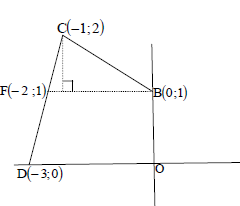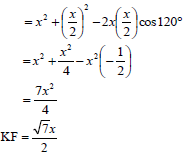MATHEMATICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2019
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMATHEMATICS PAPER 2
NOVEMBER 2019
MARKING GUIDELINES
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
NOTE:
- If a candidate answers a question TWICE, only mark the FIRST attempt.
- If a candidate has crossed out an attempt of a question and not redone the question, mark the crossed out version.
- Consistent accuracy applies in ALL aspects of the marking memorandum. Stop marking at the second calculation error.
- Assuming answers/values in order to solve a problem is NOT acceptable.
| GEOMETRY | |
| S | A mark for a correct statement (A statement mark is independent of a reason) |
| R | A mark for the correct reason (A reason mark may only be awarded if the statement is correct) |
| S/R | Award a mark if statement AND reason are both correct |
QUESTION 1
Monthly income (in rands) | 9 000 | 13 500 | 15 000 | 16 500 | 17 000 | 20 000 |
Monthly repayment (in rands) | 2 000 | 3 000 | 3 500 | 5 200 | 5 500 | 6 000 |
1.1 | a = -1946,875... = -1946,88 | a = -1946,88 b = 0,41 equation (3) |
1.2 | Monthly repayment ≈ R3 727,16 (calculator) OR y = -1946,88 + 0,41(14000) | answer (2) substitution answer |
1.3 | r = 0,946 …. ≈ 0,95 | ? answer (1) |
1.4 | Not to spend R9 000 per month because the point (18 000 ; 9 000) | ?? answer |
[8] | ||
QUESTION 2
2.1 | Number people paid R200 or less = 19 | ? answer (1) | |
2.2 | 7 +12 + a + 35 + b + 6 = 100 OR 7 +12 + a + 35 + b + 6 = 100 309 = (50 x 7) + (150 x 12) + (250 x a) + (350 x 35) + (450 x b) + (550 x 6) | ? ∑x = 100 ? a = 40 - b ? ∑ fX ? ∑ fX = 309
? ∑x = 100 ? a = 40 - a ? ∑ fX ? ∑ fX = 309 (5) | |
2.3 | Modal class: 300 < x ≤ 400 | ? answer (1) | |
| 2.4 | 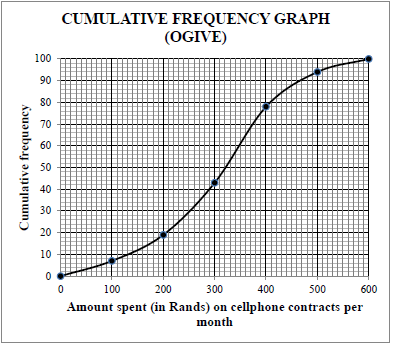 | ? grounded at (0 ; 0) | |
| 2.5 | Number of people = 100 – 82 [accept 80 – 84 people] 18 people paid more than R420 per month/. [accept 16 – 20 people] | 82 answer (2) | |
| [13] | |||
QUESTION 3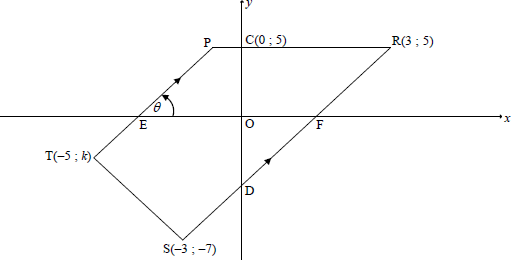
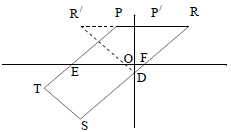
3.1 | Equation of PR: y = 5 | ? answer (1) |
3.2.1 | mRS = y2 - y1 | ? substitution of R & S into gradient formula ? answer |
3.2.2 | mRS = mPT [PT || RS] | ? mRS = mPT |
