AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2019 PREPARATORY EXAMINATIONS
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2019
PREPARATORY EXAMINATIONS
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 B ✔✔
1.1.2 C ✔✔
1.1.3 B ✔✔
1.1.4 A ✔✔
1.1.5 D ✔✔
1.1.6 A ✔✔
1.1.7 B ✔✔
1.1.8 C ✔✔
1.1.9 C ✔✔
1.1.10 D ✔✔ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 B only ✔✔
1.2.2 Both A and B ✔✔
1.2.3 None ✔✔
1.2.4 A only ✔✔
1.2.5 B only ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Biological Value/BV ✔✔
1.3.2 Drenching gun/Dosing gun ✔✔
1.3.3 Repeated Breeder Syndrome ✔✔
1.3.4 Prostate ✔✔
1.3.5 Hydrocephalus ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Maintenance ✔
1.4.2 Battery ✔
1.4.3 Super ovulation ✔
1.4.4 Acrosome ✔
1.4.5 Dry period ✔ (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
2.1 Alimentary canals of farm animals
2.1.1 Classification of farm animals
- Diagram 1 – Non-ruminant ✔
- Diagram 3 – Ruminant ✔ (2)
2.1.2 Reason for each classification
- Diagram 1 – It has a simple/monogastric stomach/ventriculus/ proventriculus ✔
- Diagram 3 – It has a complex/compound stomach ✔ (2)
2.1.3 Determination of the age of the animal in Diagram 3
- Young ruminant/calf ✔ (1)
2.1.4 ONE feature visible for the age
- Presence of oesophogal groove ✔
- Underdeveloped rumen/reticulum/omasum ✔
- Well-developed abomasum ✔ (Any 1 x 1) (1)
2.1.5 Justification of animals not digesting crude fibre
- Diagram 2 – There are no rumen micro-organisms to digest crude fibre ✔
- Diagram 3 – Rumen is still underdeveloped/not functioning ✔ (2)
2.1.6 Identification of the letter where rennin is secreted
- Diagram 1 – B ✔
- Diagram 3 – E ✔ (2)
2.2 Indication of animal feeds
- Oilcake meal ✔ (1)
- Maize meal ✔ (1)
- Sun dried hay ✔ (1)
- Green lucerne ✔ (1)
2.3 Feed composition
2.3.1 Classification of feeds
- Feed A – Concentrates ✔ (1)
- Feed B – Roughage ✔ (1)
2.3.2 Reason for classification
Feed
- A Low percentage of crude fibre ✔
- High percentage of Total Digestible Nutrients/TDN ✔
- High percentage of protein ✔ (Any 1)
Feed B
- High percentage of crude fibre ✔
- Low percentage of Total Digestible Nutrients ✔
- Low percentage of protein ✔ (Any 1) (2)
2.3.3 Calculation of nutritive ratio of FEED A
- Calculation of DNNE’s = TDN (12,5 + 6 + 60 + 1,5 = 80%)
80 – 12,5 = 67,5% ✔
Nutritive Ratio = 1 : % digestible non-nitrogen substances ✔
% digestible protein
1 : 67,5 ✔
12,5
1 : 5,4 ✔
OR - Calculation of DNNE’s = TDN (12,5 + 6 + 60 + 1,5 = 80%) ✔
Nutritive Ratio = 1 : TDN – DP ✔
DP
1 : 80 – 12,5 ✔
12,5
1 : 5,4 ✔ (4)
2.3.4 Recommendation of FEED A
- Recommended for growth purpose ✔ (1)
Reason - NR is narrow/more protein for growth ✔ (1)
2.4 Process in the alimentary canal
2.4.1 Identification of the process
- Absorption of food ✔ (1)
2.4.2 Name of the part where absorption occurs
- Small intestine ✔ (1)
2.4.3 Identification of the type of nutrient transport
- A – Passive absorption ✔
- B – Active transport ✔ (2)
2.4.4 Reason for the type of transport
- A/Passive absorption – Nutrients move along concentration gradient ✔
- B/Active transport – Nutrients move against concentration gradient ✔ (2)
2.5 Feed flow programme
2.5.1 Identification of the month for culling animals
- Month 6 ✔ (1)
2.5.2 Reason
- Feed available is the lowest ✔
- Supplementary requirement is the highest ✔ (Any 1 x 1) (1)
2.5.3 Calculation of feed available in tons during month 2
- 800 kg/ha x 14 ha ✔
11 200 kg ✔
1 000
11,2 tons ✔ (3) [35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
3.1 Graph on temperature requirement of broiler chickens
3.1.1 Deduction of the trend of temperature requirement
- From week 1 to week 5 it decreases gradually✔
- From week 5 to week 7 it is constant ✔ (2)
3.1.2 Line graph 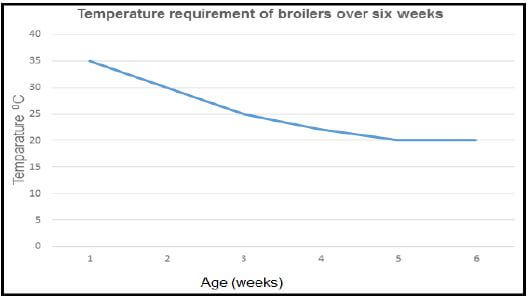
Criteria/rubric/marking guideline
- Correct heading ✔
- X-axis: Correctly calibrated and labelled (Age) ✔
- Y-axis: Correctly calibrated and labelled (Temperature) ✔
- Line graph ✔
- Correct units (Weeks and °C) ✔
- Accuracy ✔ (6)
3.1.3 Equipment that can be used if temperature drops below 10 °C
- Heaters/Infrared lights/Air conditioner ✔ (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.2 Bull under stress
3.2.1 THREE visible signs showing distress
- Pawing ✔
- Raised hair ✔
- Snorting ✔
- Raised tail ✔
- Feigned charging movements ✔ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.2.2 Effect of the behaviour to handlers
