CIVIL TECHNOLOGY(CONSTRUCTION) GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2019
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupCIVIL TECHNOLOGY(CONSTRUCTION)
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
NOVEMBER 2019
REQUIREMENTS:
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable calculator
- ANSWER BOOK
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2, 3.6, 5.4, 6.8 and 6.9 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments where necessary.
- Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale due to electronic transfer
- Google Images was used as the source of all photographs and pictures
QUESTION 1: OHSA, SAFETY, MATERIALS, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND JOINING (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A-K) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.9 L.l
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.1.1 PVA paint 1.1.2 Guard rail 1.1.3 Powder coating 1.1.4 Builder's hoist 1.1.5 Ladder 1.1.6 Diagonal brace 1.1.7 Galvanising 1.1.8 Chute |
|
(8 x 1) (8)
1.2 Explain TWO advantages of electroplating.
1.3 Name the process when freshly cast concrete is kept moist for a specific period of time.
1.4 Explain the purpose of keeping freshly cast concrete moist for a certain period of time after the concrete has been cast.
1.5 You are transporting material on a construction site from one place to another. Describe TWO safety precautions that you will adhere to while transporting the material.
1.6 Describe ONE safety factor that must be considered when using scaffold planks to erect a scaffold platform.
1.7 FIGURE 1.7 below shows a surveying tool used on a building site.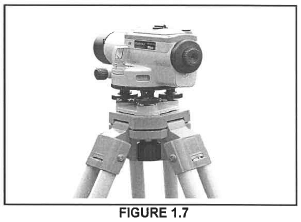
1.7.1 Identify the tool above.
1.7.2 Predict ONE consequence if the instrument is NOT set level.
1.8 FIGURE 1.8 below shows a joining fixture that is used on building sites and in workshops.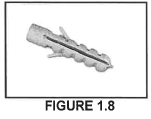
1.8.1 Identify the joining fixture above.
1.8.2 Name the fixing agent that should be used with this joining fixture.
1.8.3 Explain ONE use of this joining fixture.
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (GENERICS)
Start this question on a NEW page.
FIGURE 2 on the next page shows different drawings that appear on a building plan. Analyse the drawings and complete the table on ANSWER SHEET 2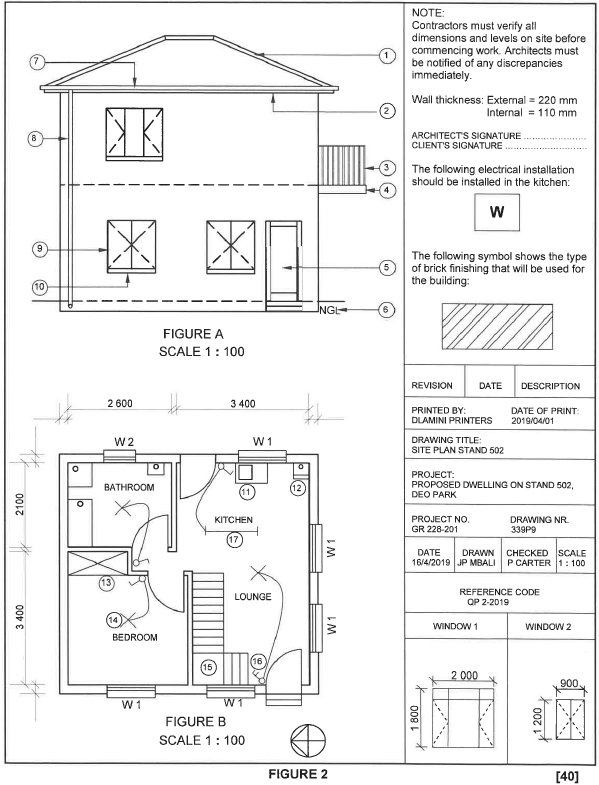
QUESTION 3: ROOFS, STAIRCASES AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions by choosing a word/term from the list below. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (3.1.1 to 3.1.3) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 3.1.4 50 mm round poles.
| 15°; 800 mm; 36 mm round poles: 10° 38 mm round poles 650 mm; 45°; 550 mm; 40 mm round poles |
3.1.1 What is the minimum pitch of a roof when Class B fibre-cement tiles are used to cover a roof?
3.1.2 What is the maximum distance of the spacing between roof trusses for concrete roof tiles?
3.1.3 What are the dimensions of a purlin for thatch roofs ?
Recommend ONE method of fixing balusters to the landing of a staircase.