3.2.3 | Equation of RS: y - 5 = 2(x - 3) or y - (-7) = 2(x - (-3)) or 5 = 2(3) + c OR | ? substitution ? equation of RS ? coordinates of D ? equating gradients ? value of y ? coordinates of D (3) |
| 3.3 | ST = 2√5 = √[-5 - (-3)]2 + (k - (-7))2 OR ST = 2√5 =√[-5 - (-3)]2 + (k - (-7))2 | ? substitute S and T into distance formula ? isolate square ? square root both sides ? answer ? substitute S and T into distance formula ? standard form ? factors ? answer |
| 3.4 | Method: translation OR Midpoint of TN = Midpoint of SD | ? method ? x-coordinate ? y-coordinate (3) ? method: midpoint of diagonals ? x-coordinate ? y-coordinate (3) |
| 3.5 |
OR OR OR 62 = 45 + 45 - 2(45)(cos RDˆ R/ ) | ? b = 63,43° ? ODˆ F = 26,57° ? answer (3) ? Rˆ = 63,43° ? RR/D = 63,43° ? answer (3) ? trig ratio ? ODF = 26,565..° ? answer (3) ? R/ (-3; 5) OR RD = 45 = R//D ? substitution into cosine rule ? answer (3) |
| [19] |
QUESTION 4 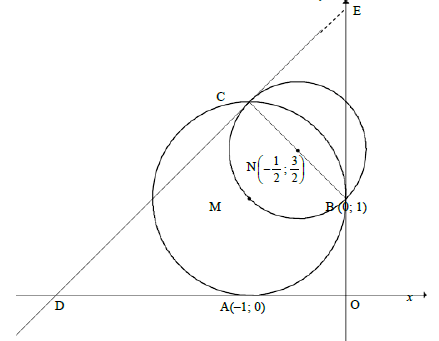
4.1 | M(-1;1) | ? M(-1;1) ?LHS ? RHS (3) |
4.2 | Midpoint of CB, N: (– 0,5 ; 1,5) OR B→N: | ?x value ? y value (2)
?x value ? y value (2) |
| 4.3 | mtangent = 1 OR mradius = 2 -1 | ? mradius ? mtangent ? substitute (– 1 ; 2) and m ? simplification (4) ? mradius ? mtangent ? substitute (– 1 ; 2) and m ? simplification (4) |
| 4.4 | Tangents to circle: y = x + 3 and y = x +1 | ? y = x +1 |
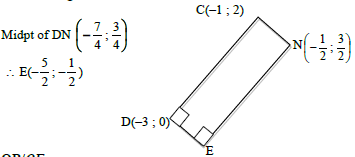
| 4.5 | Draw rectangle CNED: OR | ? midpt of DN ?x value ? y value ? coordinates of D ?x value ? y value (3) |
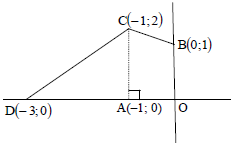
| 4.6 |
area of DACD = ½(2)(2) area of quadrilateral OBCD = 3½ square units OR BM produced cuts the tangent at F. area of ΔCFB = ½ (2)(1) 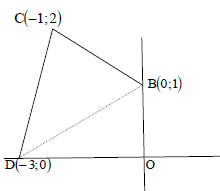 Join DB OR Let E be the point of intersection of DC with the positive y–axis. | ? substitution into area of trapezium form ? area of trapezium ? area of triangle ? area of OBCD ? equating area OBCD to 2a2 (5) ? area of triangle ? substitution into area of trapezium ? area of trapezium ? area of OBCD ? equating area OBCD to 2a2 (5) ? area of Δ ? subst into area of Δ ? area of Δ ? area of OBCD ? equating area OBCD to 2a2 (5) ? area of Δ ? subst into area of Δ ? area of Δ ?area of OBCD ? equating area OBCD to 2a2 (5) |
| [20] |
QUESTION 5
5.1 | sin x + sin(180° + x) cos(90° - x) | ? –sin x ? sin x | |
5.2 | sin 2 35° -cos 2 35° | ? - (cos2 35° - sin2 35° ) ?– cos 70° ? 2sin 20° ? answer (4) | |
