MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY:WELDING AND METAL WORK GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2019
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: WELDING AND METALWORK
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MAY/JUNE 2019
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your centre number and examination number in the spaces provided on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational acceleration should be taken as 10 m.s-2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- A formula sheet is attached at the end of the question paper.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time.
| QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME in minutes |
| GENERIC | |||
| 1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | Safety | 10 | 10 |
| 3 | Materials | 14 | 14 |
| SPECIFIC | |||
| 4 | Multiple-choice questions | 14 | 10 |
| 5 | Terminology (Templates) | 23 | 20 |
| 6 | Tools and Equipment | 18 | 15 |
| 7 | Forces | 45 | 30 |
| 8 | Joining Methods (Inspection of Weld) | 23 | 20 |
| 9 | Joining Methods (Stresses and Distortion) | 18 | 20 |
| 10 | Maintenance | 8 | 10 |
| 11 | Terminology (Developments) | 21 | 25 |
| TOTAL | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.7 E.
1.1 Which Act is the code of good practice with regard to HIV/Aids and employment at the workplace?
- The Act on safety states that all employees must make sure that the workplace is safe and that employers are not at risk of becoming infected with HIV at work.
- The Act contains common guidelines on how employers, employees and trade unions should respond to HIV in the workplace.
- Employers may demote employees based on their HIV status (Act 33 of 2000).
- Employers can simply dismiss a person who has HIV (Act 34 of 2000). (1)
1.2 Which ONE of the following is a reason why oil and grease must NOT be allowed to come into contact with oxygen and acetylene fittings? It will …
- cause blockages.
- form a flammable mixture.
- make the oxygen fittings slippery.
- accumulate dust. (1)
1.3 Which ONE of the following is an advantage of the process workshop layout?
- There is high machine utilisation because more than one product is manufactured.
- Production is not always continuous.
- Transportation costs between process departments may be high.
- There may be damage to fragile goods as a result of extra handling. (1)
1.4 Which ONE of the following factors is important in the heat treatment of steel?
- Temperature
- Colour
- Length
- Shape (1)
1.5 What is the purpose of annealing steel?
- Harden it
- Temper it
- Harden the core
- Relieve internal stresses (1)
1.6 Which ONE of the following sounds will indicate cast iron when a sound test is carried out?
- Loud and clear sound
- Very dull sound
- High ringing sound
- High-frequency sound (1)
[6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 A welded joint needs to be ground using an angle grinder. State TWO safety measures to be observed when using the angle grinder. (2)
2.2 Give TWO reasons why it is important to wear welding goggles during gas welding. (2)
2.3 Name TWO items of personal protective equipment (PPE) that one will use when working with a bench grinder. (2)
2.4 Explain the difference between the process workshop layout and the product workshop layout. (2)
2.5 Describe the employer's responsibility regarding equipment in the workplace. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Name and describe the FOUR tests used to distinguish between the different types of materials. (8)
3.2 Give the reason why the following heat-treatment processes are performed on steel:
3.2.1 Tempering (2)
3.2.2 Normalising (2)
3.2.3 Hardening (2)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1 to 4.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 4.15 E.
4.1 What is the main reason for having permanent base and centre lines on the floor in the template loft? To …
- minimise accidents.
- assist with welding.
- save time when marking out.
- keep the floor clean. (1)
4.2 What does the abbreviation OSU stand for with regard to templates?
- Only straight up
- Only side up
- Other steel users
- Other side up (1)
4.3 What does 12 in FIGURE 4.3 below represent of the weld?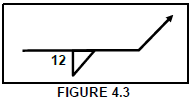
- Length
- Size
- Pitch
- Root (1)
4.4 What is the function of a chuck on a drill press?
- Changes the speed of the drill.
- Adjusts the feed of the drill.
- Holds the drill bit in position.
