ECONOMICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2019
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupECONOMICS PAPER 2
GRADE 12
MARKING GUIDELINES
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
NOVEMBER 2019
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 D - can easily enter and exit the market✓✓
1.1.2 A - external benefit ✓✓
1.1.3 C - positively ✓✓
1.1.4 A - price ✓✓
1.1.5 B - high unemployment✓✓
1.1.6 B - Stockholm Protocol ✓✓
1.1.7 C - Cape Fynbos Region ✓✓
1.1.8 D - conservation ✓✓ (8 x 2)
(16)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 D - actual expenditure of a business on the purchase or hire of inputs required for the production process ✓
1.2.2 I - removal of unnecessary laws and regulations to improve efficiency ✓
1.2.3 F - group of producers that operates similarly to a collective monopoly ✓
1.2.4 B - set below market equilibrium to make goods more affordable ✓
1.2.5 H - measured where imported goods enter the country and manufactured goods leave the factory ✓
1.2.6 A - sustaining development in ways that protect the environment ✓
1.2.7 C - continuous decrease in the general price level over a period of time✓
1.2.8 E - people travelling from their own countries to visit other countries ✓(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 GIVE THE TERM
1.3.1 Break-even point/normal profit ✓
1.3.2 Monopolistic competition ✓
1.3.3 Short run/short term ✓
1.3.4 Tourism/tourists ✓
1.3.5 All-inclusive ✓
1.3.6 Marketable permit ✓(6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer TWO of the three questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Give any TWO examples of fixed cost.
- insurance ✓
- rent / lease contracts / property taxes ✓
- depreciation ✓
- salaries ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why are businesses under the perfect market structure price takers?
Due the large number of businesses the market determines the price / individual suppliers are too small to influence the market price ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 DATA RESPONSE
2.2.1 Give an example of a negative externality.
Pollution / substance abuse / traffic congestion ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1)
2.2.2 Name the shaded area (A) in the graph above.
Welfare loss / deadweight / external cost / negative externality ✓ (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term social cost.
Social cost is the cost to society which includes private cost and external cost / Combined costs of goods or services to producers and consumers and society as a whole ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.4 Explain a lack of information to entrepreneurs as a cause of market failure.
A lack of information on costs, availability and productivity of factors of production will reduce its effectiveness in production / incomplete or inaccurate information leads to incorrect decision-making about what, for whom and how to produce, so resources are wasted ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.5 Why is the socially optimal output more beneficial to society?
- At the socially optimal output companies would pay for the external cost (externality) which would benefit society ✓✓
- Firms would reduce the production that will lower the impact of the negative externality on society which is more beneficial ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
2.3 DATA RESPONSE
2.3.1 Name the Act that gives all South Africans an equal opportunity to participate fairly in economic activities.
Competition Act of 1998 ✓ (1)
2.3.2 Which institution accepts or rejects recommendations from the Competition Commission?
Competition Tribunal ✓(1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the role of the Competition Appeal Court.
To rule on cases in which businesses appeal the rulings made by the Competition Tribunal / review, amend or confirm orders made by the Competition Tribunal✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.4 How can small, medium and microenterprises contribute to the goals of the competition policy?
- They provide more competition which will prevent monopolies from abusing their power / Prevent some firms from using restrictive practices like price fixing ✓✓
- SMMEs are an indication that all South African businesses, small and big are provided with equal opportunities to participate in the economy✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.5 If the merger were allowed, how would it benefit the companies involved?
- By merging, the company would have different services available to cater for consumer demand ✓✓
- FlySafair will have access to more routes which can improve their profit ✓✓
- Production processes would be economically used lowering the operation cost / Using fewer personnel and maintenance cost will come down / Eliminate the duplication of management personnel ✓✓
- Risks and responsibilities will be shared because they access to more capital ✓✓
- Due to the advantage of combined resources, the new company can afford to undertake product innovation ✓✓
- Increased revenue and profit can be earned as a result of larger market share (or reduction in competitors) ✓✓
- Economies of scale can be achieved as the new firm can be able to negotiate larger discounts due to its increased size of production ✓✓
- Business will have an already established customer base ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Briefly discuss productive inefficiency and allocative inefficiency in terms of market failure.
