AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MAY/JUNE 2021
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 D ✓✓
1.1.2 B ✓✓
1.1.3 C ✓✓
1.1.4 C ✓✓
1.1.5 D ✓✓
1.1.6 C ✓✓
1.1.7 A ✓✓
1.1.8 B ✓✓
1.1.9 D ✓✓
1.1.10 B ✓✓
(10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 D ✓✓
1.2.2 F ✓✓
1.2.3 H ✓✓
1.2.4 C ✓✓
1.2.5 B ✓✓
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Shortage ✓✓
1.3.2 Contract ✓✓
1.3.3 Dominant ✓✓
1.3.4 Epistasis ✓✓
1.3.5 Heredity ✓✓
(5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Green marketing/eco-labelling ✓
1.4.2 Motivation ✓
1.4.3 Pedigree ✓
1.4.4 Haemophilia ✓
1.4.5 Polygenic inheritance ✓
(5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
2.1 Marketing
2.1.1 Definition of the concept marketing
The process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion ✓ and distribution of ideas, goods and services to consumers ✓ (2)
2.1.2 The differences between marketing and selling
- Marketing ✓ (1)
- Selling ✓ (1)
- Selling ✓ (1)
2.2 Inelasticity of demand
2.2.1 Deduction of the marketing concept
Price inelasticity of demand ✓ (1)
2.2.2 A reason for the answer
The demand changed slightly despite the huge change in price ✓ (1)
2.2.3 Explanation of the reason why consumers responded in this way
Maize meal is a necessity/staple food ✓ people will therefore buy maize meal even with a price increase ✓ (2)
2.2.4 Identification of the factor leading to the differences in the number bags demanded
Price ✓ (1)
2.3 Cooperative marketing of avocadoes
2.3.1 Identification of the agricultural marketing system
Cooperative marketing ✓ (1)
2.3.2 Indication of the role of agricultural marketing system
Production/selling/marketing ✓ (1)
2.3.3 TWO benefits for the marketing system to farmers
- Lower marketing costs/cost distribution ✓
- Requirements/services are supplied cheaper/bulk purchasing ✓
- More bargaining power ✓
- Access to funding/credit to producers ✓
- Higher prices are obtained ✓
- Elimination of the intermediaries ✓
- Potential for growth ✓
- Access to better infrastructure ✓
- Branding ✓
- Risk sharing ✓
- Farmer spend more time on producing than on marketing ✓
- Access to professional expertise ✓ (Any 2) (2)
2.3.4 TWO factors that may hamper the marketing of avocadoes
- Perishability/spoilage ✓
- Seasonal fluctuations in production ✓
- Lack of capital ✓
- Poor infrastructure ✓
- Wide distribution of production areas ✓
- Ineffective control over production ✓
- Risk/theft/accidents ✓
- Standardization ✓
- Large volume in relation to value/bulkiness ✓
(Any 2) (2)
