CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: CONSTRUCTION GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - 2018 SEPTEMBER PREPARATORY EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupCIVIL TECHNOLOGY: CONSTRUCTION
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
MEMORANDUM
SEPTEMBER 2018
QUESTION 1: SAFETY, MATERIAL AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
1.1
1.1.1 True (1)
1.1.2 False (1)
1.1.3 False (1)
1.1.4 True (1)
1.2 Any THREE requirements to which a trestle scaffold must comply.
- Soundly constructed with a solid material
- Prevent spreading of supporting legs
- Not higher than 3 m
- Consists of not more than 2 tiers (3 x 1) (3)
1.3 Similar answer.
(1) Aluminium conducts (2) electricity / workers subjected to electrical shock (2)
1.4 Similar answer.
(1) Paint will cover (2) weaknesses (2)
1.5
1.5.2 Improves the durability of concrete. (1)
1.5.5 It improves the strength of concrete. (1)
1.5.7 It makes concrete more watertight. (1)
1.5.8 It improves the resistance to abrasion. (1)
1.6 (1) Plastic finish / coating (2) in powder form by (3) using a spray-gun (3)
1.7 Briefly describe any ONE use of the dumpy level.
- (1) Determine (2) height differences
- (1) Determine (2) levels and slopes
- (1) Setting out (2) of buildings
- (1) Transferring of (2) levels and heights
- (1) Determine horizontal (2) distances (1 x 2) (2)
1.8
1.8.1 1.5 m (1)
1.8.2 1.535 – 1,47 x 100 = 6,5 m (4)
1.9 Any THREE materials which can be detected in walls by the multi-detector.
- Ferrous metals
- Non-ferrous metals
- AC wiring
- Wood
- Metal studs
- Steel bars
- Copper pipes (3 x 1) (3)
1.10
1.10.1 Dry, soft cloth / Not cleaning agents or solvents (1)
1.10.2 Remove battery (1)
[30]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS AND JOINING (GENERIC)
2.1 Use the information on ANSWER SHEET A and complete the site plan on scale 1 : 200 according to the following requirements:
2.1.1 The site boundaries are measured from point A
The site boundaries in front and back are 23 m long
The site boundaries on the sides are 25 m long (2)
2.1.2 The front building line is 4 m from the site boundary
The back and side building lines are 2 m from the site boundaries (2)
2.1.3 Show the site entrance, 3 m from the western site boundary (1)
2.1.4 Show the datum level in the north-eastern corner of the site
Complete the sewage lay-out and abbreviations of the sewage appliances according to the following requirements: (1)
2.1.5 The main sewage from the bathroom to the municipal connection (2)
2.1.6 The branch sewage to the bathroom and kitchen (2)
2.1.7 Manhole on the site, before the municipal connection (2)
2.1.8 Rodding eyes (4)
2.1.9 Inspection eyes (4)
2.2
- Length of shank
- Diameter
- Type of thread
- Head size (4 x 1) (4)
2.3 (1) When square shoulder is driven in (2) it resists rotation (2)
2.4
2.4 A – Nut
2.4 B – Thread
2.4 C – Runout
2.4 D – Shank (4)
[30]
QUESTION 3: CONCRETE, EXCAVATIONS, FOUNDATIONS & QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
3.1
3.1.1 Rib-and-block floor (1)
3.1.2
3.1.A – Concrete floor block (1)
3.1.B – Precast concrete rib (1)
3.1.3 ONE instance where this type of floor construction will be used:
- Basements
- First floors
- Roof slabs (1)
3.1.4 150 mm (1)
3.1.5 200 mm (1)
3.2
3.2.1 Slump test (1)
3.2.2 Any TWO purposes of the slump test:
- Test the density by determining the water content
- Determine the workability and consistency of batches
- Determine the slump of the mixture (2 x 1) (2)
3.2.3 16 mm (1)
3.2.4 25 Times (1)
3.2.5 On the building site (1)
3.3 Any THREE – describe the purpose of curing concrete:
- That the hydration of cement can continue
- Newly placed concrete must be protected against quick drying
- Achieve optimal strength
- Achieve optimal hardness (3 x 1) (3)
3.4 Any THREE methods of curing concrete:
- Sprinkling
- Cover with water-retaining substances such as sand, hessian etc.