PRODUCTIVE INEFFICIENCY:
- When businesses do not maximise outputs from given inputs ✓✓
- A business does not produce goods at the lowest possible cost✓✓
- There is room to reduce costs without producing fewer goods or without producing a lower quality good ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 4)
ALLOCATIVE INEFFICIENCY:
- The product mix does not reflect consumers' tastes ✓✓
- Businesses are allocated resources inefficiently and produce goods and services that consumers do not want ✓✓
- The quantities required by the consumers are not available ✓✓(Max 4)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 4)
(A maximum of 4 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
2.5 Evaluate the impact of imperfect competition on consumers.
Negative impact
- Most businesses operating in imperfect markets maximise profits by supplying less than the optimal quantity of goods or services produced which means that some consumers needs may not be met ✓✓
- Reduced quantities lead to higher prices which may exclude lower income groups ✓✓
- New businesses are sometimes prevented from entering the industry, thereby limiting competition, which prevents consumers from enjoying lower prices and a variety of goods ✓✓
- Collusion which is rife in oligopoly markets results in higher prices which at times prevent some consumers to afford the product✓✓
- Consumers pay higher prices in the imperfect markets due to the fact that production does not take place at the lowest point of the LAC-curve ✓✓
Positive impact
- Imperfect markets can stabilise supply or output of certain goods and services, that requires a vast amount of input capital, ensuring a variety of goods available to consumers ✓✓
- Imperfect markets can also provide a better quality product to the consumer; large corporations have Research and Development units that constantly develop new technology and improved production methods ✓✓
- Patent rights give the patent holder exclusive rights to produce a product; this stimulate innovations and inventions (new products) that could be beneficial to consumers ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 2 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Give TWO reasons for growth in the tourism industry in South Africa.
- weak exchange rate ✓
- the world in one country ✓
- peaceful transition to democracy ✓
- the pleasant climate ✓
- relaxation of VISA regulations ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 Why is core inflation lower than headline inflation?
Core inflation excludes products with volatile prices while headline inflation includes them ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 DATA RESPONSE
3.2.1 Where did most inbound tourists come from during 2017?
Europe ✓(1)
3.2.2 What was the percentage increase of tourists from the Middle East?
6.2% / 151% ✓ (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term business tourism.
Visiting a place for the purpose to attend meetings and conferences ✓✓
(Accept other correct relevant responses) (2)
3.2.4 Why is job creation easy in the tourism industry?
- It is labour intensive ✓✓
- Employs many skills ✓✓
- Provides immediate employment ✓✓
- Provides entrepreneurial opportunities ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.2.5 What should government do to promote tourism?
Government should:
- drive a strong marketing campaign in foreign countries to sell the beauty and uniqueness of the country ✓✓
- improve the security system of the country to safeguard the stay of tourists✓✓
- provide a market with a diversity of products and leisure ✓✓
- maintain and upgrade infrastructure✓✓ for example tarred roads / accommodation ✓
- improve social infrastructure such as clinics and availability of ambulances ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant responses) (Max 4) (4)
3.3 DATA RESPONSE
3.3.1 Which country has the highest population in the world?
China ✓ (1)
3.3.2 Identify the environmental problem related to removing of trees and plant life.
Deforestation / loss of biodiversity / erosion ✓ (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term biodiversity.
The existence of the generic variety and number of species of animal and plant life in the eco-system ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.4 In what way can the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) address the loss of biodiversity?
CITES issues permits and quotas to regulate trade in certain species ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.5 How can environmental subsidies be used to reduce environmental damage?