- Adjusts the drill table. (1)
4.5 Which type of member of a steel framework is represented by AB in FIGURE 4.5 below?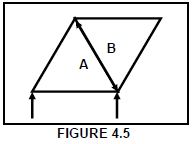
- Strut
- Tie
- Force
- Stress (1)
4.6 Identify the type of load applied to the work piece in FIGURE 4.6 below.
- Tensile
- Torsional
- Shear
- Compressive (1)
4.7 Which ONE of the following steps can be taken to reduce the cause of a transverse crack?
- Quick cooling after welding
- Slow cooling after welding
- Using the correct welding current
- Preparing the root gap correctly (1)
4.8 Which ONE of the following tests is an example of a non-destructive test?
- Ultrasonic test
- Machinability test
- Nick-break test
- File test (1)
4.9 Which ONE of the following is a cause of a malfunctioning guillotine?
- Incorrect chuck key size
- Incorrect cutting angle size
- Incorrect arc wire
- Overloading (1)
4.10 Which ONE of the following is a method used to reduce distortion during the welding process?
- Continuous welding
- Controlled cooling
- Round-step welding
- Intermittent welding (1)
4.11 Which ONE of the following is a reason for lock-out and tagging of equipment during maintenance? To inform other workers that …
- maintenance work is being done.
- an accident has happened.
- maintenance work has been completed.
- there is a power failure. (1)
4.12 What is the colour of the oxygen cylinder that is used during gas welding?
- Black
- Red
- Maroon
- Yellow (1)
4.13 What is the value of X in FIGURE 4.13 below?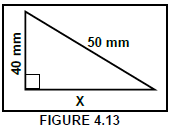
- 90 mm
- 60 mm
- 30 mm
- 120 mm (1)
4.14 Which formula will you use to calculate angle β?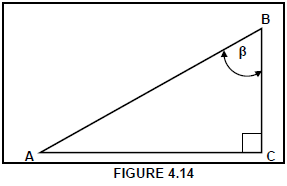
- cosβ = AC
AB - cosβ = BC
AB - cosβ = AB
AC - cosβ = AB
BC
[14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (TEMPLATES) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 below indicates a roof truss. Label parts A–E. (5)
5.2 Draw a neat sketch of a welding symbol indicating the following information for a T-joint done with arc welding: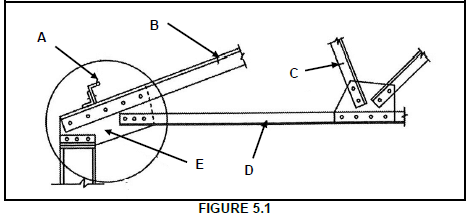
The fillet weld on both sides is 6 mm in size. The lengths of the weld beads are 40 mm each and the pitch of the weld is 90 mm. (8)
5.3 A mild steel ring must be manufactured using a 20 x 20 mm square mild steel bar. The inside diameter of the ring is 215 mm.
5.3.1 Calculate the dimensions of the material needed to manufacture the ring. (6)
5.3.2 Draw a neat sketch of the ring indicating the dimensions. (4)
[23]
QUESTION 6: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Explain the operating principles of a punch and shear machine. (5)
6.2 Describe the operating principles of the plasma cutter. (4)
6.3 Describe the process of cutting an internal thread on a work piece using taps. (3)
6.4 Describe the Brinell hardness test process. (4)
6.5 What is the advantage of using Rockwell hardness testing over the Brinell hardness testing? (2)
[18]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Graphically determine the magnitude and type of member in the framework shown in FIGURE 7.1 below. Members: AE, BF, CF, DE and EF.
SCALE: Space diagram: 1 : 100
Force diagram: 1 mm = 5 N (19)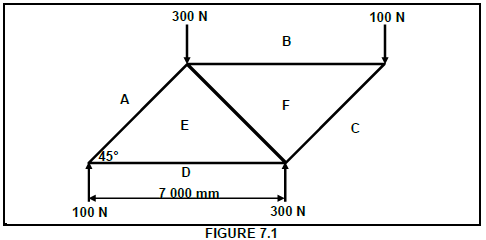
7.2 FIGURE 7.2 below shows a uniform beam. The beam is supported at points RL and RR. Three point loads of 4 N, 5 N and 3 N are exerted onto the beam.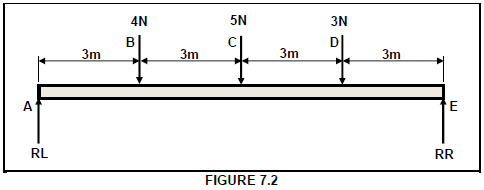
7.2.1 Calculate the reactions at supports RL and RR. (4)
7.2.2 Calculate the bending moments at point B, C and D. (6)
7.2.3 Draw a bending-moment diagram of the beam.
SCALES: Space diagram: 10 mm = 1 m
Bending-moment diagram: 5 mm = 1 N.m (5)
7.3 A steel shaft of diameter 32 mm is lengthened by 0,5 mm when a tensile load of 100 kN is applied to it. The original length of the shaft is 120 mm.
