MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: FITTING AND MACHINING GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: FITTING AND MACHINING
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
1.1 A ✔ (1)
1.2 C ✔ (1)
1.3 A ✔ (1)
1.4 B ✔ (1)
1.5 D ✔ (1)
1.6 A ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 1: [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Angle grinder: (Before using)
- The safety guard must be in place before starting. ✔
- Protective shields must be placed around the object being grinded to protect the people around. ✔
- Use the correct grinding disc for the job. ✔
- Make sure that there are no cracks in the disc before you start. ✔
- Protective clothing and eye protection are essential. ✔
- Check electrical outlets and cord/plugs for any damages. ✔
- Ensure that lockable switch is disengaged. ✔
- Ensure that the disc and the nut are well secured. ✔
- Ensure that the removable handle is secured. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Welding goggles:
- To protect your eyes against sparks ✔
- To protect your eyes against heat ✔
- To be able to see where to weld ✔
- To protect your eyes from UV rays ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3 PPE for Hydraulic Press:
- Overall ✔
- Safety shoes / boots✔
- Safety goggle ✔
- Leather gloves ✔
- Face shield ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4 Workshop layouts:
- Process layout ✔
- Product layout ✔ (2)
2.5 Employer’s responsibility regarding first-aid:
- Provision of first-aid equipment ✔
- First aid training ✔
- First-aid services by qualified personnel ✔
- Any first aid procedures / treatment ✔
- Display first aid safety signs ✔
- First aid personnel must be identified by means of arm bands or relevant personal signage ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 2: [10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Bending test:
- Ductility ✔✔
- Malleability ✔✔
- Brittleness ✔✔
- Flexibility ✔✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Heat-treatment:
3.2.1 Annealing:
- To relieve internal stresses ✔
- To soften the steel ✔
- To make the steel ductile ✔
- To refine the grain structure of the steel ✔
- To reduce the brittleness of the steel ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2.2 Case hardening:
- To require a wear resistant surface ✔ and it must be tough enough internally ✔ at the core to withstand the applied loads.
- Hard case ✔ and tough core. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.3 Tempering process:
- To reduce ✔ the brittleness ✔ caused by the hardening process.
- Relieve ✔ strain ✔ caused during hardening process.
- Increase ✔ the toughness of the steel. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.4 Factors for heat-treatment processes:
- Heating temperature / Carbon content ✔
- Soaking (Time period at temperature) / Size of the work piece ✔
- Cooling rate / Quenching rate ✔ (3)
3.5 Hardening of steel:
- Steel is heated to 30 – 50°C above the higher critical temperature. (AC3) ✔
- It is then kept at that temperature to ensure (soaking) that the whole structure is Austenite. ✔
- The steel is then rapidly cooled by quenching it in clean water, brine or oil. ✔ (3)
TOTAL QUESTION 3: [14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 C ✔ (1)