The environmental subsidies can be used to reduce environmental damage by:
- developing new techniques or equipment to save energy and reduce smoke ✓✓
- using environmental friendly energy such as wind ✓✓
- encouraging the production of environment-friendly substitutes such as unleaded petrol ✓✓
- encouraging the recycling of waste such as bottles and cans✓✓
- offering subsidies for companies to lower pollution emissions✓✓
- Subsidies to provide individuals to install solar panels to their households to decrease electricity consumption ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant responses) (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Briefly discuss the benefits of tourism for the government and infrastructure.
GOVERNMENT:
- Tourism contributes to the income of the government through taxes such as airport departure taxes ✓✓
- Taxes are charged to recover external costs which is the amount not included in the price ✓✓
- The amount compensates the host community for providing infrastructure and basic amenities ✓✓
- It is an important foreign exchange earner and boosts the country’s foreign exchange reserves ✓✓
- Enables government to achieve its socio-economic objectives of informal sector growth, black economic empowerment and SMME development✓✓
(Max 4)
INFRASTRUCTURE:
- Adequate and well-maintained infrastructure is essential for tourism ✓✓
- The tourists and residents often share the infrastructure ✓✓
- Governments have prioritised maintaining economic infrastructure ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 4)
(A maximum of 4 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples) (8)
3.5 How can countries contribute to reducing ocean (sea) pollution?
Countries could contribute towards solving sea pollution by:
- imposing strong penalties on sea pollution because sea-life is destroyed through human action ✓✓
- being pro-active against apathy in managing economic activities such as oil drilling can result in oil spillages which often harm the water species✓✓
- being involved in the cleaning of increased plastic deposits in the oceans that destroys sea life ✓✓
- educating people on the dangers of the consumption of polluted fish products ✓✓
- monitoring the river-mouths to prevent plastic waste flowing to the sea ✓✓
- educating large shipping companies to use bio-degradable products where possible ✓✓
- following South Africa’s example by being a signatory to sea life and management resources ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 2 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name TWO features of public goods.
- Non-excludable ✓
- Non-rival ✓
- Non-rejectable ✓
- Social benefits outweigh private benefits ✓
- Continuous consumption✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How does inflation affect investors positively?
They are able to build wealth as the value of the fixed assets will rise with or increase more than inflation / higher returns on investments✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 DATA RESPONSE
4.2.1 Where does the marginal cost curve (MC) intersect the average cost curve (AC)?
The MC curve intersects the AC curve at its minimum point / e1 / at price of R7,00 and quantity 500✓ (1)
4.2.2 Identify the price where the individual producer will make an economic profit.
R10 ✓ (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term marginal cost.
Additional cost incurred when one more unit of a product is produced ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.4 Why is the marginal revenue (MR) curve in the perfect market the same as the demand curve?
Each additional unit would be sold at the same price which is the horizontal demand curve ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.5 Explain how long-run equilibrium is achieved in the market.
- Economic profits attract new entrants into the market which will increase the market supply thus lowering its price✓✓
- The individual firm is a price taker and the lower price will wipe out economic profits until the price (average revenue) will be equal to average cost ✓✓
- The long run equilibrium position is where normal profit will prevail ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
4.3 DATA RESPONSE
4.3.1 What type of tourism is depicted in the picture above?
Eco-tourism / leisure and recreational ✓(1)
4.3.2 Which organisation is responsible for marketing tourism in South Africa?
South Africa Tourism / SATOUR ✓ (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term indigenous knowledge systems.
The traditional practices, heritage, cultural ceremonies and way of life that makes a country unique ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.3.4 Why is it necessary to have controlled visits to the various SANParks in South Africa?
