AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2019
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MAY/JUNE2019
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 A.
1.1.1 The process during which a farm animal takes in food through its mouth:
- Egestion
- Digestion
- Ingestion
- Absorption
1.1.2 Substances given to farm animals to balance their nutrient intake are called ...
- antibiotics.
- supplements.
- enzymes.
- neutralisers.
1.1.3 A … ration is given to an unproductive farm animal.
- nutritive
- maintenance
- fodder
- production
1.1.4 The following statements refer to the adaptation features of the structure below: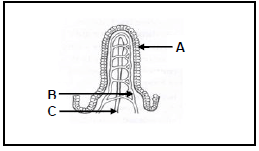
- Part B represents blood capillaries where amino acids are absorbed.
- Digested fat is absorbed in part C.
- Part A decreases the surface area for absorption.
- Absorption of glucose occurs in part B.
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
1.1.5 The production system where chickens are allowed to roam freely during the day and confined to a shed at night is called a/an … system.
- free-range
- deep-litter
- open
- cage
1.1.6 The following is NOT a result of incorrect handling of farm animals:
- Animals …
- will fear being approached.
- become agitated.
- will be much more difficult to handle.
- become tame when handled.
1.1.7 Zoonotic diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans:
- Anaemia and polyneuritis
- Anthrax and rabies
- Tuberculosis and heartwater
- Ringworm and sway-back
1.1.8 A poisonous plant with a bad smell and taste:
- Poison bulb
- Maize fungus
- Thorn apple
- Ammonia poison
1.1.9 The following occurs during lactation in cows:
- When milk production reaches its peak, the butterfat content is at its lowest.
- If a cow is fed a more fibrous feed, the milk will have a lower fat content.
- The more concentrates in a feed, the lower the fat content of the milk.
- When milk production decreases, the butterfat content reaches its peak.
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
1.1.10 The equipment used to harvest embryos from a donor cow is called a/an …
- pistolette.
- artificial vagina.
- syringe.
- Foley catheter. (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN B applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN A. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.6 B only.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B | |
| 1.2.1 |
| Movement of digested nutrients from a low to a high concentration area |
| 1.2.2 |
| The energy available for production and maintenance |
| 1.2.3 |
| Animals are kept at high densities |
| 1.2.4 |
| The larvae, nymph and adult stages occur on three different animals |
| 1.2.5 |
| The removal of the nucleus from an egg cell during cloning |
(10) (5 x 2)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for EACH of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the alimentary canal for the movement of food
1.3.2 A structure on a farm where animal feeds are stored
1.3.3 Advanced biotechnology used to produce identical offspring from an organism with superior qualities
1.3.4 The changing of the oestrus cycle of all the female animals in a herd so that they come into oestrus at approximately the same time
1.3.5 A sterile female calf born as a non-identical twin of a male calf
(5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in EACH of the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question numbers (1.4.1 to 1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Nitrogen-free extract is the measure of the protein quality of a feed.
1.4.2 Acute disease is long-lasting and recurs repeatedly in a farm animal with less severe symptoms.
1.4.3 Cryptorchidism is a condition where the testes are underdeveloped.
1.4.4 Maceration is the hardening and drying out of a dead foetus after the skeleton has been formed.
1.4.5 Fertilisation is the process during which the blastocyst attaches to the wall of the uterus. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The diagram below shows the alimentary canal of a farm animal.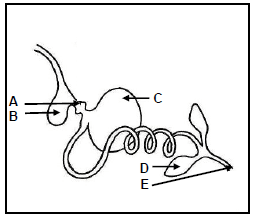
2.1.1 Name the farm animal represented in the diagram above. (1)
2.1.2 Write down the letter (A–E) of the part of the alimentary canal where EACH of the following occurs:
- Physical digestion(1)
- Egestion of undigested food(1)
- Chemical digestion(1)
2.1.3 State the role that part B plays in the digestion of food. (2)
2.1.4 Write down the letter of the part that corresponds to the stomach of a pig. (1)
2.2 Study the schematic representation below which illustrates the digestion of nutrients in the stomach and small intestine.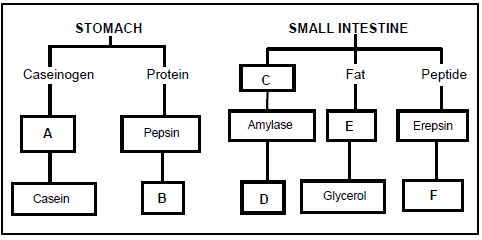
2.2.1 Name the enzymes represented by A and E. (2)
2.2.2 Identify B, C and F. (3)
2.2.3 Name the part of the small intestine where the digestion illustrated above occurs. (1)
2.2.4 Explain the importance of fat emulsification by bile during digestion.(2)
2.3 Choose ONE mineral or vitamin from the list below that matches the following descriptions. Write only the mineral or vitamin next to the question numbers (2.3.1 to 2.3.4) in the ANSWER BOOK.
