AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2019 PREPARATORY EXAMINATIONS
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2019
PREPARATORY EXAMINATIONS
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The following are features of controlled marketing except …
- subsidies.
- production quotas.
- single-channel marketing.
- stimulates entrepreneurship.
1.1.2 A type of buyer who is not afraid to try a new product, but will do research about it first, is referred to as …
- traditionalist.
- adopter.
- innovative.
- early majority.
1.1.3 The benefits of co-operative marketing are …
- lower marketing costs per unit
- more bargaining power
- autocratic member control
- meet market requirements for volume and consistent supply
Choose the correct combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.4 A cashflow budget is used to …
- estimate the profitability of a specific business enterprise.
- manage the farm’s assets.
- plan for possible borrowing.
- estimate the profitability of the whole farm.
1.1.5 Workers who are employed during peak labour demand periods, such as harvesting time, are referred to as …
- permanent workers.
- seasonal workers.
- casual workers.
- part-time workers.
1.1.6 A business has total assets worth R325 500 and its liabilities amount to a total of R400 000. The net worth of this business is …
- R74 500.
- R725 500.
- -R74 500.
- R325 500.
1.1.7 … is an example of an internal cause of variation.
- Recombination of genes
- Diseases
- Climate
- Feeding
1.1.8 … is an example of a polygenic trait.
- Milk yield
- Coat colour in shorthorn cattle
- Extra toes in horses
- Streaked hairlessness in Holstein cattle
1.1.9 Mendel’s law of independent assortment applies to …
- monohybrid inheritance.
- co-dominance.
- incomplete dominance.
- dihybrid inheritance.
1.1.10 … is the selection of individuals based on the quality of their offspring.
- Family selection
- Pedigree selection
- Mass selection
- Progeny selection (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–H) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.2.1 The effective combination and co-ordination of human, physical and financial resources to maximise profit 1.2.2 A method of reducing the risk of loss caused by price fluctuations 1.2.3 An operation that changes produce from its natural form to a form that satisfies consumers’ needs 1.2.4 The crossing of parents with their own offspring 1.2.5 The degree to which a characteristic is determined by genetic factors as opposed to environmental factors |
(5 x 2) (10) |
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A cross between individuals of the same breed of a species that are not closely related
1.3.2 The path followed by an agricultural product from the farmer to the consumer
1.3.3 The relationship between change in price and change in demand or supply
1.3.4 A management strategy in which the cost of the consequences of risk is distributed among several stakeholders
1.3.5 General expenses that cannot be linked to a specific enterprise (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in each of the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question number in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Market intelligence is the process of dividing up the market into smaller groups of buyers with similar characteristics.
1.4.2 The practice of putting labels onto products to promote them as environmentally friendly is referred to as green-labelling.
1.4.3 Marketing strategy is the combination of product, price, placement and promotion.
1.4.4 Conceptual skills allow one to be able to process and analyse information.
1.4.5 DNA that is altered by receiving genes from another organism is called transgenic DNA. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The graph below shows the effect of price on demand and supply. 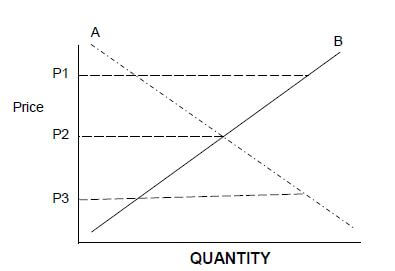
2.1.1 Identify the letter representing the demand curve. (1)
2.1.2 Describe what would happen on the market if produce is sold at prices P1 and P3 respectively. (2)
2.1.3 Suggest TWO strategies farmers can employ to deal with the situation P1 in QUESTION 2.1.2 above. (2)
2.1.4 List TWO factors that would influence the shape of Curve B. (2)
2.2
| South African farmers used to market their maize through a government regulated single channel marketing system, but nowadays there is no intervention and the maize price is determined entirely in the market place according to the laws of supply and demand. All participants, both buyers and sellers, are therefore affected by price movements and many unknowns which is the nature of the free market. |
2.2.1 Identify the TWO marketing systems discussed in the passage above. (2)
2.2.2 Deduce ONE disadvantage of a free market from the passage above. (1)
2.2.3 Supply TWO advantages of a free marketing system. (2)
2.3 You have just identified an agri-business opportunity in your community. As an Agricultural Sciences student enthusiastic about entrepreneurship, you have decided to grab the opportunity.