Prevent the loss of wildlife species through poaching / to retain its natural beauty / prevents environmental stress for example veld fires / to ensure safety of both the animals and visitors ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant responses) (2)
4.3.5 How can the marketing of World Heritage Sites benefit the local communities?
Local communities could benefit by:
- finding employment in businesses being established in the area✓✓ for example guided tours, curio shops ✓
- improved infrastructure such as roads, electricity and an advanced communication system ✓✓
- becoming part of the informal sector as entrepreneurs selling unique items that showcase their cultures ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant responses) (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 With the aid of a graph, explain the impact of minimum prices on the market.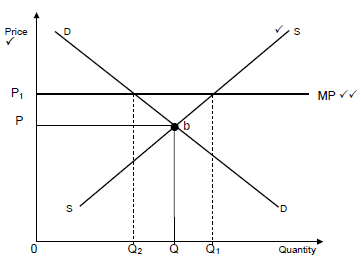
Allocation of marks:
- Correct indication of minimum price = 2 marks
- Correct labelling of axes = 1 mark
- Correct labelling of curves = 1 mark
- A minimum price is set to help producers because the equilibrium price is too low✓✓
- It enables producers to make a comfortable profit ✓✓
- It encourages producers to supply important essential goods ✓✓
- A minimum price will create a surplus in the economy (difference between Q2 and Q1) ✓✓
- A surplus will mean that government will have to buy the surplus and dump it locally or abroad ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant responses) (8)
4.5 How successful has South Africa been in using education to ensure environmental sustainability?
South Africa has been successful because:
- the national education framework integrated environmental themes into school subjects ✓✓
- private–public partnerships between schools and businesses help to empower young people by connecting them with projects related to the environment ✓✓
- the Cape Leopard Trust involve learners of between 10 to 18 years in educational environmental trips ✓✓
- municipalities have policies that makes people aware of the importance of protecting the environment ✓✓ e.g. water conservation✓
- non-profit organisations such as National Recycling Forum promotes recycling and they have been successful for the past seven years to outperform European countries in recycling ✓✓
- environmental advisors have been employed and based at municipal offices ✓✓
South Africa has not been successful because:
- despite the national environmental education policy, environmental problems such as pollution in urban areas keep on increasing ✓✓
- in the rural areas deforestation keep on escalating as people use indigenous trees as firewood✓✓
- land degradation persists especially due to poor farming methods and over-grazing in poor communities ✓✓
- the environmental policies are often not implemented at the municipal level✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant responses)
(A maximum of 2 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
Your answer will be assessed as follows:
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS
- With the aid of graphs, discuss how economic profit and economic loss is determined in a monopoly market. (26 marks)
- Why does the performance of natural monopolies contradict (deny) the long-run equilibrium position of a monopoly? (10 marks)
[40]
INTRODUCTION
A monopoly is a market structure where only one seller operates. Entry is blocked and the product has no close substitutes ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) Max (2)
BODY: MAIN PART
Economic profits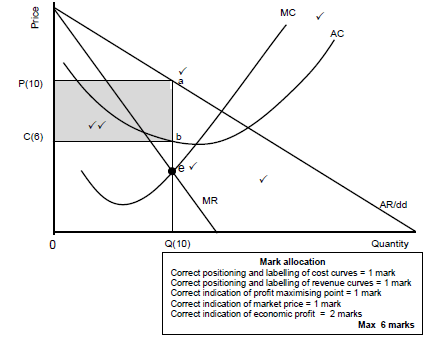
- Monopoly is subject to same technological and cost constraints as other market structures ✓✓
- The cost structure of the monopoly is the same than that of competitive businesses where the monopolist will try to maximize both short and long-term profit ✓✓
- Location of SAC in relation to market price determines profit or loss ✓✓
- The MR curve lies below the AR curve, halfway between the AR and the origin ✓✓
- The MC curve intersects the AC curve at its minimum point ✓✓
- Determine point where SMC = MR – point where production cost of last unit is equal to revenue it earns (point e) – profit-maximising production quantity of Q on horizontal axis ✓✓
- The monopolist will produce at the output (Q[10]) where MR=MC, because it can maximise profit at this level ✓✓
