LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - 2018 SEPTEMBER PREPARATORY EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupLIFE SCIENCES PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
SEPTEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answer to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- ALL drawings MUST be done in pencil and labelled in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, flow charts or tables ONLY when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You must use non-programmable calculators, protractor and a compass, where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The phase in meiosis during which individual centromeres split is …
- anaphase I.
- anaphase II.
- metaphase I.
- metaphase II.
1.1.2 What is biogeography?
- The study of fossil organisms in order to learn about earlier forms of life.
- The idea that worldwide disasters have caused the widespread extinction of species.
- The idea that Earth and all living things have been created in their present forms and are unchangeable.
- The observed patterns of distribution of species.
1.1.3 A mutation is any change …
- that is harmful to an organism.
- in a gene or chromosome.
- that is useful to an organism.
- in the phenotype of a cell.
1.1.4 The scientist who came up with the law of inheritance of acquired characteristics is …
- Gregor Mendel.
- Charles Darwin.
- Lee Berger.
- Jean Baptiste de Lamarck.
1.1.5 Which statement concerning a pair of alleles for a gene controlling a single characteristic in humans is true?
- Both alleles come from the father.
- Both alleles come from the mother.
- One allele comes from the mother and another allele comes from the father.
- The alleles come randomly in pairs from either the mother or father.
1.1.6 Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive trait in humans.
What will the result of mating between normal (non-carrier) female and a male with haemophilia be?
- Half of the daughters are normal and half of the sons have haemophilia.
- All daughters are carriers and all sons are normal.
- All daughters are normal and all sons are carriers.
- Half of the sons are normal, half have haemophilia and all daughters are carriers.
1.1.7 The diagram below shows the nucleus of a diploid cell with two pairs of homologous chromosomes.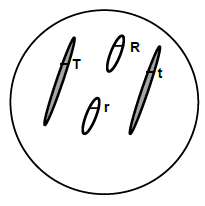
Due to independent assortment, what is the possible genetic make-up of gametes produced by this organism?
- RrTt
- Rr, Tt
- R, r, T, t
- RT, Rt, rT, rt
1.1.8 A gene in cattle controls whether horns develop or not. When cattle without horns are mated together, none of the offspring ever have horns.
A male with horns is mated with a female without horns.
If half of the offspring have horns and half do not, what is the conclusion?
- The male is homozygous dominant
- The male is homozygous recessive
- The male is heterozygous
- Only males have horns
1.1.9 Which graph BEST illustrates the expected change in the finch population if the environment changes to favour small beaks?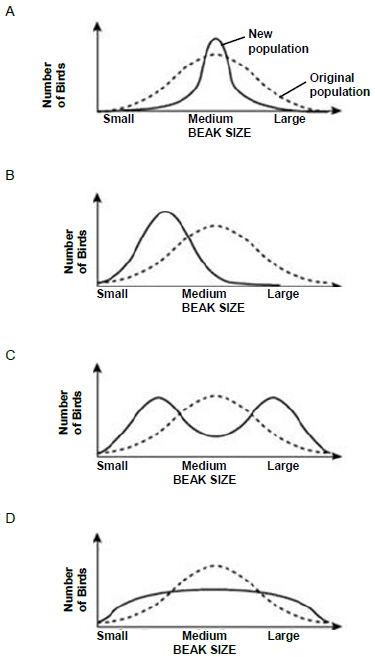
1.1.10 Study the following list of concepts in evolution.
- Similarities in protein synthesis
- Evidence for evolution
- Common ancestry
Which ONE of the following combinations can be deduced by studying the percentage DNA between species?
