AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2019
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
NOVEMBER 2019
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read the question carefully and answer only what is asked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The production factor that cannot be reclaimed easily after it has been utilised for urbanisation:
- Land
- Capital
- Labour
- Management
1.1.2 The farming system which is known for doing the right thing, in the right place, in the right way and at the right time:
- Commercial farming
- Subsistence farming
- Precision farming
- Extensive farming
1.1.3 The grazing area that provides sufficient pasture to support a specific number of animals:
- Vegetation
- Carrying capacity
- Rotational grazing
- Overgrazing
1.1.4 Money, manufactured goods and assets that are used for the production of other goods to generate income:
- Expenditure
- Source of finance
- Credit
- Capital
1.1.5 Long-term credit is a combination of the following characteristics:
- The crop is often used as security.
- The source of finance is normally a bank.
- It is usually used for durable fixed improvements.
- The repayment period is equal to or more than ten years.
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.6 The sum total of the income of all the farm enterprises plus sundry farm income:
- Gross farm income
- Gross value of production
- Gross income of the enterprise
- Gross sales
1.1.7 The effective combination and coordination of all resources to maximise profit:
- Marketing
- Production
- Market research
- Management
1.1.8 The farm implement used to reap crops:
- Plough
- Harrow
- Combine harvester
- Ripper
1.1.9 A farming business strategy focusing on one product or operation in a farming enterprise:
- Diversification
- Value adding
- Specialisation
- Hedging
1.1.10 The heating method which results in not a single living organism being present in the food product after preservation:
- Sterilising
- Pasteurisation
- Blanching
- Smoking (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2 Choose a description in COLUMN B that matches the term/phrase in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–L) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.11 M. Use each description in COLUMN B only ONCE.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.2.1 Chemical preservatives 1.2.2 Optimum resource utilisation 1.2.3 Can take responsibility 1.2.4 Strategic management 1.2.5 Price fixing 1.2.6 Standardisation 1.2.7 Soil slope 1.2.8 Labour productivity 1.2.9 Hand-picking 1.2.10 Buying | long-term management system that allows a business to adapt to possible future changes and challenges acquiring goods for cash the best possible way to use all available labour, materials and infrastructure when the marketing of the product is not controlled characteristic of an entrepreneur improves the labour input in agribusiness will prevent the activities of micro-organisms in food specification for products' grades and prices influences the drainability of the soil the control of pests inside silos artificial price setting manual method of harvesting food products |
(10 x 2) (20)
1.3 Give the CORRECT agricultural term for EACH of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.3.6 Recording.
1.3.1 The type of market where sales are done by agents on behalf of the farmer on a commission basis
1.3.2 Packaging material made of glass with aluminium or plastic lids
1.3.3 A requisition form to keep record of money taken from petty cash
1.3.4 A written instruction from the account holder to the bank authorising the bank to pay the amount specified to the payee when presented to the bank
1.3.5 The process used to distinguish size, colour, quality and form according to the present marketing procedure (5 x 1) (5)
1.4 The following statements are INCORRECT. Change the UNDERLINED word(s) to make the statements CORRECT. Write the answer next to the question numbers (1.4.1 to 1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.4.6 Fixed capital.
1.4.1 Implementation measures the outcome of planned activities on the farm.
1.4.2 Carrying capacity is the way that pastures are utilised to keep the veld in good condition for livestock farming.
1.4.3 Overgrazing is when the livestock choose to eat only certain plants.
1.4.4 The drafting of credits and budgets are within the scope of the physical activities of a farm.
1.4.5 Motivational steps are taken against a worker to maintain good order and effective performance. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: PHYSICAL AND FINANCIAL PLANNING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Name FOUR functions of soil in crop production. (4)
2.2 Contour ploughing contributes to the prevention of soil erosion
2.2.1 Discuss how contour ploughing can be used to channel surface water into dams. (2)
2.2.2 Explain the difference between contour ploughing and terracing. (2)
2.3 A young farmer wants to plant a crop on 64 ha using conventional cultivation. Soil data was gathered by making soil pits (profile holes) and a greyish clay soil with a plate-like structure was found. The soil is of moderate depth and rich in minerals. The pH test showed a reading of 7,8.
