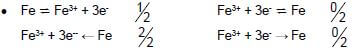PHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupPHYSICAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 C ✔✔ (2)
1.2 C ✔✔ (2)
1.3 C ✔✔ (2)
1.4 A ✔✔ (2)
1.5 D ✔✔ (2)
1.6 B ✔✔ (2)
1.7 B ✔✔ (2)
1.8 D ✔✔ (2)
1.9 D ✔✔ (2)
1.10 B ✔✔ (2) [20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 ANY ONE
- (Alcohol/ethanol) is flammable/catches fire easily.
- To heat it evenly.
- Water bath is used for low heat/low temperature.
- Alcohol/ethanol will evaporate too quickly.
Accept/
(Alcohol/ethanol) is volatile. (1)
2.2
2.2.1 Esterification/condensation (1)
2.2.2 H2SO4 (1)
2.2.3 Esters (1)
2.3
- M(ester) = 144 = 2
M(C4H8O) 72
∴ 2 x C4H8O = C8H16O2
Marking guidelines:
- If only answer given, award 2 marks on final
- If 72 g·mol-1 calculated without substituting, no mark is awarded (2)
2.4 Ethyl hexanoate (2)
Note
- Accept any other ethyl ESTER from QUESTION 2.3.
2.5 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 2.4.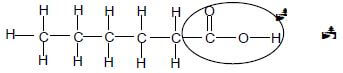
Marking criteria
- Whole structure correct 2/2
- Only functional group correct : Max: 1/2
- Accept -OH as condensed (2)[10]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Marking guidelines/
- If any one of the underlined key phrases in the correct context is omitted, deduct 1 mark
- The temperature at which the vapour pressure of a substance equals atmospheric/external pressure. (2)
3.2
3.2.1Carboxyl (group)
Accept
- Carboxylic (1)
3.2.2 Propanoic acid/propanoësuur (1)
3.2.3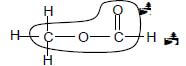
Marking criteria
- Whole structure correct: 2/2
- Only functional group correct: 1/2
IF
- More than one functional group/wrong functional group 0/2
- If condensed structural formulae used: Max: 1/2
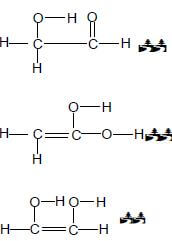
3.3 A - Lowest boiling point./Shortest chain length.
3.4
3.4.1 The same molecular mass/molecular size.
3.4.2 Primary
- OH group is bonded to a C atom bonded to one other C atom.
OR - OH group is bonded to a C atom that has two H atoms.
3.4.3 Marking guidelines
- BOTH have hydrogen bonding.
- Compare number of sites for hydrogen bonding.
- Compare strength of IMFs.
- Compare energy required.
- Both compounds/X and B have (in addition to London forces and dipole-dipole forces) hydrogen bonding.
- Compound X/CH3CH2CH2OH/propan-1-ol/alcohol has one site for hydrogen bonding and compound B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid has two/more sites for hydrogen bonding OR B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid has two/more sites for hydrogen bonding.
- Intermolecular forces in compound B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid are stronger than intermolecular forces in compound X/CH3CH2CH2OH/ propan-1-ol/alcohol.
OR
Intermolecular forces in compound X/CH3CH2CH2OH/ propan-1-ol/alcohol are weaker than intermolecular forces in compound B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid. - More energy is needed to overcome/break intermolecular forces in compound B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid than in compound X/CH3CH2CH2OH/ propan-1-ol/alcohol.
OR
Less energy is needed to overcome/break intermolecular forces in compound X/CH3CH2CH2OH/propan-1-ol/alcohol than in compound B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid. (4) [15]
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.
- (A series of organic) compounds that can be described by the same general formula/functional group. (2 or 0)
OR
(A series of organic) compounds in which one member differs from the next by a CH2 group (2)
4.1.2 Substitution/halogenation/bromination (1)
4.1.3 HBr (1)
4.1.4 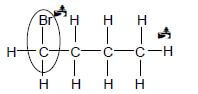
Marking criteria
- Br on first C atom: Max: 1/2
- Whole structure correct 2/2
IF
- Br2 but rest of structure correct (2)
4.1.5 C5H12 + 8O2 → 5CO2 + 6H2O Bal
Marking guidelines
- Reactants Products Balancing
- Ignore double arrows and phases.