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- Only (i) and (ii)
- Only (ii) and (iii)
- Only (i) and (iii) (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.9) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 Differences amongst individuals within a species
1.2.2 Chromosomes that are not responsible for sex determination
1.2.3 The preserved remains of ancient organisms
1.2.4 The different forms of a gene coding for a single trait
1.2.5 A genetic disorder characterised by the absence of a clotting factor
1.2.6 The use of living organisms and their biological processes to improve the quality of human life
1.2.7 A diagram showing evolutionary relationships amongst species
1.2.8 An opening in primate skulls through which the spinal cord passes
1.2.9 Evidence contained in the female line to support the Out of Africa Hypothesis
(9 x 1) (9)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN Ι applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B, or NONE of the items in COLUMN ΙΙ. Write A only, B only, both A and B, or none next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| COLUMN I | COLUMN II |
| 1.3.1 The importance of meiosis |
|
| 1.3.2 A possible explanation for an observation that can be tested by an experiment |
|
| 1.3.3 Variation that results in distinct phenotypes |
|
(3 x 2) (6)
1.4 Study the diagram below.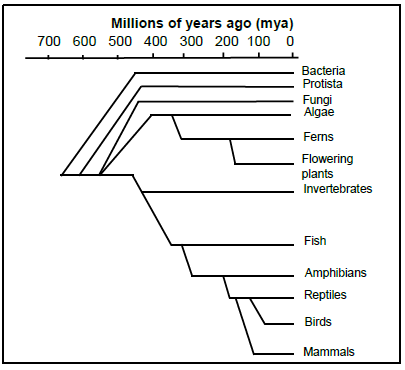
1.4 According to the diagram:
1.4.1 How many million years ago did fungi appear on Earth? (1)
1.4.2 Which were the first organisms to appear on Earth? (1)
1.4.3 Which group is the most recent ancestor to flowering plants? (1)
1.4.4 Which group appeared on Earth most recently? (1)
1.4.5 Which group of organisms is most closely related to the birds? (1)
1.4.6 Give a reason for your answer in QUESTION 1.4.5. (1)
1.5 The diagram below shows a process that could be used in the future to produce a human without sexual reproduction.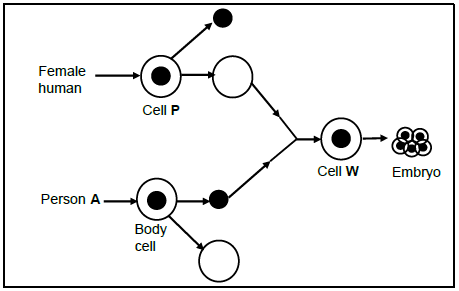
1.5.1 Name the process shown above. (1)
1.5.2 Identify cell P. (1)
1.5.3 The embryo must be placed in an adult female to develop into a child.
Where, in the adult female, should the embryo be placed? (1)
1.5.4 If this technique was used in a human, how many chromosomes would be found in cell W? (1)
1.5.5 If this process were to be allowed to be used in humans in future, describe ONE way in which it would be of benefit to humans. (1)
1.6 List FOUR mechanisms of reproductive isolation. (4)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 The following sequence represents a part of the nitrogenous base sequence on a DNA molecule.
| TAC | TCT | CCA |
| triplet 1 | triplet 2 | triplet 3 |
2.1.1 Write down the base sequence of the anticodon of triplet 1 shown above. (1)
2.1.2 The table below shows the amino acids that correspond with different mRNA codons.
| mRNA codon | AMINO ACID |
| AGA | Arginine |
| AUG | Methionine |
| GGU | Glycine |
| AUC | Isoleucine |
- Write down the correct sequence of amino acids for DNA triplets 1 to 3. (2)
- During DNA replication a mutation occurred on triplet 1 resulting in C being replaced by G. Describe how this mutation will affect the structure of the protein formed. (3)
2.2 In rabbits the dominant allele (B) produces black fur and the recessive allele (b) produces white fur. Study the genotypes of four rabbits.
| Rabbit | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Genotype | BB | Bb | Bb | bb |
2.2.1 Give the phenotypes of:
- Rabbit 2 (1)
- Rabbit 4 (1)
2.2.2 State the genotypic ratio that is shown in the table above. (2)
2.2.3 If rabbits 1 and 4 were mated together and had 12 offspring, how many of these would you expect to be black? (1)
2.2.4 Rabbit 3 was allowed to breed with rabbit 4. Use a genetic cross to show the possible phenotypes and genotypes of the F1 generation for fur colour. (6)
2.3 The diagram below shows a phase of meiosis.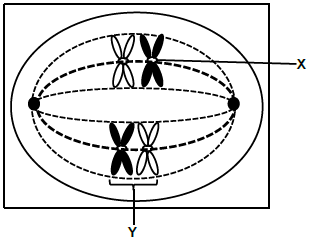
2.3.1 Name the parts labelled X and Y. (2)
2.3.2 Name the phase of shown. (1)
2.3.3 Describe the chromosomal behaviour named in QUESTION 2.3.2. (3)
2.3.4 Explain ONE importance of the chromosomal behaviour in QUESTION 2.3.3. (2)
2.4 The diagram below shows two species of pistol shrimp (A and B). The shrimps live in shallow, tropical seas on opposite sides of Panama. Panama is a narrow strip of land which today joins North America and South America. It was formed by land moving up from beneath the sea. Panama has separated the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea for the past 3 million years.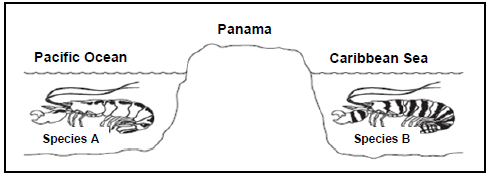
2.4.1 Describe how the two species of pistol shrimp could have developed from an ancestral species of shrimp. (7)
2.4.2 Explain what effect the process you described in QUESTION 2.4.1 had on the biodiversity of the pistol shrimp. (2)
2.5 Three babies (X, Y and Z) from three different sets of parents were born in a hospital. TWO of the babies were accidentally swopped. Blood groups of the parents were used to determine which baby belonged to which set of parents.
