LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupLIFE SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C ✔✔
1.1.2 B✔✔
1.1.3 C✔✔
1.1.4 B✔✔
1.1.5 A✔✔
1.1.6 C✔✔
1.1.7 C✔✔
1.1.8 D✔✔
1.1.9 B✔✔
1.2
1.2.1 Hydrogen✔bonds
1.2.2 Genome✔
1.2.3 Cultural✔evidence
1.2.4 Speciation✔
1.2.5 Haemophilia✔
1.2.6 Foramen magnum✔
1.2.7 Alleles✔
1.2.8 Discontinuous✔variation
1.2.9 Gonosomes
1.3
1.3.1 A only✔✔
1.3.2 Both A and B✔✔
1.3.3 A only✔✔
1.4
1.4.1
- D- Chromatid✔
E- Centromere✔
1.4.2 23✔ pairs
1.4.3
- E✔
- C✔/B
1.4.4
- Nucleus✔
Mitochondrion✔
(Mark first TWO only) - Double helix✔
- (DNA) Replication✔
1.5
1.5.1 Phylogenetic tree✔/ cladogram
1.5.2 An exoskeleton✔
1.5.3
- S✔
- T✔
1.5.4
- Trilobites✔
- Helmetids✔ or (b)Tegopeltids✔
- Tegopeltids✔ (c) Helmetids✔
- Naraoids✔
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1
- Due to non-disjunction✔/ Non-separation of a chromosome pair
- during Anaphase I✔
- Two chromosomes moved to the one pole✔ and
- none moved to the other pole✔ Any (3)
2.1.2
- Gamete A will have 24 chromosomes✔/an extra chromosome
- and when it fertilises a normal ovum✔/gamete with 23 chromosomes
- the zygote will have 3 chromosomes at position 21✔/ 47 chromosomes (3)
2.1.3
- Prophase I✔ (1)
-
- Adjacent chromatids of homologous chromosomes cross✔
- at a point called the chiasma✔
- There is an exchange of DNA segments✔/genetic material (3)
-
- Crossing over introduces genetic variation✔ in gametes
- Genetic variation may result in favourable characteristics✔
- that ensure a better chance of survival✔
- when environmental conditions change✔
OR - Crossing over introduces genetic variation ✔ in gametes
- Genetic variation may result in unfavourable
- characteristics✔
- that reduce the chance of survival✔
- when environmental conditions change✔ Any (3) (13)
2.2
2.2.1
- Female without SCID✔(1)
- Male with SCID✔ (1)
- XDXd✔✔ (2)
2.2.2
- He inherited the recessive allele✔ /Xd
- from the mother✔/individual 4 (2) (6)
2.3
2.3.1
- It allows for the production of organisms with desired characteristics✔/ high average milk yield (1)
(Mark first ONE only) -
- It reduces genetic variation✔ in offspring
- It results in no further genetic improvement✔
- It is expensive✔
- It may not be economical for commercial agriculture✔
(Mark first ONE only) Any (1)
2.3.2 LMJC 865 had a high average milk-production yield✔/ produced 78 litres per day/ had the desired characteristic (1)
2.3.3
- A diploid cell✔/ a cell with all the genetic information is needed
- An ovum is a haploid cell✔/ only contains half of the genetic information (2)
2.3.4
- The nucleus of an ovum is removed✔ and replaced with
- the nucleus of a somatic donor cell✔/ diploid donor cell
- The zygote is stimulated✔
- for mitosis✔ to occur
- The embryo is then placed into the uterus of an adult femal✔
OR - Plants may be cloned by vegetative reproduction✔/asexual reproduction /tissue culture/grafting
- A plant with the desired characteristics is selected✔
- A vegetative part of the “parent” plant structure is removed✔/(examples) and
- placed inside a growth medium✔/(examples)
- and allowed to grow✔ Any 4 (4) (9)
2.4
2.4.1 Purple✔ (1)
2.4.2
- When purple-flowering plants and white-flowering plants are crossed ✔
- all the offspring have purple flowers✔ /have no white flowers (2)
2.4.3
- The two alleles for a characteristic ✔
- separate during meiosis✔ so that
- each gamete contains only one allele✔ for that characteristic (3)
2.4.4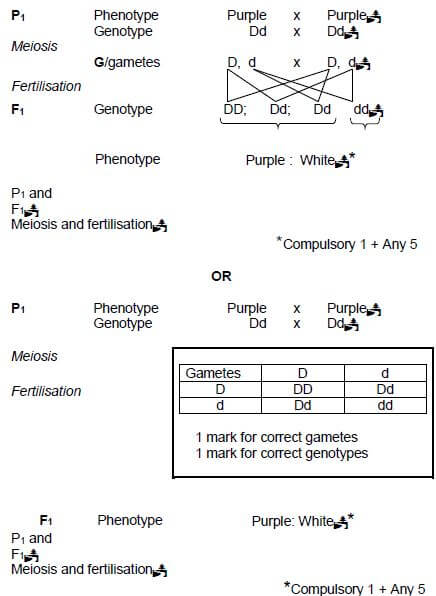
*Compulsory 1 + Any 5 [40]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1
- The jaw is large in the chimpanzee✔and small in Homo sapiens✔
- The jaw/ palate is rectangular in the chimpanzee✔and rounded in Homo sapiens✔
- Large spaces between the teeth in the chimpanzee✔ and small/no spaces in Homo sapiens✔
- Large canines/teeth in the chimpanzee✔ and small canines/teeth in Homo sapiens✔Any 1 x 2 (2)
(Mark first ONE only)
3.1.2
