Economics P2 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupQUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 B √√ structure
1.1.2 B √√ technical
1.1.3 C √√ interdependent
1.1.4 A √√ packaging
1.1.5 D √√ taxation
1.1.6 D √√ mortgage
1.1.7 C √√ transit
1.1.8 A √√ non-renewable (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 C √ determined by the interaction between demand and supply
1.2.2 E √ additional remuneration for entrepreneurship
1.2.3 I √ the value of what you have to give up in order to choose something else
1.2.4 A √ has a hybrid structure
1.2.5 D √ traditional way of doing things that are unique to a given culture
1.2.6 G √ used to calculate all-inclusive inflation
1.2.7 H √ visiting art galleries, museums, archaeological sites etc.
1.2.8 F √ when heat is trapped by CO2 layer in the atmosphere (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 GIVE ONE TERM
1.3.1 Explicit costs √
1.3.2 Long run √
1.3.3 Externalities √
1.3.4 Deflation √
1.3.5 World heritage sites √
1.3.6 Biodiversity √ (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer TWO of the three questions from this section in your ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS
2.1
2.1.1 Give any TWO examples of variable costs.
- Water √
- Electricity √
- Raw materials √
- Sales commissions √
- Direct labour costs √
- Packaging √
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why are individual market participants in a perfect market insignificant to the market as a whole?
- They have no power in the market√√
- They cannot influence the prices of products √√
- They accept the market price as given by the market as a whole √√
- They act completely independent of one another√√
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2
2.2.1 Provide a suitable label for curve A (1) Average Revenue / Demand curve √
2.2.2 What is the selling price for the business above?
- 100 √ (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term monopoly.
- Monopoly is a market structure where only one seller operates with blocked entry. √√
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.4 Explain a reason for the shape of total revenue curve.
- The slope of this curve rises as more output is produced, eventually reaching a peak, then becoming negative √√
- The changing slope of this curve is due to the changing price √√
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
2.2.5 Redraw Graph 1 in your answer book and show how a monopoly will make economic profit. 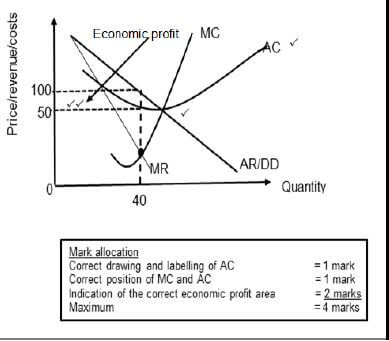
(4)
2.3 DATA RESPONSE
2.3.1 Name the market structure that led to the implementation of competition policy.
- Imperfect market /Monopoly/Monopolistic Competition/Oligopoly √ (1)
2.3.2 Which institution provides final decisions when parties are dissatisfied with rulings of the Competition Tribunal?
- Competition Appeal Court √ (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term regulation in economics.
- It is the imposition of rules by the government, backed by use of penalties that are intended to modify economic behaviour of firms. √√
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (2)
2.3.4 What is the role of the Competition Commission?
- It is to investigate, control and evaluate restrictive business practices √√ (2)
2.3.5 Why is it important for the South African government to control competition among businesses?
It is important because the government would like to:
- promote efficiency, adaptability and development of the economy √√
- provide consumers with competitive prices and product choices √√
- promote employment and advance social and economic welfare of SA √√
- expand opportunities for SA participation in world market√√
- ensure that SMMEs have equal opportunities to participate in the economy√√
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Briefly explain entry and perfect knowledge as characteristics of a perfect competitor.
