PHYSICAL SCIENCES CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2016
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupPhysical Sciences (Chemistry)
Paper Two (P2)
Grade 12
Amended Senior Certificate Exam
Past Papers And Memos 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your centre number and examination number in the appropriate spaces on the ANSWER BOOK.
- This question paper consists of TEN questions. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two subquestions, for example between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your final numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places. 11. Give brief motivations, discussions, et cetera where required.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Four options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Each question has only ONE correct answer. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1–1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 E.
1.1 A compound with the general formula CnH2n+2 is an ...
- alkane.
- alkene.
- alkyne.
- alcohol. (2)
1.2 Which ONE of the following is a product in ALL neutralisation reactions?
- H+
- H2O
- OH−
- NaCℓ (2)
1.3 Which ONE of the following pairs of products is formed during the catalytic oxidation of ammonia?
- NO2 and H2O
- NO and H2O
- NO and NO2
- H2O and HNO3 (2)
1.4 Consider the following potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction: 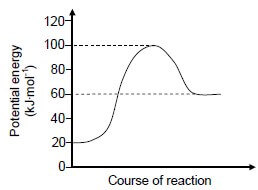
Which ONE of the following shows the values of the total energy change and the activation energy for this reaction? (2)
Energy change (kJ∙mol-1) | Activation energy (kJ∙mol-1) | |
A | 80 | 40 |
B | 60 | 100 |
C | 40 | 80 |
D | – 40 | 80 |
1.5 Which ONE of the following is a functional isomer of butanoic acid? (2) 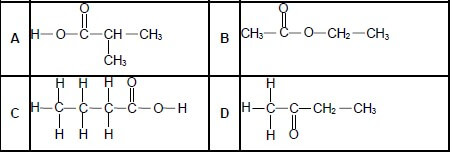
1.6 In the flow diagram below P and Q represent two organic compounds. ![]()
Compound Q is:
- CH2CH2
- CH3CH3
- CH3CH2Br
- CH3CH2OH (2)
1.7 Chromate ions and dichromate ions are in equilibrium with each other in an aqueous solution according to the following balanced equation:
2CrO2-4 (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + ⇌ Cr2O2-7 (aq) + H2O (ℓ)
yellow orange
Which ONE of the following reagents should be added to change the colour of the solution to yellow?
- HNO3
- HCℓ
- NaOH
- CH3COOH (2)
1.8 Which ONE of the following is a NON-SPONTANEOUS redox reaction? Refer to the Table of Standard Reduction Potentials (Table 4A or 4B).
- Zn(s) + 2HCℓ(aq) → ZnCℓ2(aq) + H2(g)
- Cu(s) + FeCℓ2(aq) → CuCℓ2(aq) + Fe(s)
- 2AgNO3(aq) + Cu(s) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
- 2Aℓ(s) + 3Ni(NO3)2(aq) → 2Aℓ(NO3)3(aq) + 3Ni(s) (2)
1.9 In the electrochemical cell below the letters X and Y represent two metal electrodes. 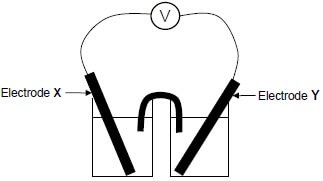
When the cell is functioning, ELECTRODE X GAINS MASS.
Which ONE of the following is the CORRECT cell notation for this cell?
- Y(s) | Y2+(aq) || X+(aq) | X(s)
- X(s) | X+(aq) || Y2+(aq) | Y(s)
- X+(aq) | X(s) || Y(s) | Y2+(aq)
- Y2+(aq) | Y(s) || X(s) | X+(aq) (2)
1.10 Graph Q (the solid line) below was obtained for the reaction of 100 cm3 of a 0,1 mol∙dm-3 HCℓ solution with excess magnesium powder.
Which graph (A, B, C or D) most probably represents the reaction of 100 cm3 of a 0,1 mol∙dm-3 CH3COOH solution with excess magnesium powder? (2)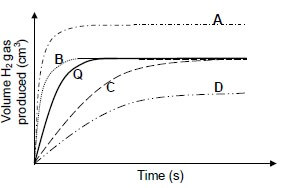
[20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a new page.)