4.2 A ✔ (1)
4.3 D ✔ (1)
4.4 A ✔ (1)
4.5 B ✔ (1)
4.6 A ✔ (1)
4.7 B ✔ (1)
4.8 B ✔ (1)
4.9 D ✔ (1)
4.10 C ✔ (1)
4.11 B ✔ (1)
4.12 D ✔ (1)
4.13 D ✔ (1)
4.14 C ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 4: [14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (LATHE AND MILLING MACHINE) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Advantages of using the tailstock to cut an external taper:
- Long an accurate taper can be cut. ✔
- The automatic feed can be used which result in a good finish. ✔ (2)
5.2 Calculate the compound slide set-over:
- Tan θ = D - d
2 2L
Tan θ = 60 - 28
2 2 × 85
= 0,188 ✔ ✔
θ = 10,66 º
2
OR 
- X = D - d
2
= 60 - 28
2
= 16 mm - Tan θ = 16
2 85
θ = 10,66 º (5)
2
5.3 Centre gauge:
- To measure the form and angle of the screw cutting tool angle while grinding the tool ✔
- To set the screw cutting tool square/perpendicular to the axis of the work piece ✔ (2)
5.4 Parallel key:
Length:
- Length = 1,5 × diameter
= 1,5 × 42 ✔ ✔
= 63 mm ✔ (3)
5.5 Advantages of up-cut milling:
- Deeper cuts can be made as the cutting pressure on the cutter is lower than down cut milling. ✔
- The process enables hard steel to be cut, because the total cutting pressure is absorbed by the material at the back of the edge. ✔
- Metal with hard scale, such as castings or forgings, the cut is started under the scale where the material is softer which extends the life of the cutter. ✔
- A quicker/course feed can be used. ✔
- The strain on the cutter and arbour will be less. ✔
- Vibration is limited ✔
- Good finish ✔
- Low noise level ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.6 Disadvantage of down-cut milling:
- Vibration in the arbour is unavoidable. ✔
- A fine feed must be used. ✔
- When milling a material with hard scale the milling cutter will be damaged. ✔
- Process takes time because of slower feed. ✔
- Noisy process. ✔
- Bad finish because of vibration. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.7 Methods of centring a milling cutter:
- Square and ruler method. ✔
- Set-over method by milling machine dial. ✔
- Dial indicator method ✔
- Using reference points on digital read out equipment ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 5: [18]
QUESTION 6: TERMINOLOGY (INDEXING) (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Spur gear:
Chordal tooth thickness: 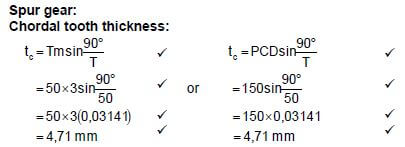 (4)
(4)
6.2 Calculate simple indexing:
- Simple Indexing = 40
N
= 40
13
= 3 1
13
= 3 1 × 3
13 3 - = 3 3
39
3 full turns and 3 holes in a 39 hole circle (4)
6.3 Differential indexing:
6.3.1 Indexing required:
- Indexing = 40 = 40
n 127
= 40 = 40 ÷ 5
A 125 5
= 8
25
Indexing 8 holes on the 25 hole circle (3)
6.3.2 Change gears required:
- Dr = A-n × 40
Dn A 1
= 125 - 127 × 40
125 1
= 2 × 40
125 1
= -80 ÷ 5
125 5
= -16 × 4
25 4
= -64
100 (5)
6.3.3 Direction of rotation of index plate:
- The index plate will turn the opposite ✔ direction as the index crank handle. (1)
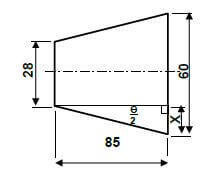
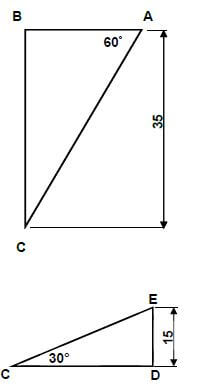
6.4 Calculate distance “x” between rollers:
- "x"=150 +2(AB)− 2(CD)− 2r
tanθ = BC
AB
AB = BC
tanθ
= 35
tan 60º
= 20,207 mm
= 20,21 mm - tanθ = DE
CD
CD = 15
tanθ
CD = 15
tan30º
= 25,98 mm 
- " x" = 150 + 2(AB) - 2(CD) - 2r