2.4 Marketing function
2.4.1 Identification of the marketing function.
Packaging ✓ (1)
2.4.2 THREE characteristics of the cardboard boxes which make them suitable
- Clean/dry/undamaged/suitable for the product ✓
- No foreign tastes/odours ✓
- Free of visible signs of fungal growth ✓
- Strong/rigid/solid ✓
- Recyclable/biodegradable ✓
- Easy to handle ✓
- Identification ✓
(Any 3) (3)
2.4.3 Reason for using cardboard boxes with holes
Allow air flow/reduce spoilage/health reasons ✓
(Any 1) (1)
2.5 Drawing up a business plan
2.5.1 ONE aspect that should be included in
- The title page
- Name of the business/person ✓
- Logo ✓
- Address ✓
- Contact details of the business/person ✓
(Any 1) (1)
- Human resource plan
- Number and type of employees ✓
- Competencies and skills needed ✓
(Any 1) (1)
2.5.2 Indication of an electronic resource
Computer software programmes ✓ (1)
2.5.3 TWO reasons for drawing up a business plan
- To test the feasibility/economic viability of the business idea ✓
- To secure funding ✓
- To determine financial needs/budget ✓
- To guide daily operations/outlines roles and responsibilities ✓
- To allow the entrepreneur to foresee problems ✓
- To reposition/analyse the business ✓
- To gain knowledge about marketing opportunities and competitors ✓
- To ensure effective business management ✓
- Mapping out the objectives/goals of the enterprise ✓
- Provides information on the internal/external business environment ✓
- Provision of time frames ✓
(Any 2) (2)
2.5.4 ONE problem encountered when drawing up a business plan
- Incomplete/with gaps ✓
- Vague ✓
- Unrealistic assumptions/over ambitious ✓
- Hiding weaknesses and risks ✓
- Not taking the competition into account ✓
- Using the incorrect format ✓
- Insufficient research ✓
- Insufficient technical details ✓
(Any 1) (1)
2.6 Entrepreneurship
2.6.1 Rearrangement of the phases of the entrepreneurial process
- D ✓ (1)
- A ✓ (1)
- C ✓ (1)
- B ✓ (1)
2.6.2 TWO aspects of the SWOT analysis
- Internal - Strength ✓ weaknesses ✓ (2)
- External - Opportunities ✓ threats ✓(2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
3.1 Land
3.1.1 The life of soil is unlimited if used correctly - Durability ✓ (1)
3.1.2 12% of the soil in South Africa can be cultivated - Availability ✓ (1)
3.1.3 Soil may be damaged but cannot be destroyed - Indestructibility ✓ (1)
3.2 TWO economic functions of land
- Land provides space/area ✓
- Provides raw materials ✓
- Provides minerals ✓
- Food security ✓
- Serves as collateral/security ✓
(Any 2) (2)
3.3 Labour
3.3.1 Labour legislation
Basic Conditions of Employment Act (Act 75 of 1997)/BCEA ✓ (1)
3.3.2 TWO problems experienced by farm workers
- Long working hours ✓
- HIV/AIDS infections ✓ (2)
3.3.3 TWO ways to address the impact of HIV/AIDS infections on farms
- HIV/AIDS awareness campaigns/education/workshops ✓
- Provisions of condoms ✓
- Nutritional schemes ✓
- Provision of ARV's ✓
- Avoid multiple partners ✓
- Support groups ✓
- Treatment of STI’s ✓
(Any 2) (2)
3.3.4 TWO types of temporary farm workers
- Casual worker ✓
- Seasonal worker ✓ (2)
3.4 Income and expense record of a farm
3.4.1 Calculation of the profit or loss of the cattle enterprise
- Profit/loss = total income – total expenditure ✓
- = R455 000 – R13 041 ✓
- Profit = R441 959 ✓ (3)
3.4.2 Comparing the profit of the tomato and maize enterprises
- The profit of tomatoes is higher ✓ than that of maize ✓
- The profit of maize is lower ✓ than that of tomatoes ✓
(Any 1) (2)
3.4.3 TWO overhead expense items
- Fuel ✓
- Truck licence ✓ (2)
3.5 Capital
3.5.1 Indication of the types of capital
- Fixed ✓
- Movable ✓
- Floating/working/production ✓
(Any 2) (2)
3.5.2 Total value of the assets
- R20 300 000 ✓ (1)
3.5.3 Deduction of the type of credit obtained by the farmer