iron; zinc; phosphorus; vitamin B1; vitamin A; vitamin K
2.3.1 A deficiency of this causes parakeratosis in pigs (1)
2.3.2 Improves vision, especially at night (1)
2.3.3 A deficiency of this causes animals to chew dry bones (1)
2.3.4 Necessary for blood clotting in chickens (1)
2.4 The following are the nutritive ratios of different feeds:
Feed A – 1 : 4
Feed B – 1 : 10
Feed C – 1 : 8
2.4.1 Recommend the feed (A, B or C) that a farmer can use in EACH of the following situations:
- Animals that are fattened(1)
- Lactating animals(1)
- Animals that are maintained(1)
2.4.2 Indicate the part of the ratio in Feed C that represents non-nitrogen digestible nutrients. (1)
2.4.3 Feed A is recommended for feeding a one-month-old calf. Justify this statement. (2)
2.5 A farmer used maize meal and sunflower oilcake meal to prepare a ration containing 16% DP. The DP of maize meal is 14% and the DP of sunflower oilcake meal is 45%.
2.5.1 Name a feed formulation method used to prepare a ration that contains a DP of 16% by mixing maize meal and sunflower oilcake meal. (1)
2.5.2 Use the method in QUESTION 2.5.1 to calculate the ratio of maize meal to sunflower oilcake meal. (4)
2.5.3 Calculate the percentage of sunflower oilcake meal in the mixture. (3)
2.6 State TWO roles of a good fodder flow programme. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The photographs below show TWO livestock farming systems.
3.1.1 Identify farming system A and farming system B in the photographs above. (2)
3.1.2 Compare the TWO farming systems with regard to the following:
- Purpose of the output(2)
- Impact on the environment (2)
3.1.3 State ONE disadvantage of farming system B when the hygienic measures are not observed. (1)
3.1.4 State ONE economic benefit of farming system B over farming system A for the farmer. (1)
3.2 Study the THREE facilities below that are used in an animal production enterprise.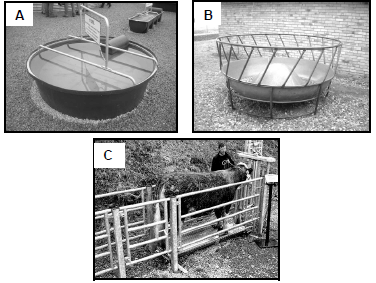
3.2.1 Identify facilities A and B. (2)
3.2.2 Indicate the purpose for which facility C is used on farms. (1)
3.3 The schematic representation below shows the life cycle of a parasite.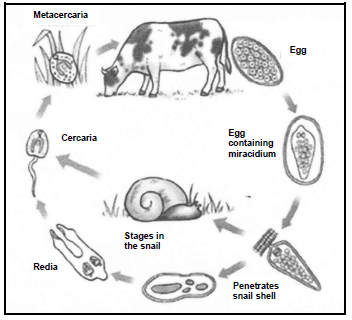
3.3.1 Classify the type of parasite above. (1)
3.3.2 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 3.3.1. (1)