= 150 + 2 (20,21) - 2 (25,98) - 2 (15)
= 150 + 40,42 - 51,96 - 30
= 108,454m m
= 108,45 m m ✔ (9)
6.5 Reasons for balancing work piece on a centre lathe:
- Prevent unnecessary bearing loads ✔
- Prevent excessive vibration ✔
- To obtain a good finish ✔
- To prevent clatter on the gear teeth ✔
- To prevent the spindle from bending ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 6: [28]
QUESTION 7: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Hardness testers:
- Brinell-hardness tester ✔
- Rockwell-hardness tester ✔
- Vickers ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
7.2 Moment tester:
- To determine the reactions ✔ on either side of a simply loaded beam. ✔ (2)
7.3 Tensile test:
- A piece of material is subjected to an increasing axial load ✔ while measuring ✔ the corresponding elongation ✔ of the material. (3)
7.4 Depth micro-meter:
- Reading = 100 + 11,00 + 0,50 + 0,09 ✔
= 111,59 mm (5)
7.5 Measure depth:
- Vernier calliper ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 7: [13]
QUESTION 8: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Forces: 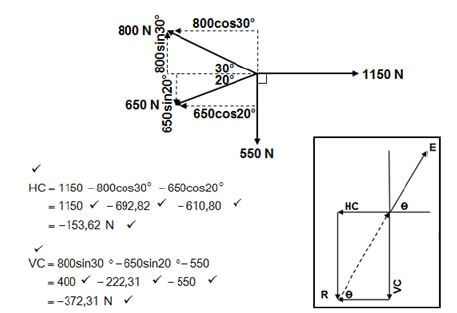 (15)
(15)
Horizontal Components | Magnitudes | Vertical Components | Magnitudes |
1150cos0° | 1150N | 1150sin0° | 0N |
800cos150° | -692,82N | 800sin150° | 400N |
650cos200° | -610,80N | 650sin200° | -222,31N |
550cos270° | 0N | 550sin270° | -550N |
TOTAL: | -153,62N | TOTAL: | -372,31N |
- E2 = HC2 + VC2
√E2 = √(53,62 + 372,312)
E = 402,76N
Tanθ = VC
HC
= 372.31
153,62
θ = 67,58º
Equilibrant = 402,76N en 67,58º North from East (15)
8.2 Moments: 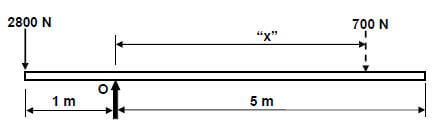
Calculate “x”:
Take moments about O.
- ∑RHM = ∑LHM
700 × "x" 2800 × 1
700 × "x" 2800
"×" = 2800
700
"x" = 4m ✔ ✔ (4)
8.3 Stress and Strain:
8.3.1 Type of stress:
- Compressive stress ✔ (1)
8.3.2 Stress:
- A = π(D2 -d2)
4
= π(0,042 - 0,032)
4
= A = 0,55 × 10σ m2
σ = F
A
= 50 × 10σ
0,55 ×10σ
σ = 90,91 × 10σ Pa
σ = 90,91 MPa ✔
(NO UNIT – NO MARK) (5)
8.3.3 Change in length:
- E = σ
ε
ε = σ
E
= 90,91 × 106 ✔
90 × 109
= 1,01 × 10-3 ✔
(IF ANY UNIT IS GIVEN – NO MARK)
- ε = ΔL
L
ΔL = ε × L
= (1,01 × 10-3) × 80
= 0,08 mm ✔ (5)
8.3.4 Safety factor:
- Safety factor = Break stress
Safe workingstress
Safe workingstress = Break stress
Safety factor
= 600 × 106
4
= 150 × 106 Pa
= 150 MPa ✔(3)
TOTAL QUESTION 8: [33]
QUESTION 9: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Lack of preventative maintenance:
- Risk of injury or death. ✔
- Financial loss due to damage suffered as a result of part failure and the waste of material. ✔
- Loss of valuable production time. ✔ (3)
9.2 Causes for the malfunctioning of chain drive systems:
- Lack of or incorrect lubrication ✔
- Lack of maintenance ✔
- Overloading ✔
- Misalignment of sprockets ✔
- Incorrect chain tension ✔
- Contamination of chain drive system such as dust or sand ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.3 Procedures to reduce the physical wear on a belt drive system:
- Check the belt alignment. ✔
- Checking the belt tension. ✔
- Prevent overloading of the system. ✔
- Keep the pulleys and belt clean. ✔
- Check that all covers are secure. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.4 Procedures to replace the belt on a belt drive system:
- Ensure that the machine is switched off ✔