Entry
- There is freedom of entry and exit in the market, i.e the market is fully accessible √√
- Entry is not subject to any restrictions e.g. financial, technological barriers √√
- If an individual business observes another business making a large profit in a specific market, it can open a similar business that supplies the same product √√
- New firms will enter and compete in a specific market as long as there are opportunities to make a profit √√
Perfect knowledge
- Both buyers and sellers have complete information about the prevailing market conditions √√
- There is no information failure or time lag in the flow of information √√
- Given that producers and consumers have perfect knowledge, it is assumed that they make rational decisions to maximise their self-interest
- consumers look to maximise their utility, and producers look to maximise their profits√√
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 4) (8)
2.5 What positive impact will an increase in suppliers of electricity have on South Africa?
The economy will benefit because this will result in:
- improving competition as more firms will enter the market and produce electricity √√
- lowering price of electricity for both consumers and producers in the economy √√
- improving the quality of service provided by electricity suppliers √√
- increasing production in the economy as a whole as there will be reduction in production costs
- creating more jobs for the people therefore improving the welfare of the consumers
- increasing economic growth due to increased number of suppliers in the economy
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2) (8) [40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
3.1 3.1.1 Name any TWO negative effects of tourism.
- Damage to the landscape
- Litter
- Erosion
- Fires
- Traffic congestion
- Pollution
- Expensive local goods (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 Why is the preservation of natural resources important?
- It is essential for promoting sustainable development
- It is important for the alleviation of poverty
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 DATA RESPONSE
3.2.1 Name the economic sector that is represented by tourism. - Tertiary/service sector (1)
3.2.2 Which type of tourism is depicted in the data above?
- Domestic tourism/local tourism (1)
3.2.3 Briefly explain the term tourism.
- Tourism refers to the activities of people travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for no more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (2)
3.2.4 Explain a reason for the growth of foreign tourism in South Africa.
- SA is a peaceful and prosperous democratic country
- It is cheaper for foreigners to visit South Africa because of the low value of rand
- SA offers a wide variety of tourism attraction – it is a world in one
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
3.2.5 How can tourism alleviate poverty in rural areas?
Tourism can alleviate poverty by:
- providing rural people with direct and indirect jobs
- hiring rural people who work directly in the sector as tour operators, travel agents, flight attendants etc.
- providing income to rural people through spending by tourists on goods and services
- allowing rural people to benefit from the infrastructure built for tourists
- acquiring skills needed in tourism industry
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
3.3 DATA RESPONSE
3.3.1 Name the organisation which has facilitated a number of agreements regarding disposal of toxic chemical waste.
- United Nations (1)
3.3.2 What could be the cause of global warming? (1)
- Emission of gases/greenhouse gases
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term climate change.
- It is the change in the composition of the atmosphere that is related to human activities
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.4 Why does the government provide environmental subsidies to businesses?
- To encourage businesses to produce environmentally friendly products
- For the development of new techniques and technology so as to reduce pollution
- To promote recycling of waste products
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
3.3.5 How are farmers affected by acid rain?
Farmers are negatively affected by acid rain because:
- crop production will decrease
- the price of agricultural products will be high
- animal husbandry will decrease as it will be affected by lack of water and food
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Briefly explain the economic benefits of tourism for the government.
The government will benefit from tourism through:
- increased revenue because tourism makes direct and indirect contribution to the government revenue through taxes, e.g. airport departure tax, air tickets etc.
- advertising and excellent service delivered to tourists, thus creating a good image of the country.
- job creation and relieve poverty especially in the informal sector e.g. musicians
- earning of foreign exchange for the country thereby increasing the foreign reserves
- recovering external costs, as the government is able to recover from tourists a portion of what serves as a compensation for providing the infrastructure
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2) (8)
3.5 How can environmental degradation be prevented?
It can be prevented by:
- planting trees as they can absorb carbon dioxide thereby providing a cleaner environment
- avoiding littering by people as it may lead to global warming
- educating people about the importance of recycling items or reusing them instead of throwing away
- avoiding burning of paper and other material as this may result into pollution
- avoiding intense agricultural practices which destroy fertile land
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2) (8) [40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
4.1
4.1.1 Name any TWO major international protocols and agreements on sustainable development.
- Rio de Janerio summit (UNCED)
- Johannesburg summit
- Rio + 20 summit
- Kyoto Protocol
- Millennium development goals
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
- Conference of the Parties (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How are consumers affected by maximum prices?