- Injury ✔ (1)
3.2.3 Equipment to calm the bull
- Electric prodder ✔ (1)
3.2.4 THREE guidelines for handling large farm animals
- Avoid yelling at animals ✔
- Do not approach animals from a blind spot ✔
- Move animals through a chute that has minimal obstructions ✔
- Never prod animals if they have no place to go ✔
- Announce your presence by touching it ✔ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.3 Production unit/ system
3.3.1 Identification of the production system
- Intensive production system ✔ (1)
3.3.2 Reason
- Presence of facilities ✔
- Animals are kept in an enclosure ✔
- High capital investment ✔ (Any 1) (1)
3.3.3 Identification of the letter
- C/D ✔
- B ✔
- D/C ✔ (3)
3.4 FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE/FMD
3.4.1 Naming the pathogen
- Virus ✔ (1)
3.4.2 Extraction of a term from scenario meaning FMD can be transferred
- Contagious ✔ (1)
3.4.3 Key symptom of FMD
- Blister-like lesions on the tongue/between the toes ✔ (1)
3.4.4 TWO state actions from the scenario
- Impose trade regulation ✔
- Veterinary services ✔
- Quarantine ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.5 Parasites
3.5.1 Choosing the parasite
- Nasal worm ✔ (1)
- Liver fluke ✔ (1)
- Bont tick ✔ (1)
- Tape worm ✔ (1)
- Blowfly ✔ (1)
3.6 THREE basic principles of good health
- Sanitation ✔
- Controlling pests and parasites ✔
- Proper handling of manure ✔
- Isolation of sick animals ✔
- Vaccination of animals ✔
- Good management ✔
- Ensure that feeds are not contaminated ✔
- Waiting for a withdrawal period before using animal product ✔
- Application of correct dosage of medication ✔
- Burning carcass of infected animals ✔ (Any 3 x 1) (3) [35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
4.1 Reproductive systems
4.1.1 Identification of the letter
- Diagram 1 – A ✔
Diagram 2 – D ✔ (2) - C ✔ (1)
- E ✔ (1)
- A ✔ (1)
4.1.2 Common congenital defect in bulls and cows causing sterility
- Hypoplasia ✔ (1)
4.1.3 TWO hormones responsible for ovulation
- Luteinizing hormone ✔
- Oestrogen hormone ✔ (2)
4.2 TWO senses regulating mating behaviour in bull
- Smell ✔
- Sight ✔
- Touch/tactile/contact ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.3 Artificial Insemination
4.3.1 Arrangement of the steps during AI chronologically
- Semen harvesting ✔
- Semen examination ✔
- Semen dilution ✔
- Heat detention ✔
- Placing of semen into the reproductive tract of a cow ✔ (5)
4.3.2 TWO economic benefits of AI for the farmer
- More female animals can be fertilised by superior male animals ✔
- It is a quick and economic way of improving the herd ✔
- Commercial value of herd is improved ✔
- No need to buy an expensive bull ✔
- Higher conception rate ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.4 Cloning
4.4.1 Identification of the process
- Cloning/Nuclear transfer ✔ (1)
4.4.2 Letter of the sheep that is identical to the cloned sheep
- Sheep A ✔ (1)
4.4.3 Letter of a sheep that will be a surrogate
- Sheep E ✔ (1)
4.4.4 Name of the processes in C
- Enucleation ✔ (1)
4.4.5 TWO aims of cloning
- To produce large number of genetically identical animals ✔
- To produce offspring from high quality animals ✔
- To preserve superior genetics ✔
- To increase the number of endangered species ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.5 Gestation stages
4.5.1 Identification of the process
- Fertilisation ✔ (1)
4.5.2 Indication of the stage of pregnancy labelled A
- Ovum stage ✔ (1)
4.5.3 Development that occurs at stage C
- Rapid increase of the uterus✔ (1)
4.5.4 TWO systems developing at stage B
- Respiratory system ✔
- Digestive system ✔
- Uro-genital and vascular system ✔
- Central nervous system ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.5.5 TWO reasons for abortion
- Hormonal or metabolic abnormalities ✔
- Malnutrition ✔
- Trauma and injuries ✔
- Poisoning ✔
- Infections ✔
- Allergies and twinning ✔
- Genetic/chromosomal defects ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.6 Parturition
4.6.1 Indication of the form of presentation
- Anterior presentation ✔ (1)
- Posterior presentation ✔ (1)
4.6.2 Presentation that will need vetenary assistance
- Posterior presentation ✔ (1)
4.6.3 TWO problems causing difficult birth
- Deviation of head ✔
- Flection of the elbow ✔
- Retention of one or both forelegs ✔
- Congenital defects/deformities ✔
- Twins ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150