- The diet changed from eating raw food✔ in Australopithecus
- to a diet of cooked food✔ in Homo sapiens (2)
3.1.3
- A transitional species shows intermediate characteristics between two genera/species✔
OR
It has characteristics common to both the ancestor species and the species that follows✔ (1) - The jaw is smaller than that of the chimpanzee but larger than that of Homo sapiens✔✔
OR
The canines/ teeth are smaller than those of the chimpanzee but larger than those of Homo sapiens✔✔
OR
The jaw/ palate shape is more rounded than that of the chimpanzee but less rounded than that of Homo sapiens✔✔
Any 1 x 2 (2)
(Mark first ONE only) (7)
3.2
3.2.1
- The bright colour pattern is associated with being poisonous✔
- thus reducing predation✔ and
- improving the chances of survival✔ (3)
3.2.2
- There is variation in the colour of kingsnakes✔
- Some are bright in colour✔/resemble the coral snakes and
- the others are dull in colour✔
- Those with dull colours are killed✔ by predators
- Those with bright colours are not eaten✔
- so they survive✔and reproduce,
- passing on the allele for bright colour to the next generation✔
Any 6 (6)(9)
3.3
3.3.1 1900✔ (1)
3.3.2
- {80/20 x 100 = 400✔%
OR
{(100−20)} x 100 = 400✔%
20
3.3.3
| Natural selection | Artificial selection |
| The environment or nature is the selective force | Humans represent the selective force |
| Selection is in response to suitability to the environment | Selection is in response to satisfying human needs |
| Occurs within a species | May involve one or more species (as in cross breeding) (5) |
1 for Table + Any 2 x 2 (9)
(Mark first TWO only)
3.4
3.4.1
- They invade farm fields
- They outcompete the crop plants for space Any (1)
3.4.2
- Type of herbicide (1)
- Time taken for development of resistance (1)
3.4.3
- Dicloflop (1)
- Trifluralin (1)
3.4.4
-
- They would apply the herbicide to the weed and
- observe if the weed survives over many generations (2)
-
- They used the same weed species as other weed species may have developed resistance to that herbicide
- Each weed species may respond differently to a herbicide
OR - It allows for a single variable
- to which all results can be attributed (2)
3.4.5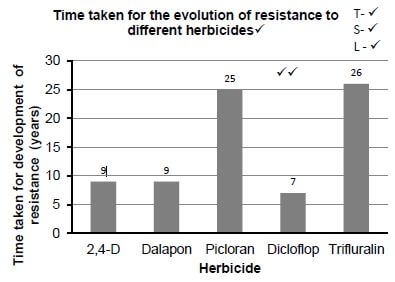
Guideline for assessing the graph
Type: Bar graph drawn (T) | 1 |
Title of graph | 1 |
Correct:
| 1 |
Correct:
| 1 |
Plotting of bars | 1- 1 to 4 bars plotted correctly 2- All 5 bars plotted correctly |
(6)(15)[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Structure (S)
- RNA is single stranded✔
- and is made up of nucleotides✔which comprise:
- ribose✔ sugar
- phosphate✔group
- nitrogenous bases✔ which are
- adenine, uracil, guanine and cytosine✔/ (A, U, G and C)
- The phosphate group is attached to the ribose sugar✔
- and the nitrogenous base is attached to the ribose sugar✔
- Bases on RNA are arranged in triplets✔
- as codons on mRNA✔
- and anticodons on tRNA✔
- tRNA has a clover-leaf✔/hairpin structure
- tRNA has a place of attachment for an amino acid✔
Any (9)
Involvement in protein synthesis (P)
- mRNA✔ forms
- during transcription✔/by copying the coded message from DNA
- and moves out of the nucleus✔
- and attaches to the ribosome✔
- During translation✔
- the anticodon matches the codon✔
- tRNA✔
- brings the required amino acid✔ to the ribosome
- Amino acids become attached by peptide bonds✔
- to form the required protein✔
Any (8)
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
(20)
ASSESSING THE PRESENTATION OF THE ESSAY
Criterion | Relevance (R) | Logical sequence (L) | Comprehensive (C) |
Generally | All information provided is relevant to the question | Ideas are arranged in a logical/cause-effect sequence | All aspects required by the essay have been sufficiently addressed |
In this essay in Q4 | Only information relevant to the:
There is no irrelevant information | All the information regarding the
| At least:
|
Mark | 1 | 1 | 1 |
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150