- Point a represents the average revenue at selling price (P[10]) while point b represents the average cost at the cost price (C[6])✓✓
- When the average revenue is more than the average cost, it results in an economic profit for the business / When the TR is more than TC it will result in an economic profit for the business ✓✓
- The monopoly makes economic profit when AC curve is below market price (AR)✓✓
- The monopoly blocks new entries so that competing businesses cannot reduce short run economic profit ✓✓
- Total income = Price x Quantity = OP(10) x OQ(10) = OPaQ (100) ✓✓
Total cost = Cost x Quantity = Oc(6) x OQ(10) = OCbQ (60)
Economics profit = Income – Cost = 10 0 – 60 = CPab (40) ✓✓ (Max 10)
Economic losses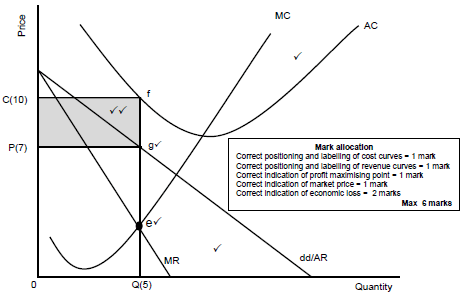
- The minimum point of SAC is higher than market price ✓✓
- A monopoly makes an economic loss when its revenue is less than its costs✓✓
- The monopoly will produce at the output level where MR=MC, because it can minimise losses at this level ✓✓
- Point g represents the average revenue at selling price (P[7]) while point f represents the average cost at the cost price (C[10])✓✓
- The average cost is more than the average revenue, resulting in an economic loss for the business / When the TC is more than TR it will result in an economic loss for the business ✓✓
- The shaded area PCef shows the economic loss ✓✓
- The monopoly suffer an economic loss in the short run when the AC curve is above the market price (g) ✓✓
- Total income = Price x Quantity = OP(7) x OQ(5) = OPgQ (35)
Total cost = Cost x Quantity = OC(10) x OQ(5) = OCfQ (50) ✓✓
Economic loss = (PCfg)15 ✓✓ (Max 10)
(Max 26)
ADDITIONAL PART
Why does the performance of natural monopolies contradict the long-run equilibrium position of a monopoly? (10 marks)
Natural monopolies' performances are not always in line with the long-run equilibrium position of a monopoly because:
- compared to a typical monopoly where economic profit always prevails over the long run, natural monopolies do not enjoy the benefits experienced by other monopolies✓✓
- natural monopolies require high development cost which prevent others from entering the market ✓✓
- natural monopolies supply goods and services to the nation as a whole and therefore it is difficult to set very high prices ✓✓
- Eskom is subjected to the National Energy Regulator in South Africa (NERSA) that determines the selling price of electricity in South Africa✓✓
- a natural monopoly has experienced high maintenance cost compared to artificial monopolies, that compromises profits ✓✓
- natural monopolies cannot manipulate its quantities to increase prices ✓✓
- revenue seems to be less than cost due to corruption, non-payment by a large number of electricity users✓✓
- under normal circumstances, a monopoly will shut down if average cost exceeds average revenue in the long run, but natural monopolies like SAA are often bailed out by the government due to its strategic position in the country ✓✓
- the internal (private cost) structure of natural monopolies have increased, but the private benefits (revenue of sales) stagnated due to poor maintenance of infrastructure✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 10)
CONCLUSION
The monopoly can continue to earn economic profit for as long as the demand for its product continues and its production costs stay the same ✓✓
(Accept any other higher order conclusion) Max (2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
- Examine in detail the causes of cost-push inflation. (26 marks)
- Analyse the negative impact of administered prices on the economy. (10 marks)
[40]
INTRODUCTION
Inflation is a sustained and considerable increase in the general price level over a particular period / Cost-push inflation is the result of an imbalance between supply and demand due to cost factors, usually where an inelastic demand is found✓✓
(Accept any other correct, relevant response) Max (2)
BODY: MAIN PART
Wages
- Wage increases that are higher than productivity cause a cost increase for producers ✓✓
- Single most important cost item in any economy and contributes most to the value added to basic prices ✓✓
- An increase in administered prices may result in trade unions demanding higher wages, because producers may simply add the increase to the price of the final product ✓✓
Strikes and stayaways ✓
- Strikes reduce production output and cause a drop in the supply ✓✓
Taxes ✓
