the volume of concrete required:
- Volume = length x width x thickness
= 14,7 m x 0,7 m x 0,2 m
= 2,058 m³ (4) [30]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY GENERIC | NAME: |
2.2 Use the information on sheet A and complete the floorplan to scale 1 : 100. 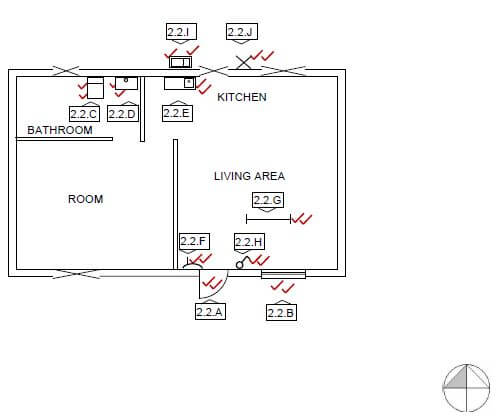
Outside door at 2.2.A | 2 | |
Window at 2.2.B | 2 | |
Water closet at 2.2.C | 2 | |
Wash basin at 2.2.D | 2 | |
Single sink unit at 2.2.E | 2 | |
One-way switch single pole at 2.2.F | 2 | |
Fluorescent light at 2.2.G | 2 | |
Socket outlet at 2.2.H | 2 | |
Grease trap at 2.2.I | 2 | |
Wall-mounted light at 2.2.J TOTAL: 20 | 2 | |