- They will buy goods and services at a price lower than the market price
(Accept any relevant correct response) (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 DATA RESPONSE
4.2.1 What is the nature of the service offered by the firms above?
- Homogenous / Differentiated (1)
4.2.2 How is the shape of the demand curve of the oligopoly?
- Kinked (1)
4.2.3. Briefly describe the term oligopoly.
- A market structure where only a few sellers operate
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.4 What does it mean for Vodacom to be a dominant firm?
- It has a significantly larger market share than its competitors or rivals
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.5 How do oligopoly competitors benefit from collusion?
Oligopoly competitors benefit by:
- having their performance increased
- preventing uncertainties that may occur
- having a large market share by preventing entry of new organisation
(Accept any relevant correct response) (2 x 2) (4)
4.3 DATA RESPONSE
4.3.1 What is the group of animals in the picture above called?
- The Big FIVE (1)
4.3.2 Which international treaty is concerned with endangered species?
- The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term endangered species.
- A species of animal or plant that is seriously at risk of extinction.
(Accept any other correct relevant response). (2)
4.3.4 How can education be used as a measure to ensure sustainability?
- People should be made aware of environmental issues and the consequences of their actions
- Innovative approaches can be tried to educate people, e.g. setting up community wildlife reserves
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
4.3.5 Why were the Millennium Development Goals not achieved? Millennium development Goals were not achieved because:
- of a lack of proper monitoring systems
- the earth forest areas still continue to shrink
- there are declining trends in productivity
- illicit poaching and tracking wildlife continue to prevent conservation
(Accept any relevant correct response) (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 With the aid of a well labelled graph, explain economic loss in a perfect market. 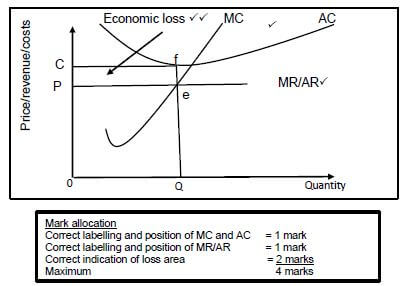
- The business is in equilibrium at point e where MR=MC and optimal quantity produced is Q at price P and cost C
- Economic loss is made where AR is less than AC which is indicated by the CPef area (8)
4.5 Examine the success of marketing as a strategy to promote tourism in South Africa.
Marketing has been successful in promoting tourism by:
- having a modern looking website which has been used to build the brand for tourist services and has attracted many tourists to South Africa
- utilising the online bookings and payments ensures that tourists pay for their hotel rooms and book recreational activities online prior their travel
- providing information to tourists about their safety and security through reduction of crime and violence on tourists, has attracted many visitors to the country through tourism indabas
- devoting adequate resources to provide for safety of tourists through speedy and effective legal procedures
- emphasising the diversity of the tourism products which include, cruise tourism, sports, wildlife safari’s etc. has attracted tourists both nationally and internationally
- making travel more accessible and affordable to all through Sho’t left campaign
- providing reliable and affordable mode of transportation in accordance with tourist demand and tourism has provided services that are tailor made to the needs of the tourists, for example Gautrain
- maintaining and upgrading infrastructure to improve accessibility and mobility to tourist destination, has improved the tourism sector e.g. information centres, rail and road network, telecommunication etc.
(Accept correct and relevant response) (8) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE of the two questions from this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 5
- Discuss in detail the causes of market failure focusing on the following:
- Missing markets
- Lack of information (26)
- Evaluate the success of the government intervention in markets in distributing wealth. (10)
INTRODUCTION
Market failure means that the best available/optimal production outcome has not been achieved.
Markets fail when they are unable to allocate resources efficiently.