Consider the organic compounds A to F below. 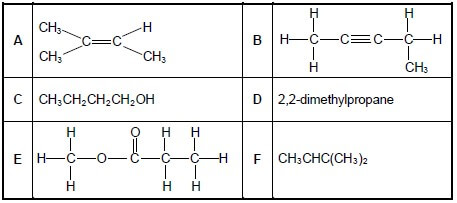
2.1 Write down the LETTER that represents a compound that:
2.1.1 Has a carbonyl group (1)
2.1.2 Is an alcohol (1)
2.1.3 Is a CHAIN ISOMER of CH3(CH2)3CH3 (1)
2.2 Write down the:
2.2.1 IUPAC name of compound B (2)
2.2.2 Structural formula of compound F (2)
2.2.3 IUPAC name of a POSITIONAL isomer of compound A (3)
2.3 Compound E is formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with another organic compound.
Write down the:
2.3.1 Homologous series to which compound E belongs (1)
2.3.2 NAME or FORMULA of the catalyst used for the preparation of compound E (1)
2.3.3 IUPAC name of compound E (2)
[14]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a new page.)
The relationship between boiling point and the number of carbon atoms in straight chain molecules of alkanes, carboxylic acids and alcohols is investigated. Curves P, Q and R are obtained.
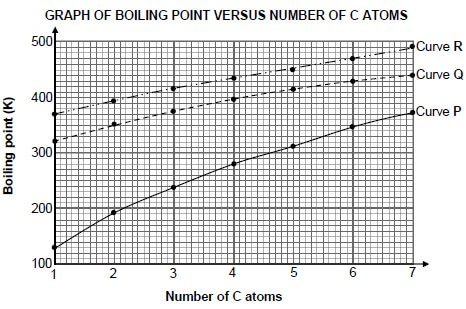 3.1 Define the term boiling point. (2)
3.1 Define the term boiling point. (2)
3.2 For curve P, write down a conclusion that can be drawn from the above results. (2)
3.3 Identify the curve (P, Q or R) that represents each of the following:
3.3.1 Alkanes (1)
3.3.2 Carboxylic acids (1)
3.4 Explain the answer to QUESTION 3.3.2 by referring to the:
- Types of intermolecular forces present in alkanes, carboxylic acids and alcohols
- Relative strengths of these intermolecular forces
- Energy needed (5)
[11]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a new page.)
The flow diagram below shows how prop-1-ene can be used to prepare other organic compounds.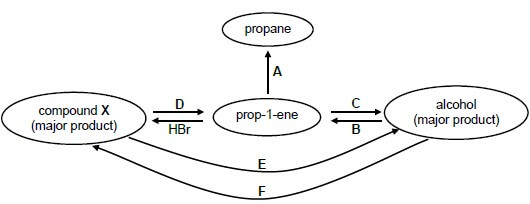 4.1 Write down the type of reaction represented by:
4.1 Write down the type of reaction represented by:
4.1.1 A (1)
4.1.2 D (1)
4.1.3 F (1)
4.2 Write down the:
4.2.1 NAME or FORMULA of the catalyst needed for reaction A (1)
4.2.2 NAME or FORMULA of the inorganic reagent needed for reaction B (1)
4.2.3 Type of addition reaction represented by reaction C (1)
4.2.4 IUPAC name of compound X (2)
4.3 Use structural formulae to write down a balanced equation for reaction B. (5)
4.4 Both reactions D and E take place in the presence of a strong base. State TWO conditions that will favour reaction D over reaction E. (2)
[15]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a new page.)
The reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3) is used to investigate one of the factors that influences reaction rate. The balanced equation for the reaction is:
Na2S2O3(aq) + 2HCℓ(aq) → 2NaCℓ(aq) + S(s) + H2O(ℓ) + SO2(g)
The hydrochloric acid solution is added to the sodium thiosulphate solution in a flask. The flask is placed over a cross drawn on a sheet of white paper, as shown in the diagram below. The time that it takes for the cross to become invisible is measured to determine the reaction rate. 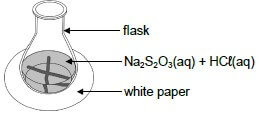 Four experiments, A to D, are conducted during this investigation. The volumes of reactants used in each of the four experiments and the times of the reactions are summarised in the table below.
Four experiments, A to D, are conducted during this investigation. The volumes of reactants used in each of the four experiments and the times of the reactions are summarised in the table below.
Experiment | Volume of Na2S2O3(aq) (cm3) | Volume of H2O(ℓ) (cm3) | Volume of HCℓ(aq) (cm3) | Time (s) |
A | 25 | 0 | 5 | 50,0 |
B | 20 | 5 | 5 | 62,5 |
C | 15 | 10 | 5 | 83,3 |
D | 10 | 15 | 5 | 125,0 |
5.1 State TWO factors that can influence the rate of the reaction above. (2)
5.2 Write down the NAME or FORMULA of the product that causes the cross to become invisible. (1)
5.3 Give a reason why water is added to the reaction mixture in experiments B to D. (1)
5.4 Write down an investigative question for this investigation. (2)
5.5 In which experiment (A, B, C or D) is the reaction rate the highest? (1)
5.6 Use the collision theory to explain the difference in reaction rate between experiments B and D. (3)
5.7 The original Na2S2O3 solution was prepared by dissolving 62,50 g Na2S2O3 crystals in distilled water in a 250 cm3 volumetric flask.
Calculate the mass of sulphur, S, that will form in experiment D if Na2S2O3 is the limiting reactant. (7)
[17]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a new page.)
Carbon dioxide reacts with carbon in a closed system to produce carbon monoxide, CO(g), according to the following balanced equation:
CO2(g) + C(s) ⇌ 2CO(g) ΔH > 0
6.1 What does the double arrow indicate in the equation above? (1)
6.2 Is the above reaction an EXOTHERMIC reaction or an ENDOTHERMIC reaction? Give a reason for the answer. (2)
Initially an unknown amount of carbon dioxide is exposed to hot carbon at 800 °C in a sealed 2 dm3 container. The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the reaction at this temperature is 14.
At equilibrium it is found that 168,00 g carbon monoxide is present.
6.3 How will the equilibrium concentration of the product compare to that of the reactants? Choose from LARGER THAN, SMALLER THAN or EQUAL TO.
Give a reason for the answer. (No calculation is required.) (2)
6.4 Calculate the initial amount (in moles) of CO2(g) present. (9)
6.5 State how EACH of the following will affect the yield of CO(g) at equilibrium. Choose from INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME.
6.5.1 More carbon is added at constant temperature. (1)
6.5.2 The pressure is increased. (1)
6.5.3 The temperature is increased. (1)
[17]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a new page.)
7.1 Hydrogen carbonate ions react with water according to the following balanced equation:
HCO-3 (aq) + H2O(ℓ) ⇌ H2CO3(aq) + OH −(aq)
7.1.1 Define an acid according to the Lowry-Brønsted theory. (2)
7.1.2 Write down the FORMULAE of the two acids in the equation above. (2)
7.1.3 Write down the formula of a substance in the reaction above that can act as an ampholyte. (1)
7.2 During an experiment 0,50 dm3 of a 0,10 mol∙dm-3 HCℓ solution is added to 0,80 dm3 of a NaHCO3 solution of concentration 0,25 mol∙dm-3. The balanced equation for the reaction is:
NaHCO3(aq) + HCℓ(aq) → NaCℓ(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(ℓ)
Calculate the:
7.2.1 Concentration of the hydroxide ions in the solution on completion of the reaction (8)
7.2.2 pH of the solution on completion of the reaction (4)
[17]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a new page.)