- Release the tension on the belt ✔
- Remove the belt from the pulleys ✔
- Fit the correct size replacement belt onto the pulleys ✔
- Check the pulley alignment ✔
- Apply adequate tension according to specification and lock the system ✔
- (Any 5 x 1) (5)
9.5 Properties of materials:
9.5.1 Poly vinyl chloride (PVC):
- Flexible ✔
- Rubber-like substance ✔
- Makes a dull sound when dropped ✔
- Tough ✔
- Act as an insulator ✔
- It is durable ✔
- Highly resistant to oxidative material ✔
- Oil, water and chemical resistant ✔
- (Any 1 x 1) (1)
9.5.2 Carbon fibre:
- Strong ✔
- Tough ✔
- Light weight ✔
- Good electrical conductor ✔
- (Any 1 x 1) (1)
9.6 Difference between “Thermoplastic” and “Thermo hardened (thermosetting)” composites:
- Thermoplastics can be reheated and deformed. / Recyclable ✔
- Thermo hardened cannot be reheated. / Non-recyclable ✔ (2)
9.7 Examples of thermo hardened composites:
- Carbon fibre or (Any application) ✔
- Glass fibre or (Any application) ✔
- Bakelite or (Any application) ✔
- Teflon or (Any application) ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 9: [18]
QUESTION 10: JOINING METHODS (SPECIFIC)
10.1 Square thread:
10.1.1 The lead of the thread:
- Lead = pitch × no of starts
= 5 × 2 ✔
= 10 mm ✔ (2)
10.1.2 The helix angle of the thread:  (5)
(5)
10.1.3 The leading tool angle:
- Leadingtoolangle 90º helix angle + clearanceangle
= 90º - (2,29º + 3º)
= 84,71º /84º 42'36"
OR - Leadingtoolangle 90º helix angle + clearanceangle
= 90º - (7,17º + 3º)
79,83º / 79º 49'48" (2)
10.1.4 The following tool angle:
- Followingtoolangle = 90º + (helix angle - clearanceangle)
= 90º + (2,29º - 3º)
= 89,29º /89º 17'24"
OR - Following toolangle = 90º + (helix angle - clearanceangle)
= 90º + ( 7,17º - 3º)
= 94,17º / 94º 10'12" (2)
10.2 Measurements of a screw thread :
10.2.1 Metric screw thread ✔ (1)
10.2.2 Crest / Major / External / Basic / Nominal / Outside diameter ✔ (1)
10.2.3 Pitch ✔ (1)
10.3 Angles of a square thread cutting tool:
- A – Helix angle ✔
- B – Clearance angle ✔
- C – Leading tool angle ✔
- D – Following tool angle ✔ (4)
TOTAL QUESTION 10: [18]
QUESTION 11: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (DRIVE SYSTEMS) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 Advantages of a belt drive system compared to a chain drive system:
- Silent operation ✔
- Less expensive ✔
- Drive can take place over a longer distance ✔
- No lubrication needed ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
11.2 Hydraulics:
11.2.1 Fluid pressure:  (4)
(4)
11.2.2 Diameter of the ram:  (6)
(6)
11.3 Hydraulic symbols: One-way valve  (1)
(1)
11.4 Belt drives:
Rotation frequency of the drive pulley:
- NDRDDR = NDNDDN
NDR = NDN × DDN
DDR
= 80 × 240
75
= 256 r/min ✔ ✔ ✔ (4)
11.5 Gear drives:
11.5.1 Rotation frequency of the output:
- NA = Product of Driven gears
ND Product of Driver gears
ND = TA × TC
NA TB × TD
ND = TA × TC × NA
TB × TD
= 20 × 25 × 3000
35 × 30
ND = 1428,57 r/min
60
= 23,81 r/sec ✔
OR  (6)
(6)
11.5.2 Gear ratio:
- Gear ratio = Product of the number of teeth on driven gears✔
Product of the number of teeth on driver gears
=35 × 30
20 25
= 2,1 : 1 (3)
11.6 Work done:
- Work done F × s
= 250 × 15
= 3750 Jouleor N.m ✔(2)
TOTAL QUESTION 11: [28]
TOTAL: 200
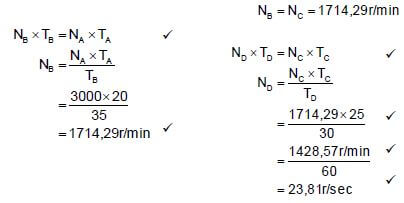 (6)
(6)