- An increase in direct taxes may lead producers to increase prices to offset their extra tax burden ✓✓
- An increase in indirect taxation such as VAT, customs or excise duty will be added to the final price ✓✓
Key inputs ✓
- When the price of imported key inputs increases, the domestic costs of production increase resulting in imported inflation ✓✓
- Producers recover these costs by increasing the prices of their products ✓✓
- The high cost of inputs in the agricultural sector such as diesel and fertilisers are added to the price of products ✓✓
- Supply-shocks might have a knock-on effect on other products due to higher fuel prices and transport costs ✓✓
Profit margins ✓
- When businesses push up their profit margins / the monopoly-effect, they increase the cost of production and the price that the consumers have to pay, contributing to inflation ✓✓
- This is because manufacturers recover the higher prices they have to pay by increasing their prices ✓✓
- In the US ethanol production was subsidised which caused farmers to switch to corn production for energy. This led to a shortage of food and led to an increase in prices✓✓
Productivity ✓
- If various factors of production become less productive while still receiving the same remuneration, the cost of producing each unit of output increases ✓✓
- A systematic drop in productivity while employment and wages remain constant✓✓
Exchange rate ✓
- If the rand depreciates against the major currencies, imports from such countries will be more expensive ✓✓
- Producers have to pay more money for the same quantity of products than before; as such, they often shift the increase to the consumers ✓✓
Natural disasters ✓
- Disasters, such as floods and droughts, affect the cost of production negatively✓✓
- Food prices is one of the most volatile price items as a result of the effect of weather changes ✓✓
- External shocks like OPEC controlling the world's oil supply/natural disasters leading to low production ✓✓
- Exhaustion of natural resources leads to limited supply which will increase prices for example fish stocks ✓
Theft by employees/Shoplifting ✓
- Many businesses make provision for losses caused by theft by employees and shoplifting, which increases the prices of goods ✓✓
- Cost of installing security measures increases the input costs ✓✓
Interest rates ✓
- An increase in interest rates means businesses will pay more for loans – this increase may also be added to the selling price✓✓
- An increase in international borrowing and national debts affects interest rates that affects prices to rise ✓✓
Low savings levels ✓
- Low savings lead to limited investment which pose a barrier to expand production capacity decreasing the supply of goods ✓✓
(Allocate a maximum of 8 marks for mere listing of facts/examples)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) Max (26)
ADDITIONAL PART
Administered priced goods impact the economy negatively because:
- the government has not been able to keep administered prices within the inflation target range (above 10%) ✓✓
- a significant number of administered priced goods is used in the calculation of the CPI and puts pressure on prices that limits competitiveness✓✓
- sharp increases in the prices of electricity, water tariffs and municipal services has threatened the mining and manufacturing capacity causing foreign investors to withdraw their investments ✓✓
- the government has limited control over fuel price increases which is determined by the exchange rate (the depreciation of the rand) and international oil prices ✓✓
- the increases in fuel prices (above the inflation target of 6%) has increased the cost of production of all goods and services ✓✓
- the cost of the CPI basket of goods will increase further due to increased transport costs ✓✓
- the increased transport cost will limit the supply of goods, impacting negatively on the consumer through higher market prices ✓✓
- the price of fuel in South Africa includes various levies for example the road accident fund, which has increased above the CPI ✓✓
- the increased pressure on the CPI can lead to a situation of stagflation (high unemployment, low growth and high inflation) ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant higher order responses) (Max 10)
CONCLUSION
It is important for a country to implement various measures to control inflation, as its consequences can be devastating. ✓✓ Max (2)
TOTAL SECTION C:40
GRAND TOTAL:150