Magnesium (Mg) reacts with a dilute hydrochloric acid solution, HCℓ(aq), according to the following balanced equation:
Mg(s) + 2HCℓ(aq) → MgCℓ2(aq) + H2(g)
8.1 Give a reason why the reaction above is a redox reaction. (1)
8.2 Write down the FORMULA of the oxidising agent in the reaction above. (1)
It is found that silver does not react with the hydrochloric acid solution.
8.3 Refer to the relative strengths of reducing agents to explain this observation. (3)
The reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric acid is used in an electrochemical cell, as shown in the diagram below. The cell functions under standard conditions. 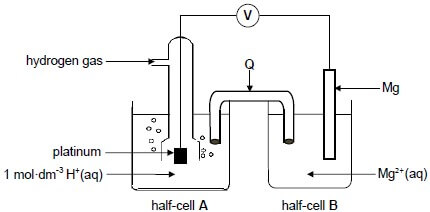
8.4 What is the function of platinum in the cell above? (1)
8.5 Write down the:
8.5.1 Energy conversion that takes place in this cell (1)
8.5.2 Function of Q (1)
8.5.3 Half-reaction that takes place at the cathode (2)
8.5.4 Cell notation of this cell (3)
8.6 Calculate the initial emf of this cell. (4)
8.7 How will the addition of concentrated acid to half-cell A influence the answer to QUESTION 8.6? Choose from INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME. (1)
[18]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a new page.)
The diagram below shows an electrochemical cell used to purify copper. A solution that conducts electricity is used in the cell. 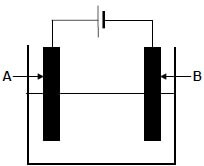
9.1 Write down:
9.1.1 ONE word for the underlined phrase above the diagram (1)
9.1.2 The type of electrochemical cell illustrated above (1)
9.2 In which direction (from A to B or from B to A) will electrons flow in the external circuit? (1)
9.3 Which electrode (A or B) is the:
9.3.1 Cathode (1)
9.3.2 Impure copper (1)
9.4 How will the mass of electrode A change as the reaction proceeds? Choose from INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME.
Give a reason for the answer. (2)
[7]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a new page.)
A chemical company produces ammonium sulphate, (NH4)2SO4, starting from the raw materials P, Q and R, as shown in the flow diagram below. 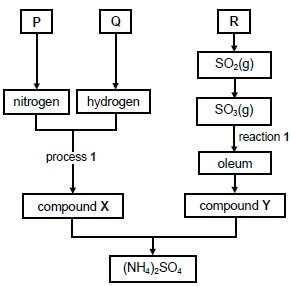
10.1 Write down the NAME of raw material:
10.1.1 P (1)
10.1.2 Q (1)
10.1.3 R (1)
10.2 Write down the:
10.2.1 NAME of process 1 (1)
10.2.2 NAME of compound X (1)
10.2.3 FORMULA of compound Y (1)
10.2.4 Balanced equation for reaction 1 (3)
10.3 The company compares the nitrogen content of ammonium sulphate with that of ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3.
