AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2019
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
NOVEMBER 2019
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 A.
1.1.1 ONE of the following factors will influence the supply and demand of a product:
- Increasing the supply of the product
- The range of products available
- The price of the product
- The attitude and values of consumers
1.1.2 The process whereby products are moved from the farm to the consumer:
- Grading
- Processing
- Standardisation
- Transportation
1.1.3 A measure of how much the demand for a product changes if there is a change in price:
- Equilibrium
- Fluctuation
- Price elasticity of demand
- Price elasticity of supply
1.1.4 The practice of putting labels on products to promote them as environmentally friendly:
- Sustainable marketing
- Green marketing
- Standard labelling
- Ecolabelling
1.1.5 ONE of the following is NOT an example of labour legislation:
- Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993, (Act 85 of 1993)
- Cosmetics and Disinfectants Act, 1993, (Act 18 of 1993)
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act, 1997 (Act 75 of 1997)
- Labour Relations Act, 1995 (Act 66 of 1995)
1.1.6 An example of production capital in a dairy enterprise:
- Silage
- Breeding cows
- Electric fence
- Milking machines
1.1.7 The net worth of a business is defined as the …
- total assets of the business minus the liabilities.
- owner's equity.
- expenditure of the business minus the income.
- total assets of the business plus liabilities.
1.1.8 ONE of the following is NOT an economic characteristic of land:
- Soil is found in a specific environment
- Soil is destructible
- Soil is durable
- Soil has different production potentials
1.1.9 The following with regard to family selection are TRUE:
- Based on the performance of its own relatives
- Faster than pedigree selection
- The most accurate method
- Based on one generation
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.10 The pictures below are an example of …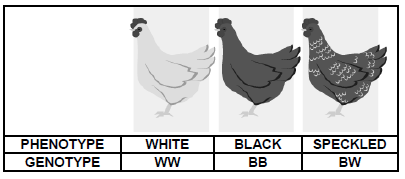
- partial dominance.
- co-dominance.
- complete dominance.
- incomplete dominance. (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2 Choose a term from COLUMN B that matches a description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–H) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.6 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.2.1 The process of planning, production, pricing, promotion and distribution of goods and services 1.2.2 The quantity of products offered exceeds the quantity required 1.2.3 An area used for agricultural production 1.2.4 The costs that are not limited to a specific enterprise in a farming business 1.2.5 The inheritance of one trait does not depend on the inheritance of another |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A marketing approach that focuses on the needs of only a small portion of the mainstream consumers
1.3.2 The process of developing long-term and short-term objectives for the farm business
1.3.3 The use of statistics to analyse biological data
1.3.4 A pattern of inheritance which involves more than two alleles
1.3.5 An organism with genes from another organism (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD in EACH of the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question numbers (1.4.1 to 1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 An agri-agent recognises opportunities and is willing to take the risk of starting a new business.
1.4.2 Overcapitalisation is when too little capital is invested in a farming enterprise in relation to other production factors.
1.4.3 A syringe is an apparatus used to fire desired genes into a plant.
1.4.4 The expression of one gene that is influenced by another gene is referred to as atavism.
1.4.5 Prepotency is the degree to which a characteristic is influenced by genes. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 A business plan explains how an entrepreneur wants to start a business, as well as its goals and objectives.
2.1.1 Give TWO reasons for drawing up a business plan. (2)
2.1.2 State TWO factors that should be considered when developing a market. (2)
2.2 A subsistence farmer producing watermelons and spinach wants to sell the products for additional income and to grow the business.