- Marking rule 6.3.10/Nasienreël 6.3.10.
- If condensed structural formulae used : Max: 2/3 (3)
4.1.6 Marking guidelines/Nasienriglyne
- If any one of the underlined key phrases in the correct context is omitted, deduct 1 mark
The (chemical) process in which longer chain hydrocarbons/longer chain alkanes are broken down to shorter/more useful hydrocarbons/molecules/ chains/alkanes and alkenes. (2)
4.1.7 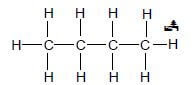
Marking guidelines
- One or more H atoms omitted : Max: 1/2
- Condensed or semi-structural formula:Max: 1/2 (2)
4.2
4.2.1 Butan-2-ol OR 2-butanol
IF:
- Butanol or butan-1-ol 1/2 (2)
4.2.2 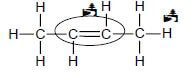
Marking criteria
- Only functional group correct: Max/Maks: 1/2
- Whole structure correct: 1/2 (2) [17]
QUESTION 5
5.1Temperature (1)
5. 2 NOTE
Give the mark for per unit time only if in context of reaction rate.
ANY ONE
- Change in concentration of products/reactants per (unit) time.
- Change in amount/number of moles/volume/mass of products or reactants per (unit) time.
- Amount/number of moles/volume/mass of products formed/reactants used per (unit) time.
- Rate of change in concentration/amount/number of moles/volume/mass. (2 or/of 0) (2)
5.3 14 (min) (2)
5.4
5.4.1 Graph B
- (Experiment 3) has the highest (acid) concentration/more particles/higher number of moles. (2)
5.4.2 (Graph/grafiek) C
- (Experiment 5) is at highest temperature/more particles with sufficient kinetic energy/HCℓ is at 35oC (2)
5.5
5.5.1 Speeds up the reaction./Increases the reaction rate./Provides alternate pathway./Lowers the (net) activation energy. (1)
5.5.2 Equal to (1)
5.6 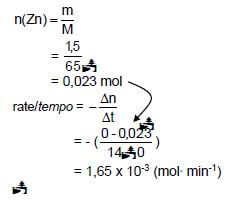
Marking guidelines
- Substitute 65 g∙mol-1 in n = m
M - Substitute change in mol to calculate rate.
- Substitute change in time to calculate rate.
- Final answer:
1,65 x 10-3 mol∙min-1
Range/Gebied:
1,43 x 10-3 to/tot 1,65 x 10-3 (mol∙min-1)
Notes
- Ignore if zeros omitted in calculation of reaction rate.
- Accept negative answer i.e. -1,65 x 10-3 mol·min-1 (4) [15]
QUESTION 6
6.1
- When the equilibrium in a closed system is disturbed, the system will re- instate a (new) equilibrium by favouring the reaction that will cancel/oppose the disturbance. (2)
6.2 Endothermic
- Decrease in temperature favours the exothermic reaction.
- The reverse reaction is favoured.
OR
Number of moles/amount/concentration of N2O4/colourless gas increases.
OR
Number of moles/amount of NO2/brown gas decreases. (3)
6.3
6.3.1 Increases (1)
6.3.2 Remains the same (1)
6.3.3 Increases (1)
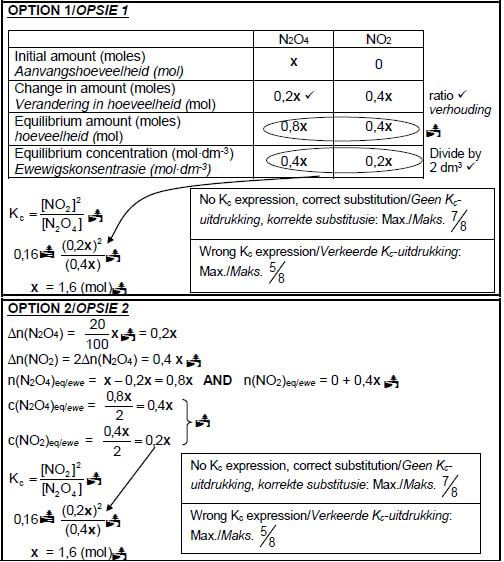
6.4 CALCULATIONS USING NUMBER OF MOLES
Marking guidelines/Nasienriglyne
- ∆n(N2O4) = 20% of x/0,2x.