3.3 Recommend ONE type of fastener one will use to fix galvanised steel straps to roof trusses.
3.4 Use ANSWER SHEET 3.4 and draw a neat line diagram of the sectional front view of a staircase with a landing.
Use the assessment criteria on the ANSWER SHEET as a guide. (10)
3.5 Use ANSWER SHEET 3.5 and draw to scale 1:20 a close-coupled roof truss with a pitch of 30° and a span of 3 metres resting on two supporting walls. The eaves overhang is 400 mm.
Use the assessment criteria on the ANSWER SHEET as a guide. (15)
[30]
QUESTION 4: EXCAVATIONS, FORMWORK, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The excavation of soil on a building site is necessary to establish a firm foundation
4.1.1 What is the minimum distance that excavated soil can be stored from the trench?
4.1.2 What is a safe distance for heavy machinery to move around a deep excavation?
4.1.3 Describe TWO reasons why an excavation can collapse.
4.1.4 What is the maximum depth of a trench in which workers can work without the sides of the trench being braced?
4.1.5 What can help to prevent the sides of excavations from collapsing? (1)
4.2 FIGURE 4.2 below shows two types of shuttering used in excavations. Study FIGURE 4.2 below and answer the questions that follow.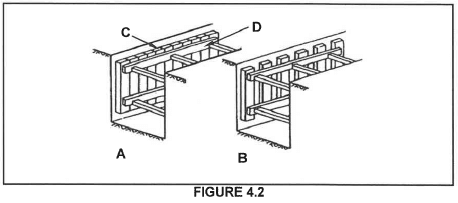
4.2.1 State where shuttering A and B will be used respectively.
4.2.2 Name C and D.
4.2.3 Compare FIGURE A with FIGURE B and state the difference between the types of shuttering.
4.3 FIGURE 4.3 below shows a construction machine that is used on a building site. Study FIGURE 4.3 and answer the questions that follow.
4.3.1 Identify the construction machine.
4.3.2 Describe TWO methods that can be used to take care of this construction machine.
4.3.3 Describe TWO safety aspects that must be checked before using the construction machine.
4.4 What should be the minimum compressive strength of high-strength concrete after 28 days if all conditions have been met?
4.5 Name the THREE outcomes of the slump test.
4.6 Which water-retaining material can be used to keep fresh concrete moist?
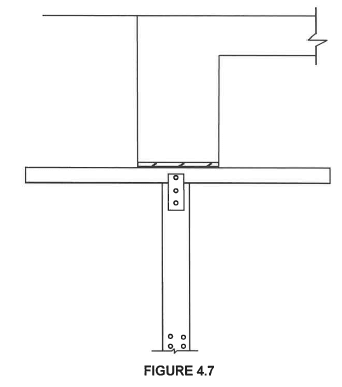
4.7 Use ANSWER SHEET 4.7 and complete the drawing of a vertical section of the formwork for a concrete beam with the floor slab in good proportion.
Use the assessment criteria on the ANSWER SHEET as a guide. (18)
[40]
QUESTION 5: PLASTER AND SCREED, BRICKWORK AND GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 Name ONE type of plaster finish that can be applied to brick walls.
5.2 State the first step before plastering an internal wall two weeks after it has been built.
5.3 State ONE property of good plaster.
5.4 State the average thickness of screed.
5.5 FIGURE 5.5 below shows a vertical sectional view through paving. Study FIGURE 5.5 and answer the questions that follow.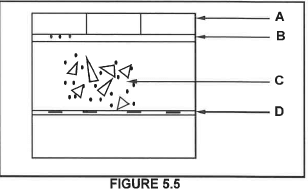
5.5.1 Name A to D.
5.5.2 Give ONE reason why construction failure can occur in paved areas.
5.6 ANSWER SHEET 5.6 shows the outlines of the top view of a cavity wall with a dead end.
Use ANSWER SHEET 5.6 and draw ONE brick course of the cavity wall with a wall tie.