2.3.1 List, in chronological order, the FOUR phases to follow in the entrepreneurial journey. (4)
2.3.2 Outline THREE questions to be asked so as to evaluate the feasibility of the business idea. (3)
2.3.3 Describe TWO ways in which a business plan will be helpful in the entrepreneurship process. (2)
2.3.4 Describe TWO ways to draw up a business plan by using electronic resources. (2)
2.3.5 Deduce TWO entrepreneurial qualities from the passage above. (2)
2.4 The table below shows the marketing approaches of two farmers.
| FARMER A | FARMER B |
| Limited capital Has a unique product Is targeting a small section of the market | Large capital outlay |
2.4.1 Recommend the appropriate marketing approach for FARMERS A and B above. (2)
2.4.2 Suggest TWO methods to be used by FARMER B to advertise the products described in the table above. (2)
2.4.3 List TWO advantages of the approach recommended for FARMER A. (2)
2.5
| Sustainable marketing is a fast-growing marketing approach. It entails adapting activities on every level of operation to be ecologically friendly and safe, as well as socially acceptable and healthy. |
2.5.1 Indicate how farmers can implement sustainable marketing in the following farming activities:
- Production process (1)
- Packaging (1)
2.5.2 Provide TWO disadvantages of the sustainable marketing approach. (2) [35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The graph below depicts the law of diminishing returns as it applies to farming. 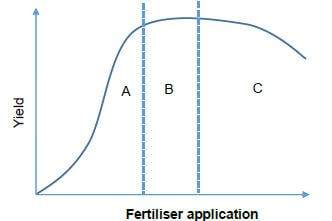
3.1.1 Identify the part of the graph A, B or C that shows diminishing returns. (1)
3.1.2 Comment on the effect of input application rates on enterprise profitability at stage B of the graph. (3)
3.1.3 The land is often referred to as the primary production factor. Justify this statement by providing TWO economic functions of land. (2)
3.2 The South African labour market is regulated by various Acts of Parliament, which include the following:
- The Labour Relations Act (Act 66 of 1995)
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act (Act 75 of 1997)
- Occupational Health and Safety Act (Act 85 of 1993)
- Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases Act (Act 130 of 1993)
- Skills Development Act (Act 97 of 1998)
Choose the legislation above which is applicable to each of the statements below. Write only the letter (A–E) next to the question number (3.2.1–3.2.4) in your ANSWER BOOK.
3.2.1 Farmers were trained to use hazardous chemicals. (1)
3.2.2 A farm worker who was injured driving a tractor without lights at night is taking the farmer to court. (1)
3.2.3 Workers wish to join a trade union. (1)
3.2.4 Farm workers signed a labour contract. (1)
3.3
| To be successful, farmers need to be good producers. Farmers also need to be financial managers; that means keeping accurate farm records and establishing and maintaining a proven record keeping system. Keeping the books up-to-date makes farm management easier and improves ongoing profitability. |
3.3.1 Deduce TWO benefits of record-keeping on farms from the passage above. (2)
3.3.2 Suggest TWO records that can be used to manage each of the following:
- Assets (1)
- Livestock/Stock (1)