- Medium term credit ✓ (1)
3.5.4 Justification of the answer
- It is used to purchase movable capital/truck ✓ (1)
3.5.5 Capital item regarded as a liability
- Truck ✓ (1)
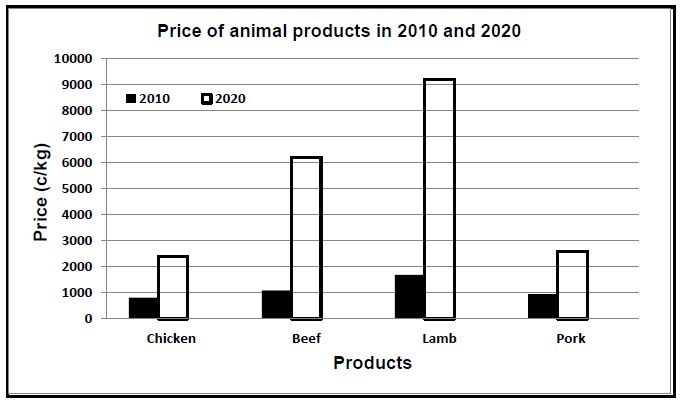
3.6 Graph
- Bar graph showing the prices of animal products in 2010 and 2020
CRITERIA/RUBRIC/MARKING GUIDELINES
- Correct heading ✓
- X-axis: Correctly calibrated with label (Products) ✓
- Y axis: Correctly calibrated with label (Price) ✓
- Correct units (c/kg) ✓
- Bar graph ✓
- Accuracy ✓ (6)
3.7 Differentiation between the internal and external forces
Internal forces - Those that have their origin on the farm and can be dealt
with on the farm ✓ (1)
External forces - Those factors the farmer has no control over ✓ (1)
3.8 Definition of risk sharing as a strategy of management
The strategy in which the cost of consequences of a risk ✓ is distributed amongst several stakeholders ✓ (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
4.1 Variation
4.1.1 Identification of the number of cows with the highest milk yield
6 ✓ (1)
4.1.2 Identification of the factor leading to the differences in milk yield
Feeding/Nutrition ✓ (1)
4.1.3 Indication of the cause of the differences in milk production
Environmental ✓ (1)
4.1.4 TWO genetic causes of variation
- Meiosis/crossing over/recombination of genes ✓
- Fertilisation ✓
- Mutation ✓
(Any 2) (2)
4.2 Crossing of white rose with a red rose to produce pink flowers
4.2.1 Determination of the type of dominance
Incomplete dominance ✓ (1)
4.2.2 Punnett square determining the genotypes/phenotypes of the F2
| Gametes | R | W |
| R | RR | RW |
| W | RW | WW |
MARKING CRITERIA
- Correct gametes for parent 1 ✓
- Correct gametes for parent 2 ✓
- Correct offspring ✓
- Punnett square with gametes and offspring ✓ (4)
4.2.3
- Phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation
1 red : 2 pink : 1 white ✓ (1) - Calculation of the pink offspring
2 x 700 ✓
4
= 350 ✓ (2) - The percentage of red offspring - 25% ✓
(1)
4.3 Breeding systems
4.3.1 Identification of the animal breeding system
Cross breeding ✓ (1)
4.3.2 Reason for the answer
Two different breeds are crossed/Hereford and Nguni ✓ (1)
4.3.3 TWO characteristics of the offspring that makes it better
- Higher growth rate ✓
- More resistant to pests/parasites/diseases ✓ (2)
4.3.4 TWO advantages of inbreeding
- Uniform/homozygous offspring are produced ✓
- Farmer obtain pure-bred groups ✓
- Good characteristics from the ancestors are maintained ✓
- Bad recessive genes can be eliminated ✓
- Help with selection between family groups ✓
- Herd has greater prepotency ✓
(Any 2) (2)
4.4 Pedigree
4.4.1 Determination of homozygous or heterozygous
- 4 - Homozygous ✓ (1)
- 5 - Heterozygous ✓ (1)
4.4.2 Reason for the answer
The offspring has the recessive allele from the male parent/offspring 7 is homozygous recessive because it received one of its recessive allele from parent 5 ✓ (1)
4.4.3 Indicate the genotype of individual:
- 2 - Rr ✓ (1)
- 7 - rr ✓ (1)
4.5 Mutations
4.5.1 Definition of mutation
Is a sudden change ✓ in the genetic composition of an organism ✓ (2)
4.5.2 TWO types of mutagenic agents
- Physical ✓
- Chemical ✓
- Biological ✓
(Any 2) (2)
4.6 Genetic modification technique in plants
4.6.1 Identification of the genetic modification technique
Agrobacterium tumefaciens/bacterial carriers ✓ (1)
4.6.2 Labelling structures
A - Recombinant plasmid ✓ (1)
D - Transgenic plant/Genetically modified plant/GMO ✓ (1)
4.6.3 Definition of genetically modified plant
A plant whose DNA has been manipulated through technology ✓ to change its original DNA ✓ (2)
4.6.4 ONE advantage of genetic modification
It is faster ✓
More precise ✓
Not limited to organisms of the same species ✓
(Any 1) (1)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150