3.3.3 Identify the intermediate host of the parasite in the diagram above. (1)
3.3.4 Indicate the environmental condition that is necessary for the survival of the intermediate host. (1)
3.3.5 State TWO precautionary measures that can be taken to prevent the infestation of this parasite. (2)
3.4 Farm animals should always be handled with care to avoid accidents and stress.
3.4.1 Give TWO reasons for handling farm animals. (2)
3.4.2 Indicate the effect of the following INCORRECT handling practices:
- Approaching an animal from its blind spot(1)
- Catching sheep by their wool(1)
- Putting unfamiliar animals together(1)
3.5 Briefly describe TWO basic requirements of housing for an intensive production system. (2)
3.6 The table below shows diseases caused by micro-organisms in farm animals.
| DISEASES | ORGANISMS | SYMPTOMS | ANIMALS |
| (a) | Bacteria | Swollen udder | Cows |
| Foot-and-mouth disease | (b) | Blister-like lesions on the mouth and tongue | Cattle |
| Redwater | Protozoa | (c) | Cattle |
| Lumpy wool | Fungus | Scabs grow in the wool | (d) |
| Coccidiosis | (e) | Thin watery diarrhoea | Pigs, poultry |
3.6.1 Identify (a), (b), (c), (d) and (e) above. (5)
3.6.2 State TWO roles of the government in controlling diseases in farm animals. (2)
3.7 Salt is one of the essential mineral nutrients needed by farm animals, but intake in large quantities can be fatal to livestock.
3.7.1 Name TWO symptoms of salt poisoning. (2)
3.7.2 State TWO ways of treating farm animals with salt poisoning. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The diagram below illustrates a sperm cell.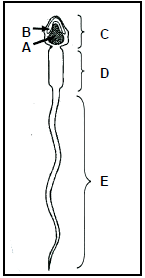
4.1.1 Identify part A in the diagram above. (1)
4.1.2 Write down the letter of the part that represents the acrosome. (1)
4.1.3 State ONE function of:
- Part D(1)
- Part E(1)
4.2 Indicate the male reproductive organ responsible for EACH of the following:
4.2.1 Transportation of semen from the epididymis to the urethra (1)
4.2.2 Secretion of a sticky alkaline mucus that gives semen a characteristic smell (1)
4.2.2 Secretion of a buffer that protects the sperm cells against pH changes (1)
4.3 The schematic representation below indicates the sequence of hormone levels resulting in changes that occur during the oestrus cycle as well as some structures involved.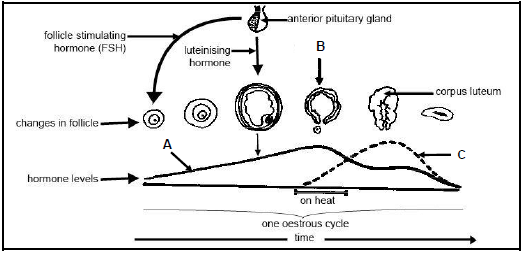
4.3.1 Define the term oestrus cycle. (2)
4.3.2 Name the process at B. (1)
4.3.3 State ONE function of the luteinising hormone. (1)
4.3.4 State THREE signs of oestrus in cows. (3)
4.4 The table below shows the duration (in days) of the different stages in the oestrus cycle in various female farm animals.
| STAGES OF THE OESTRUS CYCLE | COW | EWE | SOW | MARE |
| Pro-oestrus | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Met-oestrus | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| Di-oestrus | 14 | 10 | 13 | 12 |
Draw a bar graph of the duration (in days) of the different stages in the oestrus cycle in various female farm animals. (6)
4.5 The diagram below illustrates a technique used by farmers to improve their cattle herds.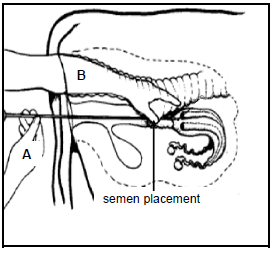
4.5.1 Identify the technique in the diagram above. (1)
4.5.2 Name TWO characteristics of high quality semen. (2)
4.5.3 Name the apparatus held by hand A in the diagram above. (1)
4.5.4 Write down the best time of the day for inseminating a cow that shows the first signs of oestrus in the evening. (1)
4.5.5 State ONE negative effect if an inexperienced person performs the technique in QUESTION 4.5.1. (1)
4.6 The statements below indicate the main stages of a reproductive technique used in cows:
- Flush the embryo from the donor cow
- Artificial insemination of the donor cow
- Super ovulation of the donor cow
- Place the embryo in the recipient cow
- Synchronisation of both the donor and recipient cows
4.6.1 Name the reproductive technique above. (1)
4.6.2 Write down the letters (A–E) that represent the FIRST TWO stages, in sequence, of the reproductive technique above. (2)
4.6.3 State TWO benefits of this reproductive technique to farmers. (2)
4.7 A fertilised diploid cell divides through mitosis to form a solid ball containing 16 cells, which will later divide to form a blastocyst.
4.7.1 Write down the term that describes a fertilised diploid cell. (1)
4.7.2 Name the solid ball containing 16 cells in the stage above. (1)
4.7.3 State TWO non-infectious causes of abortion. (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150