2.2.1 Name TWO factors that the farmer should consider when setting the prices of the produce.(2)
2.2.2 State TWO ways that the farmer can use to promote the produce. (2)
2.3 The table below summarises supply and demand of sugar cane.
| TIME (YEARS) | ||||
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |
| Sugar cane supplied (million tons) | 180 | 190 | 200 | 220 |
| Price per ton (R/ton) | 150 | 500 | 650 | 720 |
| Sugar cane demanded (million tons) | 230 | 210 | 175 | 165 |
2.3.1 Use the data in the table above to draw a bar graph showing the supply and demand of sugar cane from 2015 to 2018. (6)
2.3.2 Deduce the relationship between the supply and demand of sugar cane from 2015 to 2018. (2)
2.4 The diagram below gives the descriptions of the different main phases of the entrepreneurial process.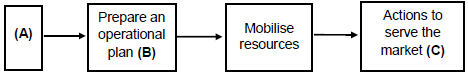
Identify the phases of the entrepreneurial processes represented by A, B and C. Write down the letter (A to C) and the correct answer. (3)
2.5 Different marketing functions need to be performed for effective marketing of products.
2.5.1 Give a marketing function that matches EACH of the following statements:
- Products are placed into boxes.(1)
- Products are kept in a cool place giving them a longer shelf-life.(1)
- Changing a product from its raw form.(1)
2.5.2 Give TWO advantages of the processing of agricultural products. (2)
2.6 The marketing channels below are related to a free marketing system.
2.6.1 Give ONE marketing channel for EACH of the statements by choosing from the list below. Write only the channel next to the question numbers (2.6.1(a) to 2.6.1(c)) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| internet marketing; stock sales; fresh produce market; farm-gate marketing; contract marketing |
- A farmer sells spinach direct from the farm.(1)
- Goats, sheep and cattle are sold to the highest bidder.(1)
- Products are electronically advertised and sold.(1)
2.6.2 Name TWO disadvantages of a free marketing system. (2)
2.7 The line graph below shows the equilibrium price for a particular agricultural product.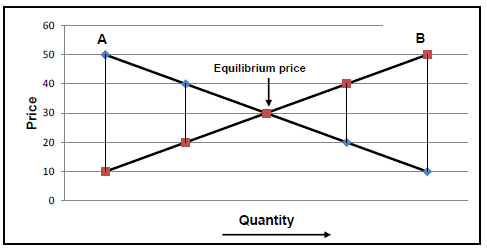
2.7.1 Identify lines A and B. (2)
2.7.2 Define the concept equilibrium price.
2.7.3 Give TWO factors, other than the price, that can affect line A. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The graph below shows the different skills of a farmer and a farm worker.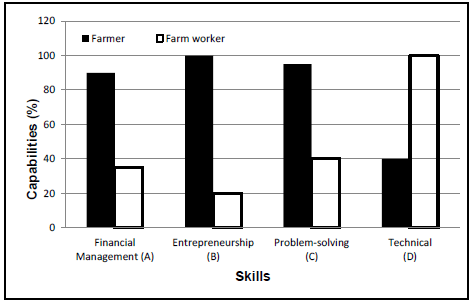
3.1.1 From the graph above, deduce the production factor that is represented by high financial management capability. (1)
3.1.2 Name TWO management skills needed to run a successful business other than those in the graph. (2)
3.1.3 Compare skills C and D of a farm worker with those of a farmer. (4)
3.2 The table below shows the income and expenditure of a farm for July.
| EXPENDITURE | INCOME | ||||
| DATE | ITEM | COST (R) | DATE | ITEM | COST (R) |
| 02/07 | Transport | 1000 | 04/07 | Tomatoes | 2800 |
| 06/07 | Manure | 620 | 06/07 | Tomatoes | 2940 |
| 06/07 | Pesticides | 750 | 07/07 | Sheep | 9080 |
| 06/07 | Rent | 2250 | 08/07 | Onions | 3010 |
| 12/07 | Fuel | 2650 | 10/07 | Old cows | 45500 |
| 15/07 | Insurance | 1100 | 11/07 | Tomatoes | 2140 |
| 20/07 | Electricity | 455 | 26/07 | Onions | 2100 |
3.2.1 Identify the financial document in the table above. (1)
3.2.2 Identify TWO examples of EACH of the following costs in the table above:
- Fixed cost items(2)
- Variable cost items(2)
3.2.3 Use the table above and calculate the total income from tomatoes. Show ALL calculations. (2)
3.2.4 Give TWO reasons for keeping financial records. (2)
3.3 A farmer took out a loan of R195 000 for production purposes payable at an interest rate of 11.5% per annum over a period of one year. At the end of the financial year the farmer generated R240 000.