2.3.1 Describe the drainability of the greyish clay soil. (2)
2.3.2 Explain the pH scale and what it means if the pH is 7,8. (4)
2.3.3 Name the substance that must be added to the soil to improve the pH. (1)
2.3.4 Give advice to this young farmer on how the current method of cultivation can be changed to include conservation cultivation. Motivate your answer. (4)
2.4 Discuss how fair labour practices can be promoted through the proper positioning of buildings, facilities and equipment. (2)
2.5 Name the different types of capital in a farming venture and give ONE example of EACH. (6)
2.6 Different farming methods (A, B and C) are represented by the illustrations below: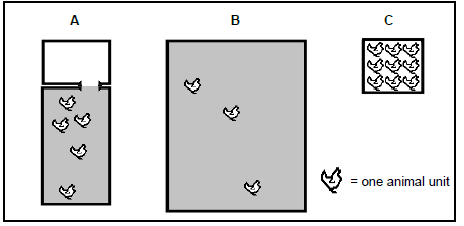
2.6.1 Name the farming methods that are represented by A, B and C. (3)
2.6.2 Explain the following factors to distinguish between farming methods B and C:
- Labour requirements(2)
- Dependence on technology (2)
2.6.3 Choose a method that can be regarded as organic farming from farming methods A, B and C. Motivate your answer. (3)
2.7 Stock farmers divide natural veld into camps to increase production without damaging the environment.
2.7.1 Identify the type of precision farming technology that can be used to assist in dividing natural veld into camps. (1)
2.7.2 Describe the requirements that make a camp suitable for animal production. (2)
2.7.3 Describe how a stock farmer can use precision farming to keep track of animals grazing in a camp without human presence. (2)
2.8 Give ONE type of budget for each of the following descriptions by choosing a word/term from the list below. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (2.8.1 to 2.8.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
whole-farm budget; enterprise budget; partial budget;
maintenance budget; cash flow budget
2.8.1 The budget that makes provision for the finances needed to keep the infrastructure, implements and equipment in a functioning order (1)
2.8.2 The budget that provides a month's expected income and expenses (1)
2.8.3 The combined budget of all the divisions in a farming enterprise (1)
2.8.4 The budget that is compiled to compare two or more practices within an enterprise (1)
2.8.5 A complete budget for a single division in a farming enterprise (1)
2.9 A budget is prepared once and then filed.
Give THREE reasons why this statement is NOT true. (3)
[50]
QUESTION 3: ENTREPRENEURSHIP, RECORDING, MARKETING, BUSINESS PLANNING AND ORGANISED AGRICULTURE
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 A good business plan involves research on the external and internal business environments.
3.1.1 Define the vision statement of a business. (1)
3.1.2 Give TWO reasons for the review of a business idea. (2)
3.1.3 Describe the usefulness of the SWOT analysis to determine the performance of a farm. (4)
3.2 An agricultural enterprise is regarded as a single-owner business. A farmer should be highly skilled as an entrepreneur.
3.2.1 State FOUR characteristics of a successful entrepreneur. (4)
3.2.2 Name TWO risks to consider when starting your own business. (2)
3.3 A crop farmer is doing market research about the general overview of the business.
Explain how the following aspects will influence the marketing plan:
3.3.1 Size of the market (1)
3.3.2 Preference of the consumers (1)
3.4 The schematic representation below shows FOUR variables involved in the marketing process.
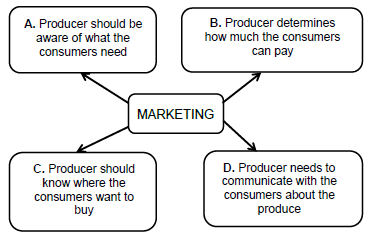
3.4.1 Identify the marketing variables that are represented by A, B, C and D in the diagram on the previous page. (4)
3.4.2 State TWO factors that a producer should consider during the marketing of variable A. (2)
3.4.3 Name TWO ways in which a producer can ensure that variable D is achieved. (2)
3.4.4 Indicate TWO aspects that influence variable B during marketing. (2)
3.5 Below is a list of the activities that are related to the production and marketing of agricultural products.
- Sales to consumers
- Planning for production
- Distribution
- Soil preparation and planting
- Storage
- Grading
3.5.1 Give the correct sequence of an agricultural business chain using the list of activities above. (6)
3.5.2 Give THREE reasons why consumers pay higher prices for agricultural products. (3)
3.5.3 Which agricultural marketing system uses the pooling system? (1)
3.6 The following data was obtained about a crop production enterprise:
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Quantity of bags of fertiliser | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Crop supply (thousand tons) | 180 | 190 | 200 | 220 |
| Crop demand (thousand tons) | 230 | 210 | 170 | 165 |
| Price per kilogram (R/kg) | 720 | 500 | 650 | 480 |
3.6.1 Draw a double bar graph of the data provided on the crop supply and the crop demand from 2014 to 2017. (6)
3.6.2 Give the year in the table in which sellers wanted to sell as much as possible. (1)
3.6.3 Give the year in the table in which buyers wanted to buy as much as possible. (1)
3.7 Below is a list of examples of product comparisons that appear in product competition in the market.
NOTE: An example can be used only ONCE.
- Margarine versus butter
- White meat versus red meat
- Canned fruit versus fresh fruit
- Coffee beans versus instant coffee
- Frozen vegetables versus fresh vegetables
3.7.1 Identify the products in direct competition. (3)
3.7.2 Identify the products in indirect competition. (2)
3.8 Farm maps provide valuable information that is used in the production process.
Give TWO examples of information that may appear on the farm map. (2)
[50]
QUESTION 4: HARVESTING, PROCESSING, MANAGEMENT AND AGRITOURISM
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Crops must be harvested at a stage of readiness that will ensure that it reaches the consumer in a good condition.
4.1.1 Name THREE physiological crop maturity indicators. (3)
4.1.2 State the disadvantages of hand-harvesting. (4)
4.2 Briefly discuss FOUR advantages of applying good agricultural practices. (4)
4.3 A farmer is starting a new production enterprise. The current labour force is not large enough and more workers need to be appointed. A job description is drawn up for each worker to ensure that all the tasks are catered for. It also ensures that the workers know how to execute their tasks. Those who reach their work targets will be rewarded with promotions and task-oriented bonuses.
On their free weekends the workers play soccer matches against workers from neighbouring farms.
From the case study above deduce FIVE different tasks that a manager should consider regarding labour. (5)
4.4 Name and discuss THREE dangers that consumers can be exposed to when using fresh produce. (6)
4.5 Name FIVE packing and transporting containers that facilitate packing produce in the field and moving produce to the pack house. (5)
4.6 Discuss the TWO main factors that determine the storage method for cultivated agricultural products. (2)
4.7 Value adding is transforming a raw agricultural product into a consumer-friendly product by changing it or adding something to it.
4.7.1 Discuss FOUR advantages of value adding in agribusiness. (4)
4.7.2 Name and discuss the use of natural preservatives in the prevention of microbial activity in food. (6)
4.8 The Foodstuffs, Cosmetics and Disinfectants Act, 1972 (Act 54 of 1972) contains the regulation according to which product labelling is controlled.
Explain THREE requirements of this law with regard to the ingredients on a label. (3)
4.9 Briefly discuss how the following factors can promote the productivity of workers:
4.9.1 Physical planning of farming (1)
4.9.2 Economic units (1)
4.9.3 Planning of the production processes (1)
4.9.4 Effective mechanisation (1)
4.10 Agritourists visit farms that have certain attractions and offer bed-and-breakfast facilities.
Name FOUR experiences that farm-stay holiday tourists can look forward to enjoy. (4)
[50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 150
GRAND TOTAL: 200