5.7 Use ANSWER SHEET 5.7 and draw to scale 1:5 a horizontal sectional view through a face brick wall to show how a timber window frame stile is built into a wall.
Use the assessment criteria on the ANSWER SHEET as a guide.(14)
[30]
QUESTION 6: REINFORCEMENT IN CONCRETE, FOUNDATIONS, CONCRETE FLOORS AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A-D) next to the question numbers (6.1.1 to 6.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 6.1.6 C.
6.1.1 The striking of formwork for a deck depends on the ...
average temperature. thickness of the concrete. properties of the concrete All the above-mentioned (1)
6.12 The minimum thickness of a suspended reinforced concrete floor
100 mm 150 mm. 160 mm. 140 mm (1)
6.1.3 What type of foundation will be used where the site is NOT level?
Strip foundation Floating foundation Step foundation Raft foundation (1)
6.1.4 The internal walls that support a suspended concrete floor must be ...
vertically in line with the external walls. one brick course below the floor. horizontally in line with the external walls. one brick course above the floor.(1)
6.1.5 The minimum cover depth for concrete with reinforcement exposed to soft unpolluted air is ...
60 mm. 40 mm. 30 mm.20 mm.
6.2 Give TWO reasons for using pile foundations
6.3 Recommend THREE types of equipment that can be used to install precast concrete piles.
6.4 Differentiate between the installation methods of steel-tube caisson piles and precast concrete piles. (2)
6.5 FIGURE 6.5 below shows a part of a floor construction. Study FIGURE 6.5 and answer the questions that follow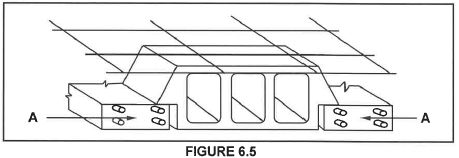
6.5.1 Name the type of floor construction.
6.5.2 Describe THREE factors that should be considered after casting the concrete for the floor construction.
6.5.3 What type of concrete is used for this type of floor?
6.5.4 What will determine the spacing between parts A?
6.5.5 Predict what will happen if the floor is subjected to a lot of movement before the concrete has reached its maximum strength. (1)
6.6 ANSWER SHEET 6.6 shows a wall and an incomplete reinforced concrete beam.
Use ANSWER SHEET 6.6 and draw, in good proportion, the reinforcement that should be placed in the beam that is resting on the wall.
Use the assessment criteria on the ANSWER SHEET as a guide (11)
6.7 FIGURE 6.7 below shows the floor plan of a building with a gable roof.
The external measurements are 9 000 mm x 4 000 mm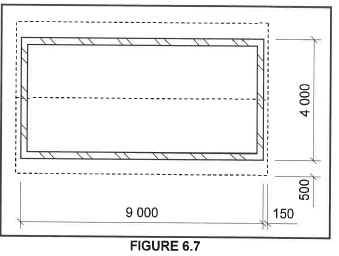
Use the following specifications:
- The walls are 220 mm thick.
- The centre-to-centre spacing of the roof trusses are 1 070 mm.