The blood groups of the parents and the babies they were given are shown in the table below.
| BABIES | BLOOD GROUPS OF PARENTS AND BABIES | |||
| Mother | Father | Baby | ||
| Mr and Mrs Muko | X | B | A | A |
| Mr and Mrs Zifo | Y | AB | B | O |
| Mr and Mrs Bata | Z | O | B | AB |
2.5.1 Of the alleles that code for blood groups, which alleles are codominant? (2)
2.5.2 Which TWO babies (from X, Y and Z) were swopped? (2)
2.5.3 Assume that Mr Muko is heterozygous for blood group A.
Give the possible genotype of Mrs Muko that will result in baby X. (2)
[40]
QUESTION 3
3.1 The following diagram shows the inheritance of a particular autosomal disease in humans.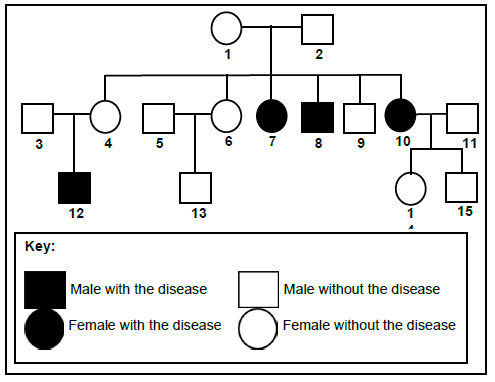
3.1.1 Name the type of diagram represented above. (1)
3.1.2 Is the disease inherited as a dominant trait or a recessive trait? (1)
3.1.3 Give a reason for your answer in QUESTION 3.1.2. (2)
3.1.4 If N represents the dominant allele and n the recessive allele.
Use these letters to assign the genotype of individual:
- 1 (1)
- 12 (1)
3.1.5 Suppose individual 11 has no family history of the disease.
Explain the probability of individual 10 and 11 having a child with the disease. (3)
3.2 Salmonberry plants produce ripe fruits that occur in two colours, red and orange. These fruits are eaten by birds and in so doing, they assist in seed dispersal.
Birds appear to choose fruits based on colour. Scientists investigated the preference for red and orange fruit amongst four bird species.
The procedure for the investigation was as follows:
- 10 birds of each species were captured and housed in separate cages of equal size
- Each bird was presented with an identical single petri dish containing four pieces of fresh salmonberry, two red and two orange
- The first choice of fruit colour made by the bird was recorded
The results are shown in the table below:
| Species | Number of birds that chose red | Number of birds that chose orange |
| Common raven | 10 | 0 |
| American robin | 5 | 5 |
| Swainson’s thrush | 7 | 3 |
| Hermit thrush | 8 | 2 |
3.2.1 Name the:
- Independent variables (2)
- Dependent variable (1)
3.2.2 Identify TWO factors that were kept constant in this investigation. (2)
3.2.3 Explain why the investigators used 10 birds of each species instead of 1 bird of each species. (2)
3.2.4 Calculate as a percentage, the number of birds that preferred red fruit. Show ALL working. (3)
3.2.5 Use the theory of evolution through natural selection to explain why you would expect an increase in the proportion of salmonberry plants that produce red fruit. (6)
3.3 The graph below shows the time of existence and cranial capacity of various primate species.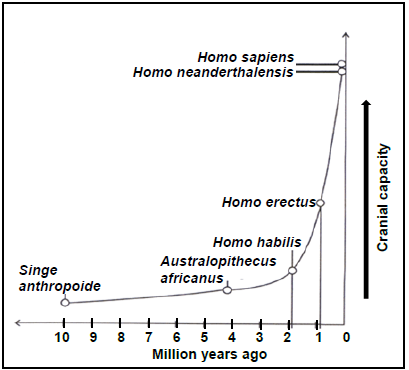
3.3.1 Name the Homo species which:
- Was the first to migrate out of Africa (1)
- Is known to be the first to use tools (1)
3.3.2 How many million years ago did Australopithecus africanus appear on Earth? (1)
3.3.3 Name ONE type of evidence that could be used to prove that Australopithecus africanus came about at the time mentioned in QUESTION 3.3.2. (1)
3.3.4 One of the fossils of Australopithecus africanus is Taung child.
- Name the scientist who discovered Taung child. (1)
- Where was Taung child discovered? (1)
3.3.5 Based on the diagram give TWO visible differences in the skulls of Australopithecus and Homo sapiens sapiens. (4)
3.3.6 Using data from the graph describe the change in cranial capacity from 2 million years ago to the present time. (1)
3.4 There has been a change of thinking with regards to the pace of evolution moving from gradualism as proposed by Darwin to punctuated equilibrium.
Describe punctuated equilibrium and how it demonstrates the pace at which evolution occurs. (4)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Define and describe the process of DNA replication, stating when it takes place as well the significance of this process. Also describe the uses of DNA profiling in everyday life. (17)
Content: (3)
Synthesis: (20)
NOTE: NO marks will be awarded for answers in the form of a table, flow charts or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150