- Cover with plastic membranes or plastic sheeting
- Commercial seal compound (3 x 1) (3)
3.5 Any THREE methods to make excavations safe at night:
- Fencing
- Visible warning signs
- Red or orange warning lights
- Covering over excavations (3 x 1) (3)
3.6 Any FOUR causes for an excavation collapse:
- Heavy rains
- Poor soil strata, structure or composition
- Sides not dug at the correct angle
- Improper use of formwork or shoring to support the walls
- Vibration by machinery or heavy vehicles nearby
- Water seeping into the excavated area
- Contact with underground services
- Access to and exit from the excavation
- Soil slides due to cracks or loose soil (4 x 1) (4)
3.7
3.7.1 False (1)
3.7.2 True (1)
3.7.3 False (1)
3.7.4 True (1)
3.8 Any FOUR advantages of using pile foundations:
- Can be used in poor soil
- Can be used anywhere, even in water
- The larger base ensures stability
- Relatively quick and easy to install if equipment is available
- If pre-fabricated piles are used, much time is saved
- Quick and less expensive to produce
- Resist tensile stress well
- Can be manufactured elsewhere and transported to the site
- Installation continue even if poor weather conditions hamper excavations
- Length of piles can be adjusted, depending on the circumstances
- It offers good resistance against moving soil (4 x 1) (4)
3.9 Any TWO types of foundations (pile- / block foundation excluded):
- Strip foundation
- Stepped foundation
- Raft foundation (2 x 1) (2)
3.10 2 / 6 000 = 12 000 mm √
2 / 4 000 = 8 000 mm √
= 20 000 mm √
Corners: 4 / 600 = - 2 400 mm √
Centre line = 17 600 mm √ (5)
[40]
QUESTION 4: REINFORCEMENT, FORMWORK, MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
4.1
4.1.1 High-tensile or high yield steel (1)
4.1.2 200 mm (1)
4.1.3 6 Bars (1)
4.1.4 12 mm (1)
4.2
4.2.1
4.2.A – Anchor bar (1)
4.2.B – Stirrups (1)
4.2.C – Main bar (1)
4.2.D – Shear bar (1)
4.2.2 Any TWO describing the purpose of the stirrups:
- Support the shear bars
- Space and support the main bars
- Prevent the tearing of concrete (2)
4.3 Compression (1); Tensile (1); Lateral (1) forces (3)
4.4 Any TWO describing the purpose of cover depth for reinforced concrete:
- To protect steel against corrosion
- To ensure adequate bonding between the steel and concrete
- To ensure adequate protection of steel in the event of a fire (2)
4.5 Any THREE materials to line formwork – smoother finish:
- Plastic
- Metal sheeting
- Hard board
- Fibre-glass (3 x 1) (3)
4.6 Any TWO defects that can occur in concrete due to shuttering:
- Blowholes
- Uneven colour (discolouration)
- Weakening of structure or collapse (2 x 1) (2)
4.7 Any FOUR properties of good formwork:
- Made accurately according to the dimensions indicated
- Sturdy enough to bear the mass of wet concrete without collapsing
- Able to bear the mass of workers and equipment
- Must be strong enough to provide sufficient support, without too much deflection, until the concrete has set
- Formwork should be easy to repair on site
- Secured with wire nails, where some should protrude for easy extracting
- Secured with bolts from 13 mm to 19 mm in diameter
- Should be sealed properly so that the concrete does not leak and form honeycombs or fins
- Should be free of dirt (sawdust or releasing agents)
- Quick and simple to erect, mechanically or by hand
- Ensure the correct cover depth for reinforcing, to prevent structural failure
- Fit plywood onto laggings if a smooth finish is required
- Remove when the concrete has cured and is able to support load on its own
- Should be easy to remove without damaging the formwork or concrete
- Close-fitting along seams and joints
- Made from recyclable components (Any 4 x 1) (4)
4.8 Choose a description in COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A.
4.8.1 C (High volumes of concrete) (1)
4.8.2 J (Used as awnings) (1)
4.8.3 I (30 MPa compressive strength) (1)
4.8.4 K (High antibacterial properties) (1)
4.8.5 G (Small volumes of concrete) (1)
4.8.6 A (Hard, brittle and breaks easily) (1)
4.8.7 B (Low toxicity) (1)
4.8.8 D (Packing of equipment) (1)
4.9 Identify the metals as FERROUS or NON-FERROUS:
4.9.1 Non-ferrous (1)
4.9.2 Ferrous (1)
4.9.3 Non-ferrous (1)
4.9.4 Ferrous (1)
4.9.5 Non-ferrous (1)
4.10
4.10.1 Portable concrete vibrator (1)
4.10.2 Concrete mixer (1)
4.10.3 Plate compactor (1)
[40]
QUESTION 5: ROOFS, BRICK WALLS AND GRAPHICS (SPECIFIC)
5.1
5.1.1 Closed eave (1)
5.1.2 Any TWO advantages of the closed eave:
- Provides a more attractive appearance
- Prevent animals from entering (insects, birds and vermin etc.)