(Accept any other correct response) (Max.2) (2)
MAIN PART
Missing markets
Markets are incomplete and cannot meet the demand for all goods.
Public goods
- Free market does not want to supply these goods, hence government supply them
- Businesses in the free market will not charge a price for these goods based on their use, so they will not supply them
- Public goods include:
- Community goods
These are goods such as defence, police services, street lighting, flood control etc.
Features of community goods: - Non-rivalry
Consumption by one person does not in any way reduce consumption by another person. E.g. street lighting, lighthouse
Consumption by one person may not prevent others from enjoying it too - Non-excludability
Consumption of a good cannot be confined to those who have paid for it, so there are free riders
They are provided for all users even those who did not pay for it, e.g. television and radio - Social benefits outstrip private benefits
Community goods often have large social benefits relative to private benefits, e.g. health care and education - Infinite consumption
Once they are provided the marginal costs of supplying one more individual is zero, e.g. traffic lights - Non-rejectability
Individuals may not be able to abstain from consuming them even if they want to, e.g. street lighting
- Community goods
- Collective goods
- These are goods like beach facilities, streets, pavements, roads, bridges etc.
- They are provided for a user fee
- Provision of some collective goods is subsidised, e.g. public transport and clean water
Merit and demerit goods
Merit goods
- They have important benefits to the user and to the general welfare of the community
- They are highly desirable for the general welfare of the people of a country but are often not highly rated by the market
- If people had to pay market prices for them, relatively little would be consumed
- In this sense, the market will fail to the detriment of the economy and society
- Examples of such goods are health care and education, skills training, safety, inoculations and car seat belts
- Markets do not reflect the full value of merit goods because markets only take the private benefits into account and not social benefits
- Markets undervalue these products and provide too few of them at prices that are too high
- If consumers were to pay a full market price, very little would be consumed and the market therefore would fail
Demerit goods
- They are over consumed by individuals
- Some consumers may be unaware of the true costs of consuming them, i.e. their negative externalities
- Government can ban their consumption or reduce it by means of taxation and provide information about their harmful effects
- Examples include: cigarettes, alcohol, tobacco, non-prescription drugs
- When the market is willing to produce them, it will supply too much of these goods
Lack of information
- Consumers, workers and entrepreneurs do not always have necessary information at their disposal to make rational decisions, hence lack of information makes markets to fail operating well
- Consumers do not have detailed information on advanced technology to be aware of the goods produced so as to maximise their utility
- Workers also need information about all job opportunities and benefits to ensure that they use their labour effectively but they are unaware of such job opportunities outside their current employment, hence markets fail to employ the required labour force
- Entrepreneurs may lack information about costs and availability of factors of production; therefore, they may be operating on the basis of incorrect information and make wrong decisions
(Accept any other relevant response)
(Allocate a maximum of 8 marks for mere listing or examples) (26)
ADDITIONAL PART
Evaluate the success of the government intervention in markets in distributing wealth.
The government has been successful in distributing wealth through:
- providing public goods for collective consumption, e.g. provision of health care services, infrastructure development etc. leading to uplifting of the welfare of individuals
- investing in education and training by providing free education in schools and tertiary institutions resulting in people getting opportunities of being employed and accumulating wealth
- reducing poverty through social transfer to the poor thus improving their welfare
- boosting participation of black entrepreneurs in economic activities thus creating employment for different skills in the economy leading to improved standard of living for all
Unsuccessful by:
- failing to reduce inequality despite the social transfers provided because the grants do not cater for the unemployed
- using an official definition of unemployment which exclude people who have given up looking for jobs
- creating jobs that barely keep up pace with the growth in labour force
- failing to have proper monitoring tools for granting tenders to empower blacks
- failing to bridge the gap between the rich and the poor
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (10)
CONCLUSION
The government is trying to safeguard the interests of the community and improve the efficiency in markets but there is still more to be done.
