TECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupTECHNICAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 B ✓✓ (2)
1.2 C ✓✓ (2)
1.3 B ✓✓ (2)
1.4 C ✓✓ (2)
1.5 A ✓✓ (2)
1.6 B ✓✓ (2)
1.7 C ✓✓ (2)
1.8 A ✓✓ (2)
1.9 D ✓✓ (2)
1.10 C ✓✓ (2) [20]
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 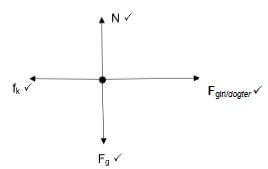 (4)
(4)
2.1.2
- fk = µkN ✓
fk = (0,2)(20)(9,8) ✓✓
= 39,2 N West ✓ (4)
2.1.3
- Fnet = fk + Fgirl✓
= (-39,2) ✓ + ( 50) ✓
= 10,8 N east ✓ (4)
2.1.4
- When a net force acts on an object of mass m, it accelerates the object in the direction of the net force. This acceleration is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ✓✓ (2)
2.1.5
- Fnet = ma ✓
10,8 = (20)a ✓
a = 0,54 m.s-2 ✓ (3)
2.2
2.2.1 Decreases ✓ (1)
2.2.2 Increases✓ (1)
2.2.3 Increases✓ (1) [20]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 When object A exerts a force on object B, object B simultaneously exerts an oppositely directed force of equal magnitude on object A. ✓✓ (2)
3.1.2 100 N due west ✓✓ (2)
3.2
3.2.1 Box thrown backward ✓✓ (2)
3.2.2 The box opposes a change in its state of rest ✓ due to its inertia ✓ according to Newton’s first law of motion. ✓ (3) [9]
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1 Impulse is the product of the net force acting on an object and the time the net force acts on the object. ✓✓ (2)
4.1.2 Vector ✓ (1)
4.1.3
- Impulse = ∆p or Impulse = m∆v ✓
Impulse = (1 500)(0 – 14) ✓✓
= (- 21 000 N.s ✓ (kg.m.s-1)
= 21 000 N.s away from the barrier (4)
4.1.4
- Fnet = Δp ✓
Δt
Fnet =-21000
0,5
Fnet = -42 000 N ✓ (3)
4.1.5
- Crumple zone helps the car to take a longer time to come to a stop ✓. Fnet∆t = ∆p, the longer the time interval, the smaller the net force acting for the same ∆p ✓.
∴ the injuries are minimised. ✓ (3)
4.2
4.2.1 Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and its velocity. ✓✓ (2)
4.2.2
- Elastic collision: A collision in which both the momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. ✓✓
- Inelastic collision: A collision in which only the momentum is conserved.✓✓ (4)
4.2.3
- The total linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant (is conserved). ✓✓ (2)
OR - Total linear momentum before collision is equal to the total linear momentum after the collision in an isolated system. ✓✓
4.2.4
- Σpbefore = Σpafter
mAvAinitial + mBvBinitial = mAvAfinal + mBvBfinal ✓ Any ONE
(800)(0) + (1000)(33) ✓ = (800)(17) + (1000)(v) ✓
v = 19,4 m.s-1 ✓ (4)
4.2.5 Inelastic ✓ (1) [26]
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 Work done is defined as the product of the force acting on an object and the displacement in the direction of the force. ✓✓ (2)
5.1.2
- W = F∆x cos θ ✓
W = (200)(5) cos 20° ✓
W = 939,69 J ✓ (3)
5.1.3 0 ✓ (J) (1)
5.1.4 Box moves with constant velocity. ✓ Net force is zero. ✓ (Hence the net work done is 0 J.) (2)
5.1.5
- No. ✓ Force of gravity is perpendicular to the direction of motion.✓✓
OR - W = F∆xcosθ ✓
= F∆xcos90o ✓
= 0 J ✓ (3)
5.2
5.2.1 Power is defined as the rate at which work is done OR rate at which energy is expended. ✓✓ (2)
5.2.2
- P = w ✓
Δt
P = (2000)(9,8)(20)
60
P = 6533,33 W ✓
P = 6533,33 = 8,76 hp / pk ✓ (4)
746
5.3
5.3.1 Sum of gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy. ✓✓✓✓ (2)
5.3.2 Energy possessed by an object due to its position above the ground. ✓✓ (2)
5.3.3 (a) Increases✓ (1) (b) Remains the same✓ (1)
5.3.4 The total mechanical energy in an isolated system remains constant. ✓✓ (2)
5.3.5
- ME (B) = mgh + 1/2 mv2 ✓
= m(9,8)(1,5) + 1/2m(8)2 ✓
= 46,7 m ✓ - ME(A) = mgh + 1/2mv2
= m(9,8)h + 0 ✓
= 9,8 mh ✓ - ME (A) = ME(B) ✓
9,8 mh = 46,7 m
h = 4,77 m ✓ (7) [32]
QUESTION 6
6.1
- A perfectly elastic body: A body which regains its original shape and size completely when the deforming force is removed. ✓✓
- A perfectly plastic body: A body that does not show a tendency to regain its original shape and size when the deforming force is removed. ✓✓ (4)
6.2 Hooke’s law: Within the limit of elasticity, ✓ stress is directly proportional to the strain.✓ (2)
6.3
6.3.1 Stress is internal restoring force per unit area of a body. ✓✓ (2)
6.3.2
- σ = F
A
σ = 200
5 × 10-5 ✓
σ = 4 000 000 Pa ✓ (3)
6.3.3
- K = σ ✓
ε
4 × 108 ✓ = 4 000 000
ε
ε = 0,01
ε = Δl
L
0,01 = Δl ✓
2
∆l = 0,02 m ✓
Final length e = 2 + 0,02 = 2,02 m ✓ (6) [17]
QUESTION 7
7.1 Viscosity is defined as the property of a fluid to oppose relative motion between the two adjacent layers. ✓✓ (2)
7.2
7.2.1 Winter ✓✓ (2)
7.2.2 10W40 ✓✓ (2)
7.2.3 5W40 ✓✓ (2)
7.3
7.3.1 Pascal's law: In a continuous liquid at equilibrium, the pressure applied at a point is transmitted equally to the other parts of the liquid. ✓✓ (2 OR 0) (2)
7.3.2
- F1 = F2 ✓
A1 A2
100 = 1200
1,2 × 10-3 A2
A2 = 0,014 m2 ✓ (3)
7.3.3 Increase the area of piston B. ✓✓ (2)
7.3.4 Bulldozer's working systems, hydraulic power brakes on automobiles, dentists' chairs, hydraulic lifts used to lift heavy loads, car jacks, or any other correct application. (ANY THREE) ✓✓✓ (3) [18]
QUESTION 8
8.1 An intrinsic semiconductor is a pure semiconductor. ✓✓ (2)
8.2 Doping is the process of adding impurities to intrinsic semiconductors. ✓✓ (2)
8.3 Phosphorous or arsenic✓✓ (2)
8.4 Negative charge/negatiewe lading ✓✓ (2) Electron [8]
TOTAL: 150