3.4 The table below shows an example of a budget used by farmers.
CASH INFLOW | 1st QUARTER | 2nd QUARTER | 3rd QUARTER | 4th QUARTER |
Crop sales Livestock sales Total inflows | 250 000 250 000 | 150 000 150 000 | 80 000 100 000 180 000 | 50 000 50 000 |
CASH EXPENDITURE Seed Fertiliser Feed Processing Marketing Total expenditures | 30 000 25 000 55 000 | 35 000 20 000 8 000 2 000 65 000 | 25 000 10 000 15 000 50 000 | 30 000 15 000 300 000 32 000 377 000 |
Opening balance Quarterly net cash flow Cumulative net cash flow | 10 000 195 000 205 000 | 205 000 85 000 290 000 | 290 000 130 000 420 000 | A B |
3.4.1 Identify the budget shown above. (1)
3.4.2 Deduce figure A. (1)
3.4.3 Calculate figure B and show all calculations. (3)
3.4.4 Deduce, with a reason, the quarter during which the farmer needs to borrow. (2)
3.5
| Two farmers applied for loans from a local bank so that they can start beef production enterprises. They received R200 000 each. Farmer A used R150 000 to purchase breeding heifers and a bull, with the remainder being reserved for purchasing feeds and remedies. Farmer B invested R160 000 in a bakkie and used the remainder to purchase breeding stock, feeds and remedies. |
3.5.1 Identify which of the two farmers overcapitalised his enterprise. (1)
3.5.2 Briefly support the answer in QUESTION 3.5.1. (2)
3.5.3 Identify ONE example of movable capital and ONE example of floating capital in the passage above. (2)
3.5.4 Predict TWO challenges the farmers above might face due to the source of capital they used. (2)
3.6 The image below shows a drought-stricken farm in South Africa.
3.6.1 Classify the source of risk shown above. (1)
3.6.2 Suggest TWO risk management strategies the farmer could have taken to avert financial losses. (2)
3.6.3 Deduce whether the risk is an internal or external force. (1)
3.6.4 List the THREE main managerial principles. (3) [35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 A floriculturist crosses two camellia plants, where one produces white flowers and the other produces red flowers resulting in a flower with alternating patches of red and white.
4.1.1 Identify the type of dominance described in the passage above. (1)
4.1.2 Justify the answer in QUESTION 4.1.1 above. (2)
4.1.3 R represents the red flower gene and W the white flower gene. Use a Punnet square to show the cross described in the passage above. (3)
4.1.4 Predict the phenotypic ratio to be produced if the floriculturist was to self-pollinate the offspring of the cross in QUESTION 4.1.3 above. (1)
4.2 The pictures below show two cattle breeds.
 | |
| A farmer has a herd of animals shown in picture B which have not been producing very well. The farmer is advised by a local extension officer to buy bull A and use it to service his cows to improve production. |
4.2.1 Identify the breeding method suggested by the extension worker to the farmer. (1)
4.2.2 Motivate the answer to QUESTION 4.2.1 above. (2)
4.2.3 Suggest TWO advantages of this breeding method to communal farmers. (2)
4.2.4 List any TWO other breeding methods that farmers can use to improve productivity. (2)
4.2.5 For each breeding method given in QUESTION 4.2.4 above, mention ONE disadvantage. (2)
4.3 The table below shows the weaning weights of weaners on a farm.
WEANING WEIGHT RANGE (kg) | NUMBER OF ANIMALS |
80–90 | 14 |
91–100 | 17 |
101–110 | 25 |
111–120 | 19 |
121–130 | 12 |
4.3.1 Translate the information in the table above into a bar graph. (6)
4.3.2 Deduce the type of variation depicted in the graph. (1)
4.3.3 Calculate the total number of calves the farmer above has and show all calculations. (2)
4.4 The diagram below shows two techniques used in plant improvement. A 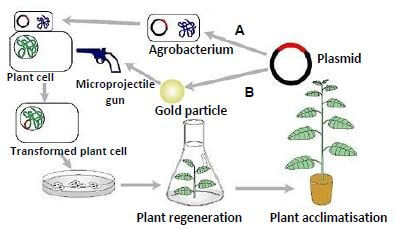
4.4.1 Identify techniques A and B shown in the diagram above. (2)
4.4.2 Give THREE advantages of modern plant improvement methods like the one shown above to plant breeders. (3)
4.4.3 Outline THREE social concerns regarding Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs). (3)
4.4.4 Give TWO implications of the use of GMO technology to improve plants in South Africa. (2) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150