- USE ratio: N2O4 : NO2 : = 1 : 2.
- n(N2O4)eq/ewe = n(N2O4)initial/begin - ∆n(N2O4).
- n(NO2)eq/ewe = n(NO2)initial/begin + ∆n(NO2).
- Divide equilibrium moles by 2 dm3
- Correct Kc expression (formulae in square brackets).
- Substitution of Kc value
- Substitution of concentrations into correct Kc expression.
- Final answer/Finale antwoord: 1,6 (mol)
CALCULATIONS USING CONCENTRATION
Marking guidelines
- Initial n(N2O4)/x divide by 2 dm3.
- ∆c(N2O4) = 20% of initial concentration/0,1x.
- USE ratio/GEBRUIK verhouding: c(N2O4) : c(NO2) = 1 : 2.
- c(N2O4)eq/ewe = c(N2O4)initial/begin - ∆c(N2O4).
- c(NO2)eq/ewe = c(NO2)initial/begin + ∆c(NO2).
- Correct Kc expression (formulae in square brackets).
- Substitution of Kc value/Vervanging van Kc-waarde.
- Substitution of concentrations into Kc expression.
- Final answer/Finale antwoord: 1,6 (mol)
OPTION 3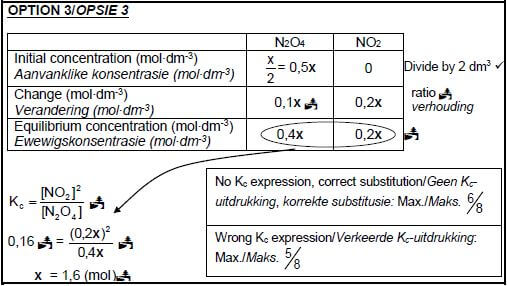 (8) [16]
(8) [16]
QUESTION 7
7.1
7.1.1 An acid is a proton donor. (2)
7.1.2 H2O (1)
7.1.3 HSO-4 (2)
7.2
7.2.1 Reaction of a salt with water/H2O.
Accept
- Reaction of cations or anions with water (2)
7.2.2 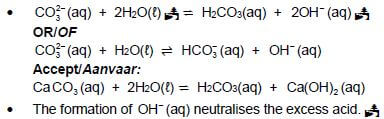
Marking guidelines
- Reactants Products
- The formation of OH (aq) neutralises the excess acid.
- Ignore single arrows and phases
- Marking rule 6.3.10
- Ignore balancing.
7.3
7.3.1
- pH = -log[H3O+]
5 = -log[H3O+]
[H3O+] = 1 x 10-5 mol·dm-3 (3)
7.3.2 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 7.3.1.
Marking guidelines
- Any formula : c = n / n = m / Ca x Va =na /c = m
V M Cb x Vb nb MV - Substitute V = 4 x 109 dm3
- Calculate na(reacted) = na(initial) - na(final)
- Use n(CaO) : n(H3O+) = 1:2
- Substitution of 56 g∙mol-1
- Final answer : m = 1,08 x 106 g to/tot 1,09 x 106 g
IF final answer is negative: Max: 6/7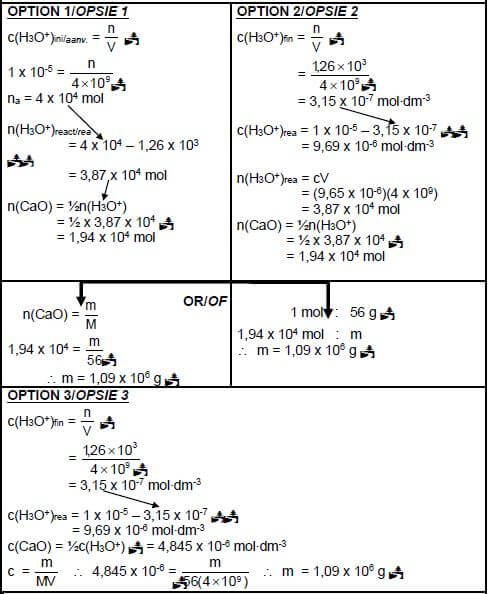 (7) [20]
(7) [20]
QUESTION 8
8.1
8.1.1 Loss of electrons./Verlies aan elektrone. (2 or/of 0) (2)
8.1.2 Fe → Fe3+ + 3e-
Marking guidelines
-

- Ignore if charge omitted on electron.