5.3 | 2sin 2 77° = 2[sin(90° -13°)]2 OR 1- 2sin 2 77° = cos154° | ? using co-ratio ? 1- 2sin 2 77° = cos154° (4) | |
5.4.1 | sin(x + 25°) cos15° - cos(x + 25°)sin15° = tan165° OR sin(x + 25°)sin 75° - cos(x + 25°) cos 75° = tan165° | ??sin(x +10°) ? - 0,2679... ?? cos(x + 100°) (6) | |
| 5.4.2 | f (x) = sin(x +10°) Answers only: Full marks | ? f (x) = sin(x +10°) | |
| [22] | |||
QUESTION 6 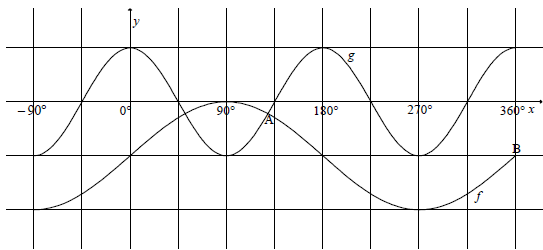
6.1 | Range of f: y ∈[- 2 ;0] OR - 2≤ y ≤ 0 | ? critical values | |
6.2 | x∈(90° ; 270°) OR x∈[90° ; 270°] | ? critical values | |
6.3 | PQ= cos 2x -(sin x -1) | ? PQ= cos 2x -(sin x -1) (6) | |
| [10] | |||
QUESTION 7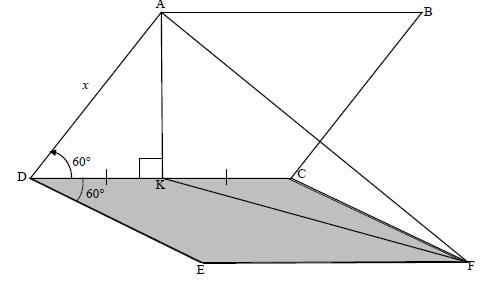
7.1 | sin 60° = AK | ? trig ratio |
7.2 | KCF= 120° | ? answer (1) |
7.3 | KF2 = CF2 + CK2 - 2CF.CKcos KCF | ? correct use of cosine rule |
[10] | ||
QUESTION 8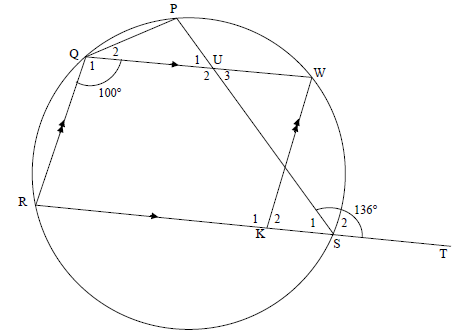
8.1.1 | Rˆ = 80° | S R (2) |
8.1.2 | Pˆ = 100° [opp ∠s of cyclic quad] | S R (2) |
8.1.3 | PQR = 136° [ext ∠ of cyclic quad] OR U3 = 180° -136° = 44° [co-int∠s; QW || RK] | S R S R S R |
| 8.1.4 | U2 = S2 = 136° [alt ∠s; QW || RK] OR OR | S R S R S R S R |
8.2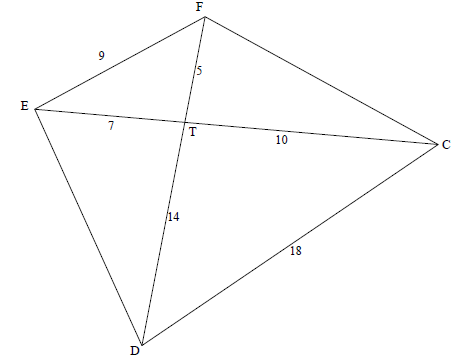
8.2.1 | In ΔEFT and DDCT: OR | all 3 ratios = ½ ∆EFT ||| ∆DCT F = 50,7° C = 50,7° |
| 8.2.2 | EFD = ECD [proved in 8.2.1] | S R |
| [16] |
QUESTION 9 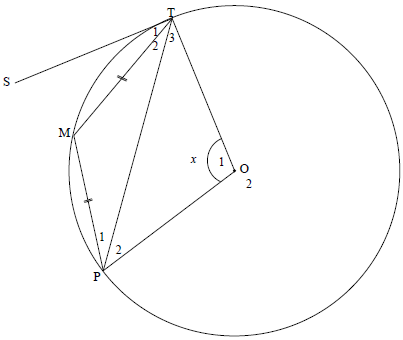
O2 =360° - x [∠s round a pt] OR | O2 =360° - x T2 + P1 = ½x O2 =360° - x |
| [7] |
QUESTION 10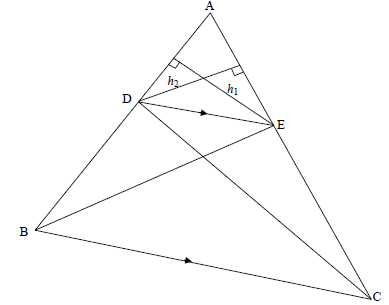
10.1 | Constr: Draw h1 from E⊥AD and h2 from D ⊥ AE area ΔADE =½ AE x h2 = AE But areaΔBDE = area ΔDEC [same base & height or DE || BC] area ΔADE = area ΔADE | ? constr OR area ΔADE =½ ADxh1= AD area ΔADE = AE ? S ?R |
10.2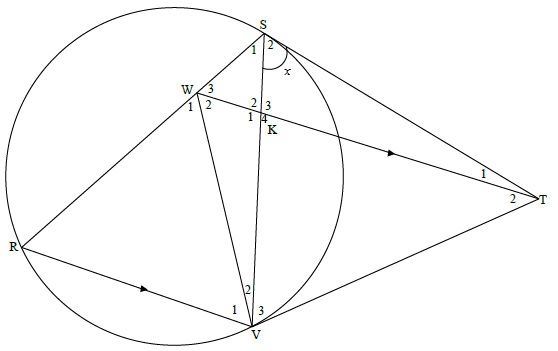
10.2.1 | V3 = x [Tans from same point] | ? S ? R |
10.2.2(a) | V3 = W3 = x [proved in 10.2.1] | ? S |
10.2.2(b) | W2 = S2 = x [∠s in the same segment] OR S2 =W2 = x [ ∠s in the same segment ] | S ?R S ?R
|
| 10.2.2(c) | In ∆WRV and ∆TSV OR | S S R (3) S S S (3) |
| 10.2.2(d) | RV = WR [ DWRV ||| DTSV] WR = KV [prop theorem; WT || RV] WR x SV = KV x SR RV x TS = KV x SR OR In ∆RVS and ∆VKT but VT = ST [tans from same point] | correct ratios WR = KV R equating WR x SV (4) identifying correct ∆s proving ||| correct ratio S (4) |
| [25] |
TOTAL: 150