10.3.1 Determine, by performing the necessary calculations, which ONE of the two fertilisers has the higher percentage of nitrogen per mass. (4)
10.3.2 Write down the name of the process that should be included in the flow diagram above if the company wants to prepare ammonium nitrate instead of ammonium sulphate. (1)
[14]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12
PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Standard pressure | pθ | 1,013 x 105 Pa |
Molar gas volume at STP | Vm | 22,4 dm3∙mol-1 |
Standard temperature | Tθ | 273 K |
Charge on electron | e | -1,6 x 10-19 C |
Avogadro's constant | NA | 6,02 x 1023 mol-1 |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE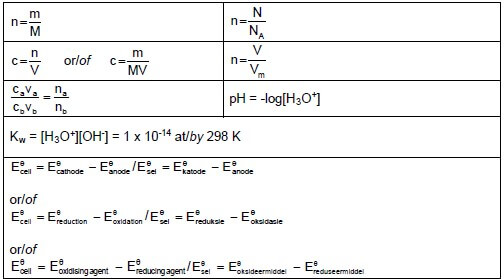
TABLE 3: THE PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS 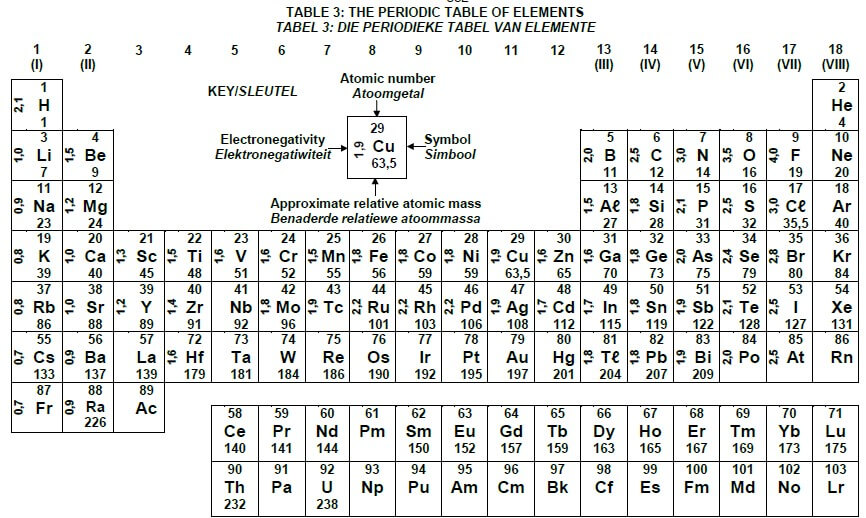
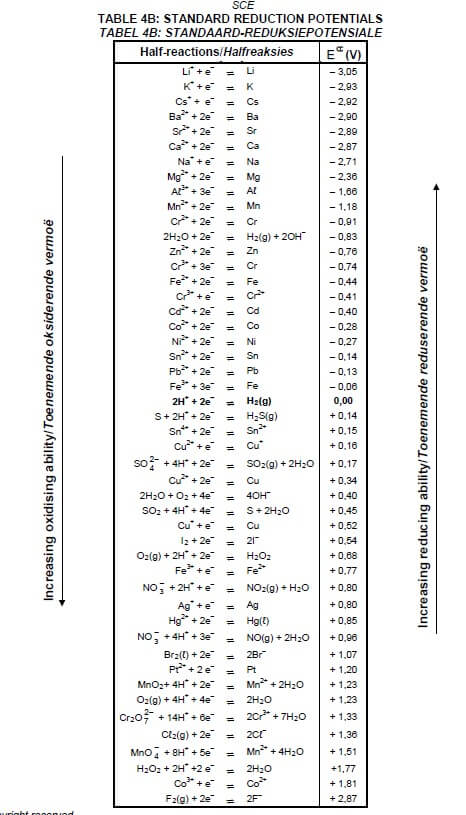
TABLE 4A: STANDARD REDUCTION POTENTIALS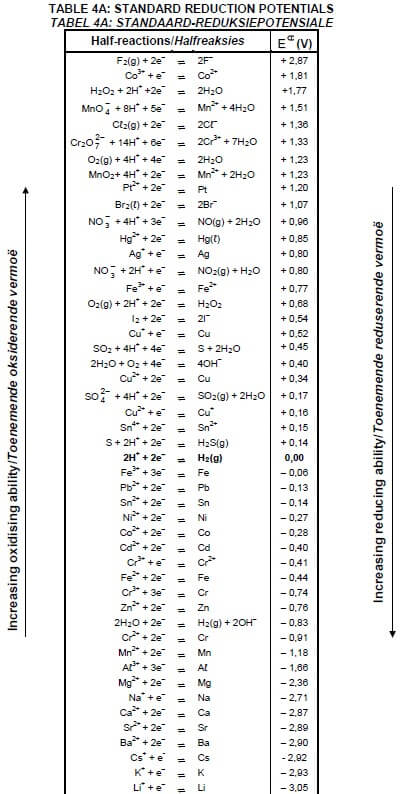
TABLE 4B: STANDARD REDUCTION POTENTIALS