- If charge (+) omitted on Fe3+: Example: Fe → Fe3 + 3e-
Max1/2 (2)
8.1.3 Reducing agent (1)
8.1.4
- Fe is a stronger reducing agent than Cu and (Fe) will be oxidised (to Fe3+).
OR - Cu is a weaker reducing agent than Fe and (Cu) will not be oxidised (to Cu2+). (3)
8.1.5 Zinc/Zn
- Stronger reducing agent (than Fe).
OR - Zn will undergo oxidation (before Fe).
OR - Cu is a weaker reducing agent (than Fe). (2)
8.2
8.2.1 3Cu2+ + 2Fe → 3Cu + 2Fe3+ Bal.
Marking guidelines/Nasienriglyne
- Reactants Products Balancing
- Ignore double arrows.
- Marking rule 6.3.10 (3)
8.2.2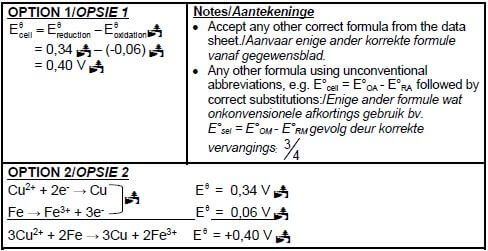
(4) [17]
QUESTION 9
9.1
- A cell in which electrical energy is converted to chemical energy. (2 or 0)
OR - A cell in which electrical energy/electricity is used to obtain a chemical change/reaction. (2 or 0) (2)
9.2 Any soluble copper(II) salt e.g
- CuSO4/Cu(NO3)2/CuCℓ2 (1)
9.3 Marking guidelines

- Ignore if charge on electron is omitted.
- If a charge of an ion is omitted e.g. Cu2 + 2e- → Cu Max.: 1/2 (3)
9.4 Platinum/Pt AND silver/Ag/ (2) [8]
QUESTION 10
10.1
10.1.1 Haber (process)
10.1.2 Ostwald (process)
10.2
10.2.1Ammonium nitrate/Ammoniumnitraat/NH4NO3
10.2.2 Iron/iron oxide/Fe/FeO
10.3
- 2NH3 + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4 Bal
Marking guidelines
- Reactants Products Balancing
- Ignore double arrows.
- Marking rule 6.3.10
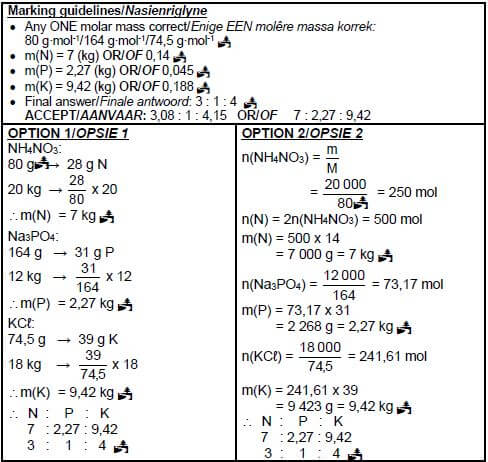
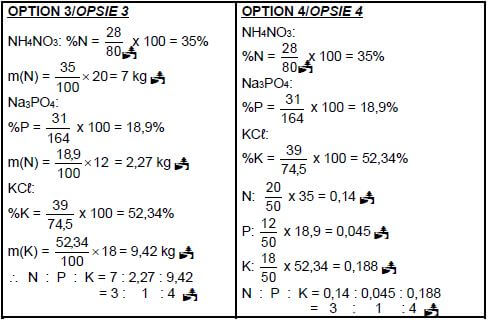 (5)
(5)
[12]
TOTAL: 150