(Accept any relevant high order conclusion) (2) [40]
QUESTION 6
- Examine in detail the causes of cost-push inflation. (26)
- How effective are interest rates in combating inflation since the introduction of inflation targeting? (10)
INTRODUCTION
- Cost-push inflation is a rise in the general prise level resulting from an increase in the costs of production
- Any costs to businesses is a potential source of cost-push inflation
- Cost-push inflation may be caused by the combination of the various components of production costs
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
BODY
MAIN PART – CAUSES OF COST-PUSH INFLATION
Increase in wages
- Remuneration of labour constitutes almost 60% of the cost of producing the GDP
- Increases in salaries and wages are therefore an important source of cost-push inflation
- When workers demand higher wages than their productivity, the increased costs are recovered by increase in prices
- If trade unions are successful in negotiating wages, the wages will go up and the producers will increase the selling price to compensate for the higher input costs
- Prices of goods/services will go up and inflation may occur
- A vicious cycle then results as labour demand even more higher wages as the cost of living goes up (Max. 6)
Increase in the prices of imported goods/key inputs
- South African manufacturers have to import most of their capital and commodities like oil and aluminium
- When these are raised, it leads to price increases because producers wish to maintain their profits
- When prices of key input goods that are imported increase (e.g. oil, energy, capital goods etc.) the domestic costs of production are pushed upwards
- and the consumer prices increase leading to inflation
- (Max. 4)
Increased profits/profit margins
- When profit margins are increased, it leads to an increase in the prices of goods
- This occurs when firms use their market power to push up prices
- When businesses push up their profit margins, they increase the cost of production and eventually the prices that consumers have to pay (Max. 4)
Low levels of productivity
- When the various factors of production become less productive while receiving the same remuneration, the costs of producing each unit of output increases, wage increases that are not accompanied by similar productivity increases have the effect of increasing inflation (Max. 4)
Natural disasters
- Natural disasters such as floods, fires, drought often occur in South Africa and can cause inflation in food prices because of shortages in agricultural production
- They impact on the costs of producers
- Food prices are one of the most volatile price items in inflation indexes as a result of the effects of weather changes (Max. 4)
Exchange rate depreciation
- Exchange rate depreciation may be the cause of price increases
- E.g. if the rand depreciates in terms of the US dollar, all imported goods and services become more expensive(Max. 4)
Sudden increase in interest rates
Increase in interest payments on loans will lead to higher costs
- Producers will recover these higher costs through increasing prices of their goods and services (Max .4)
Government induced prices
- When government induced price rises, which include increase in direct taxes or indirect taxes, the prices of goods and services are affected
- Producers normally shift the tax burden to consumers by increasing their prices of goods and services thereby leading to inflation (Max. 4)
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(Allocate a maximum of 8 marks for mere listing of facts or examples) (26)
ADDITIONAL PART
How effective are interest rates in combating inflation since introduction of inflation targeting?
The use of interest rates as an instrument to maintain inflation has been effective because:
- Changes in the repo rate have shown a positive effect so far as the inflation is maintained within the targeted range.
- Although the inflation rate was 13,51% in 2002, through the use of interest rates it declined to 6,16% in 2016 which was still outside the target range.
- The 25 basis points increase in November 2018 brought the repo and prime rates to 6,75% and 10,25% and inflation rate was within the target at 5,2%
- Increasing the interest rates will result in less money, credit and expenditure in the economy and it becomes difficult to raise prices and wages
- The repo rate is kept at 6,77% and prime rate at 10,25% in the first quarter of 2019
- The current inflation rate stands at 4,5% from 4,1% in March 2019 and this shows that SARB has effectively managed to maintain the inflation rate through the use of interest rates.
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (10)
CONCLUSION
Inflation can be a threat to the normal functioning of the economy, therefore measures like monetary and fiscal policies are vital to keep the phenomenon under control.
(Accept any relevant higher order conclusion) (2)
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150