AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2019
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MAY/JUNE 2019
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This paper consists of TWO sections.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read the questions carefully and answer only what is asked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 In winter the … slope receives light for longer during the day; therefore it is the warmest.
- eastern
- western
- northern
- southern
1.1.2 The carrying capacity of natural pastures can be increased by …
- a planned rotational grazing programme.
- an increase in animals.
- uncontrolled veld fires.
- an increase in grazing period.
1.1.3 … is the most important factor affecting the choice of a farming enterprise.
- The farm manager's qualifications
- Climatic conditions on the farm
- Natural vegetation on the farm
- Availability of labour
1.1.4 The … reflects the daily flow of money in and out of a farming enterprise.
- Balance Sheet
- budget
- Cash Flow Statement
- Income Statement
1.1.5 … farming can ensure food security for households in rural areas.
- Subsistence
- Extensive
- Commercial
- Intensive
1.1.6 Market … is where the quantity of a product that consumers require is equal to the quantity that producers wish to sell.
- value
- equilibrium
- research
- place
1.1.7 The aim of processing agricultural products on the farm is to …
- meet consumer preferences.
- produce more expensive products.
- increase income for the farmer.
- increase labour involvement.
1.1.8 A/An … is issued by a business and indicates the possible repair costs of farm equipment.
- receipt
- invoice
- credit note
- quotation
1.1.9 The Agricultural Products Standards Act, 1990 (Act 119 of 1990) controls the …
- ingredients that may be added to food during processing.
- grading of processed farm products.
- labelling requirements of processed foods.
- premises where food processing takes place.
1.1.10 … is a function of agricultural markets.
- Hedging
- Planning
- Evaluation
- Processing (10 x 2 )
(20)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term/phrase in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–L) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.11 M. Use each description in COLUMN B only ONCE.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.2.1 Movable capital 1.2.2 Long-term credit 1.2.3 Seasonal labourer 1.2.4 Agritourism 1.2.5 Extensive farming 1.2.6 Soil analysis 1.2.7 Tertiary agriculture 1.2.8 Motivation 1.2.9 Liability 1.2.10 Organisation |
|
(10 x 2) (20)
1.3 Give the CORRECT agricultural term for EACH of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.3.6 Recording.
1.3.1 The decrease in value of assets such as vehicles, machinery and tools caused by age and wear
1.3.2 Equipment needed to accurately record the application of water when using a sprinkler system
1.3.3 A document indicating the estimated income and expenditure of a farm business for a specific period
1.3.4 A complete list of items of value on a farm
1.3.5 The removal of moisture from products to prevent micro-organisms from growing (5 x 1) (5)
1.4 The following statements are INCORRECT. Change the UNDERLINED word(s) to make the statements CORRECT. Write the answer next to the question numbers (1.4.1 to 1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.4.6 Fixed capital.
1.4.1 Owner's equity is the total amount of money that is generated by a farming enterprise in one season.
1.4.2 In cooperative marketing, the farmer is obliged to deliver a certain amount of produce at a set price to a specific business as agreed.
1.4.3 Precision farming is the practice in arable sloping land where the direction of run-off water is changed from down-slope to around-the-slope.
1.4.4 Soil structure refers to soil particle size.
1.4.5 Partial farm evaluation will include the evaluation of all the different production activities on the farm. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: PHYSICAL AND FINANCIAL PLANNING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The information below shows the attendance of farm workers from Friday 1 February 2019 to Thursday 17 February 2019.
| WORKER | DATES ABSENT | REASONS |
| 1 | 4 to 7 | Took care of brother who is ill |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | 4 to 8 | Sick with flu |
| 4 | 12 to 14 | Attended study course on management |
| 5 | 1 and 4 | Looked for space in a school for children and registration |
| 6 | 6 | Went to Home Affairs to collect ID card |
2.1.1 Use the information above to draw up the attendance register of the farm enterprise for February 2019. Indicate only the days absent with the letter A. (5)
2.1.2 Determine the types of leave taken by workers 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6. (5)
2.2 Rotational grazing on a farm can only be practised if the farm is divided into camps.
2.2.1 Describe FOUR principles that must be applied when dividing grazing veld into camps. (4)
2.2.2 Explain THREE benefits of camps in a fodder crop production system. (3)
2.3 Name and explain THREE factors that determine the type of technology required in a farm. (6)
2.4 Personal funds (own savings) can be used as a source of capital for the farm.
2.4.1 Name TWO advantages of using personal funds as capital. (2)
2.4.2 Explain ONE disadvantage of using personal funds as capital. (2)
2.5 Precision farming has FOUR basic steps, namely planning, results obtained, applying and analysing. Complete the diagram below by inserting the steps in the correct sequence. (4)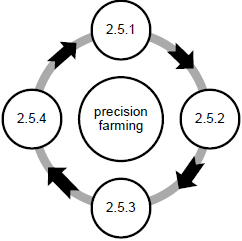
2.6 Briefly describe how the following remote sensing applications are beneficial to precision agriculture:
2.6.1 Soil maps (2)
2.6.2 Variable-rate technology (VRT) (2)
2.6.3 Water stress (2)
2.7 A farmer wants to extend a farm from 2 000 ha to 3 000 ha. He/She purchases irrigation land at an auction. Three permanent workers and two temporary workers are employed on the farm.