- No beam filling required (2 x 1) (2)
5.1.3 Any TWO types of material that can be used at the closed eave:
- Soffit board or fibre-cement board
- Wire netting
- Pegboard (2 x 1) (2)
5.2 Any THREE for discussing the purpose of beam filling:
- To keep out insects and vermin
- Prevent wind / dust from blowing under the roof
- Prevent birds from nesting in the roof
- Improve the stability of the roofing rafters
- Improve the insulation of the building (3 x 1) (3)
5.3
- Rafter (1)
- Queen post (1)
- King post (1)
- Strut (1)
- Tie beam (1)
5.4
5.4.1 50 mm (1)
5.4.2 3 m (1)
5.5 Any THREE disadvantages of cavity walls:
- Require expert designs / higher design standards
- Require highly skilled workmanship
- Constant supervision is needed during construction
- Cavities are filled with vertical damp-proof course
- More expensive than solid wall constructions
50 to 100 mm of the internal space is lost (3 x 1) (3)
5.6 Any TWO types of wall ties that can be used in cavity walls:
- Butterfly pattern
- Nylon wall tie
- Twisted pattern
- Double triangular pattern (2 x 1) (2)
5.7
- Weep hole (1)
- Concrete floor (1)
- Hard-core filling (1)
- Concrete filling (1)
5.8 See ANSWER SHEET B – Isometric view of pier on block foundation (6)
[30]
QUESTION 6: SCREEDS, STAIRS, BRICKWORK AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Any ONE type of sand that can be used as bedding sand for pavers:
- River sand
- Crusher dust (1)
6.2 Any FOUR advantages of mortar set pavers:
- Little maintenance is required
- Low life-cycle cost
- Resistant to point loads
- Resistant to fatigue and reflecting traffic patterns
- Resistant to edge movement
- User-friendly installation material is used
- No weeds will be able to grow in between the joints
- No off-gassing installation products used
- Insects will not be able to ruin the appearance of the paved structure
(4 x 1) (4)
6.3
6.3.1 True (1)
6.3.2 False (1)
6.3.3 True (1)
6.3.4 False (1)
6.4 See ANSWER SHEET C – Determine the amount of bricks needed (12)
6.5 Any THREE types of materials that can be used for cladding:
- Tile cladding
- Brick slip cladding
- Stone cladding
- Timber cladding
- Metal sheet cladding (3 x 1) (3)
6.6 Any TWO types of screeds:
- Dry screed
- Monolithic screed
- Bonded screed (2)
6.7
- Hand rail (1)
- Baluster (1)
- Thread or going (1)
- Riser (1)
[30]
TOTAL: 200
2.1 Use the information on ANSWER SHEET A and complete the site plan to scale 1 : 200.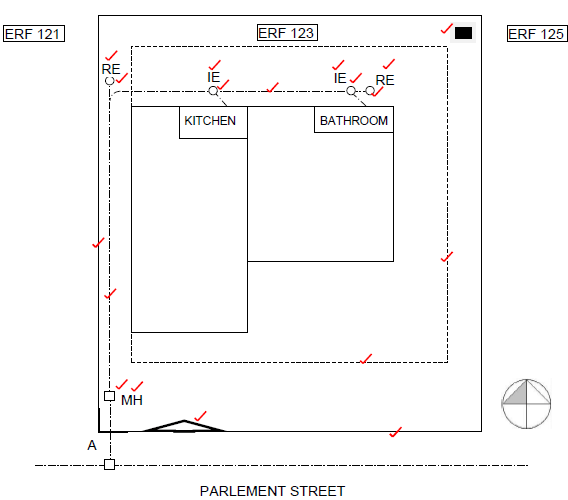
| Site boundaries | 2 |
| Building lines | 2 |
| Site entrance | 1 |
| Datum level | 1 |
| Main sewerage | 2 |
| Branch sewerage | 2 |
| Manhole | 2 |
| Rodding eyes | 4 |
| Inspection eyes | 4 |
| TOTAL | 20 |
5.8 Use ANSWER SHEET B and draw an isometric view of a pier on a block foundation. Use own scale.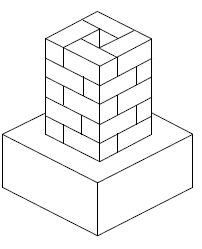
PIER ON BLOCK FOUNDATION
NOT TO SCALE
| One-and-a-half brick pier | 2 |
| Stretcher bond | 1 |
| Brick layers | 1 |
| Block foundation | 2 |
| TOTAL | 6 |
QUESTION 6.4
| A | B | C | D |
| Brick calculation: | |||
| 1/ | 6.5 m | ||
| 2.8 m √ | 18,2 m² √ | Total wall area | |
| √ | |||
| Bricks: | |||
| 1/ | 18.2 | ||
| 100 √ | 1820 √ | Total number of bricks | |
| Deductions: | |||
| 1/ | 0.9 m | Opening A | |
| √ | 2.1 m √ | 1,89 m² √ | Total area |
| 1/ | 1.89 | ||
| 100 √ | 189 √ | Total number of bricks for opening A | |
| Total number of bricks needed: | |||
| 1 820 - 189 √ = 1631 bricks √ |
(12)