3.3.1 From the scenario above, deduce the type of credit obtained by the farmer. (1)
3.3.2 Calculate the interest the farmer will pay back to the financial institution.
Show ALL calculations. (2)
3.3.3 Calculate the net income to determine the profitability of this farming enterprise. Show ALL calculations. (3)
3.3.4 State whether this farming enterprise is sustainable or not. (1)
3.3.5 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 3.3.4. (1)
3.4 The picture below represents a production factor.
3.4.1 Identify the production factor represented by A in the picture above. (1)
3.4.2 Differentiate between a casual farm worker and a seasonal farm worker. (2)
3.4.3 Give THREE problems associated with farm workers. (3)
3.5 Land is a production factor which is subjected to the law of diminishing returns.
3.5.1 Explain the law of diminishing returns as an economic characteristic of land. (3)
3.5.2 Name TWO functions of land. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 A pure-breed black cow is crossed with a pure-breed red bull. The offspring of the F1 generation have a black colour. Use the letters B and b to answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Indicate whether black or red colour is dominant. (1)
4.1.2 Justify the answer to QUESTION 4.1.1. (1)
4.1.3 Determine the following:
- Genotype of the cow(1)
- Genotype of the offspring(1)
4.2 The diagram below represents a type of crossing between two pea varieties showing two genes (colour and texture).
Characteristic 1: Colour
G – Green
g – Yellow
Characteristic 2: Texture
R – Rough
r – Smooth
| GAMETES | GR | Gr | gR | gr |
| GR | GGRR | GGRr | GgRR | GgRr |
| Gr | GGRr | GGrr | GgRr | Ggrr |
| gR | GgRR | GgRr | ggRR | ggRr |
| gr | GgRr | Ggrr | ggRr | ggrr |
4.2.1 Identify the type of crossing above. (1)
4.2.2 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 4.2.1. (1)
4.2.3 Determine TWO possible phenotypes of the F1 generation. (2)
4.2.4 Calculate the percentage of offspring that have yellow and smooth pea seeds. Show ALL calculations. (2)
4.3 The differences in the phenotypes of plants and animals of the same species are influenced by both the genes and the environment.
4.3.1 Give a genetic term for the phenomenon in the statement above. (1)
4.3.2 Name TWO environmental factors that can have an effect on this phenomenon. (2)
4.3.3 Give TWO types of selection. (2)
4.4 The pictures below show two different breeds of farm animals.
4.4.1 Name the breeding system if the animals in the pictures above are allowed to breed. (1)
4.4.2 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 4.4.1. (1)
4.4.3 State TWO advantages of the breeding system in QUESTION 4.4.1. (2)
4.4.4 Name TWO disadvantages of inbreeding. (2)
4.5 A homozygous brown ewe (A) was mated with a homozygous white ram (a). The F1 offspring were all brown. The F1 ewes were mated with an unknown ram and all the F2 generation offspring were brown.
4.5.1 Draw a Punnet square to illustrate the F2 generation. (4)
4.5.2 Indicate the following:
- Genotypic ratio of the F2 generation(1)
- The number of white offspring in the F2 generation(1)
4.6 The length of a maize plant is controlled by three pairs of genes. Assume that the base length of the recessive (aabbdd) maize plant is 40 cm. Each additive allele contributes 5 cm to the base length.
4.6.1 Determine the genotype of the highest maize plant. (1)
4.6.2 Calculate the height of the highest maize plant. Show ALL calculations. (2)
4.6.3 Name TWO genotypes that will give rise to a maize plant with a height of 55 cm. (2)
4.7 Give THREE techniques to genetically modify farm animals. (3)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150