Identify the agricultural resources in the scenario above and give a reason for your answer. (6)
2.8 Name THREE factors a farmer should consider when he/she combines the number of workers and level of mechanisation needed on a farm. (3)
2.9 Describe how information obtained from soil samples can lower costs and improve productivity on a farm. (4)
[50]
QUESTION 3: ENTREPRENEURSHIP, RECORDING, MARKETING, BUSINESS PLANNING AND ORGANISED AGRICULTURE
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The financial recording process begins with source documents received or handed out.
3.1.1 Distinguish between the following:
- Source document(2)
- Income Statement(3)
3.1.2 Give TWO examples of source documents used in agribusiness. (2)
3.2 Marketing research results in the identification of a target market.
3.2.1 Define the term target market. (2)
3.2.2 Name and describe the FOUR aspects (elements) in the marketing mix. (8)
3.3 The table below shows values of a crop product that was sold per week.
| QUANTITY OF PRODUCT (BAGS/WEEK) | PRICE (R/BAG) |
| 2 500 | 5 |
| 1 500 | 10 |
| 1 000 | 15 |
| 750 | 20 |
| 500 | 25 |
| 250 | 30 |
3.3.1 Use the data in the table above and draw a line graph to represent the relationship between the quantity sold and the price. (6)
3.3.2 Use the graph in QUESTION 3.3.1 and explain the relationship between price and quantity demanded. (4)
3.3.3 From the table above, determine the price where the biggest amount of produce was purchased by the consumers. Justify your answer. (2)
3.3.4 Explain the effects of the change in market prices on the quantity of products supplied by the farmer. (4)
3.4 Entrepreneurship is important for economic growth and this leads to the development of new businesses. Design a score card showing the factors that entrepreneurs in agriculture can use to evaluate a business opportunity. (6)
3.5 Study the Cash Flow Statement below.
| CASH FLOW SUMMARY | JAN. (R) | FEB. (R) | MAR. (R) |
| Opening balance | 10 000,00 | 7 200,00 | -2 800,00 |
Total income
| 2 000,00 | 15 000,00 | 33 000,00 |
Total expenses
| 4 800,00 | 25 000,00 | 5 500,00 |
| Profit/Loss | -2 800,00 | -10 000,00 | 27 500,00 |
| Closing balance | 7 200,00 |
3.5.1 Calculate the closing balance for the following months:
- February(2)
- March(2)
3.5.2 Advise the farmer on how to overcome the changes in income. (2)
3.6 In the list below, identify the description of an organisation that best suits EACH of the categories (3.6.1 to 3.6.5).
| DESCRIPTION OF ORGANISATIONS Cooperatives Transnational company Wholesaler Commission agent Processor Independent private enterprise |
3.6.1 Market agents operate on behalf of farmers or wholesalers (1)
3.6.2 Convert raw agricultural products into new products (1)
3.6.3 Specialised marketing where a pooling system is used for products (1)
3.6.4 Large organisations that operates in more than one country (1)
3.6.5 Distribute goods from producers to retailers (1)
[50]
QUESTION 4: HARVESTING, PROCESSING, MANAGEMENT AND AGRITOURISM
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Each harvesting method has its own advantages. Draw a table in the ANSWER BOOK and classify the advantages in the list below into manual harvesting and machine harvesting.
cheap, quick, selective harvesting, high productivity,
larger areas, less damage to product (6)
4.2 Give FIVE reasons for the sorting of farm products. (5)
4.3 Transport of agricultural produce bridge the gap between the producer and the processor or consumer by delivering the products.
4.3.1 Name FOUR methods of transport that can be used to deliver products. (4)
4.3.2 Explain FIVE factors that determine the method of transport that will be used for products. (5)
4.4 Name THREE types of cooling methods to protect the product against deteriorating after harvesting. (3)
4.5 Value-added products are produced from raw agricultural products.
4.5.1 Name the processing method used in each of the following food industries in South Africa:
- Baking industry
- Meat industry
- Fruit industry
- Dairy industry
- Snack industry (5)
4.5.2 Distinguish between the uses of the following heating techniques in food preservation:
- Pasteurisation(2)
- Sterilisation(2)
4.6 Name FOUR elements of effective decision-making. (4)
4.7 State TWO methods used as internal motivation for workers on a farm. (2)
4.8 Describe the following forms of agritourism:
4.8.1 Farm-stay holiday (2)
4.8.2 Ecotourism (2)
4.8.3 Domestic tourism(2)
4.9 Choose a product and name FOUR steps that you will follow from harvesting the final product until it is ready for the market. (4)
4.10 Explain how you will determine the expiring date of your processed product. (2)
[50]
TOTAL SECTION B:150
GRAND TOTAL: 200