Use the dimension paper in ANSWER SHEET 6.7 and calculate the quantities of the following materials:
6.7.1 Total length of wall plate needed in metres
6.7.2 Number of roof trusses needed
[40]
TOTAL:200
ANSWER SHEET 2
| NO. | QUESTION | ANSWER | MARKS |
| 1 | Identify the elevation in FIGURE A. | 1 | |
| 2 | Identify the type of roof that is used on the building in FIGURE A. | 1 | |
| 3 | Identify number 1. | 1 | |
| 4 | Identify number 4 | 1 | |
| 5 | Identify number 5 | 1 | |
| 6 | Identify number 7 | 1 | |
| 7 | Identify number 8 | 1 | |
| 8 | Identify number 12 | 1 | |
| 9 | Identify number 13 | 1 | |
| 10 | Identify number 15 | 1 | |
| 11 | Identify the company that printed the building plan. | 1 | |
| 12 | Name a suitable material that can be used for the manufacturing of number 2. | 1 | |
| 13 | Name the drawing symbol in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must be installed in the kitchen. | 1 | |
| 14 | Name the drawing symbol in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that indicates the type of bricks for the building | 1 | |
| 15 | Name a material that should NOT be used to manufacture the frame of number 9 for coastal areas. | 1 | |
| 16 | Name a material that can be used to manufacture the sanitary fitting indicated by number 11. | 1 | |
| 17 | Who checked the building plan? | 1 | |
| 18 | How many types of windows are used in FIGURE B? | 1 | |
| 19 | What does the abbreviation NGL at number 6 stand for? | 1 | |
| 20 | Give the reference code for this plan. | 1 | |
| 21 | Which room will electrical symbol 16 serve? | 1 | |
| 22 | Describe the purpose of number 3. | 2 | |
| 23 | Explain what the curved lines between the electrical installations in FIGURE B indicate. | 2 | |
| 24 | Explain why the light switch is mounted on the outside of the bathroom. | 1 | |
| 25 | Identify in FIGURE 2 which elevation does NOT have windows. | 1 | |
| 26 | Identify the thickness of the internal wall in FIGURE 2. | 1 | |
| 27 | Differentiate between symbols 13 and 15 in terms of their purpose. | 2 | |
| 28 | Justify why FIGURE B is a ground floor plan | 1 | |
| 29 | Predict what will happen if number 10 is NOT installed. | 1 | |
| 30 | Redraw the staircase in FIGURE B in the adjacent column and indicate the direction of the flight with arrows. | 2 | |
| 31 | Calculate the total length of the wall on the eastern side of the building. Show ALL calculations. | 6 | |
| TOTAL: | 40 |
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
| Wall | 1 | |
| Landing | 1 | |
| Baluster | 1 | |
| Handrails | 2 | |
| THREE treads | 1 | |
| Concrete | 1 | |
| Any TWO labels | 2 | |
| Correctness of drawing | 1 | |
| TOTAL: | 10 |
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
| Walls | 2 | |
| Wall plates | 2 | |
| Rafters | 2 | |
| Ridge beam | 1 | |
| Tie beam | 1 | |
| Any THREE labels | 3 | |
| Dimension of the span | 1 | |
| Application of scale: ONE or TWO incorrect = 3 THREE or FOUR incorrect = 2 More than FIVE incorrect = 1 | 3 | |
| TOTAL: | 15 |
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
| Shuttering board sides | 2 | |
| Cleats | 2 | |
| Fixing plates | 2 | |
| Wedges | 2 | |
| Braces/Struts | 4 | |
| Bearer | 1 | |
| Any THREE labels | 3 | |
| Correctness of drawing | 2 | |
| TOTAL: | 18 |

| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
| Correctness of drawing | 2 | |
| Dead end | 2 | |
| Inner skin of cavity wall | 1 | |
| Outer skin of cavity wall | 1 | |
| Wall tie | 1 | |
| TOTAL: | 7 |
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
| Frame stile: 105 mm x 70 mm | 2 | |
| Window stile/Casement stile: 60 mm x 45 mm | 2 | |
| Frame tie/lug: 25 mm wide | 1 | |
| Glass: 3 mm thick | 1 | |
| Putty | 1 | |
| Internal window sill | 1 | |
| External window sill | 1 | |
| DPC | 1 | |
| Any ONE label | 1 | |
| Application of scale: ONE or TWO incorrect = 3 THREE or FOUR incorrect = 2 More than FIVE incorrect = 1 | 3 | |
| TOTAL: | 14 |
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
| Anchor bar | 2 | |
| Shear bar | 2 | |
| Stirrups/Binders | 2 | |
| Main bar | 2 | |
| Minimum concrete cover | 1 | |
| Any ONE label | 1 | |
| Correctness of drawing | 1 | |
| TOTAL: | 11 |