Calculate:
7.3.1 The stress (5)
7.3.2 The strain (3)
7.3.3 Young's modulus of elasticity (3)
[45]
QUESTION 8: JOINING METHODS (WELD INSPECTION) (SPECIFIC)
8.1 State TWO factors that should be taken into account during oxy-acetylene welding to ensure quality welding. (2)
8.2 State TWO causes of incomplete penetration during arc welding. (2)
8.3 State TWO precautions to eliminate the following welding defects:
8.3.1 Slag inclusion (2)
8.3.2 Centre-line cracks (2)
8.4 Define porosity of a welded joint. (3)
8.5 Explain why non-destructive tests are preferred to destructive tests. (2)
8.6 State TWO types of welding defects that are detected when conducting an ultrasonic test onto a welded joint. (2)
8.7 Name THREE elements that should be inspected during the visual inspection process of a welded joint. (3)
8.8 Describe the steps to be followed when performing a nick-break test on a welded joint. (5)
[23]
QUESTION 9: JOINING METHODS (STRESSES AND DISTORTION) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Describe the meaning of shrinkage in a welded joint. (4)
9.2 State FOUR factors that affect distortion and residual stress during welding. (4)
9.3 Explain back-step welding as a method to reduce distortion by using a neatly labelled sketch. (6)
9.4 State FOUR factors that affect the temperature at which cold-worked steel will recrystallise when heated. (4)
[18]
QUESTION 10: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
10.1 State ONE effect of overloading on EACH of the following machines:
10.1.1 Power saw (1)
10.1.2 Bench grinder (1)
10.2 State ONE negative effect of friction on EACH of the following components:
10.2.1 Drill bit (1)
10.2.2 Roller bearings of a rolling machine (1)
10.3 State TWO general maintenance guidelines for a punch and shearing machine. Refer to the electrical switches and the condition of the electrical wiring. (2)
10.4 Give TWO reasons for the recordkeeping of machine services. (2)
[8]
QUESTION 11: TERMINOLOGY (DEVELOPMENT) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 FIGURE 11.1 below shows an off-centre rectangular to rectangular hopper.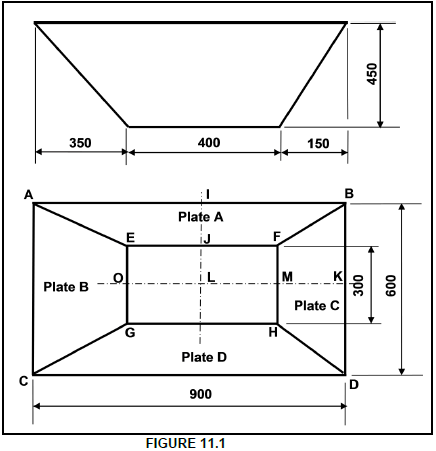
11.1.1 Calculate the plan length of IJ. (3)
11.1.2 Calculate the true length AE on plate A. (6)
11.1.3 Calculate the plan length of MK. (2)
11.1.4 Calculate the true length DH on plate C. (6)
11.1.5 Draw the pattern for plate A. (2)
11.1.6 Draw the pattern for plate C. (2)
[21]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY (WELDING AND METALWORK)
- STRESS AND STRAIN
1.1 Stress = Force or σ = F
Area A
1.2 Strain (ε) = change in length (ΔL)
original length (L)
1.3 Young's modulus ( E ) = stress or ( σ )
strain ε
1.4 Ashaft = πd 2
4
1.5 Apipe =π(D2 - d2)
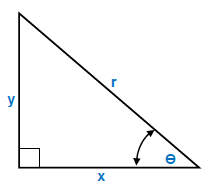
4 - PYTHAGORAS' THEOREM AND TRIGONOMETRY

2.1 sinθ = y
r
2.2 cosθ = x
r
2.3 tanθ = y
x
2.4 r2 = x2 + y2 - TEMPLATES AND DEVELOPMENTS
3.1 Mean Ø = outside Ø – plate thickness where Ø = diameter
Mean Ø = inside Ø + plate thickness
3.2 Mean circumference = π x mean diameter