PHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - 2018 SEPTEMBER PREPARATORY EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupPHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
MEMORANDUM
SEPTEMBER 2018
GENERAL GUIDELINES
- CALCULATIONS
1.1 Marks will be awarded for: correct formula, correct substitution, correct answer with unit.
1.2 No marks will be awarded if an incorrect or inappropriate formula is used, even though there are many relevant symbols and applicable substitutions.
1.3 When an error is made during substitution into a correct formula, a mark will be awarded for the correct formula and for the correct substitutions, but no further marks will be given.
1.4 If no formula is given, but all substitutions are correct, a candidate will forfeit one mark.
1.5 No penalisation if zero substitutions are omitted in calculations where correct formula/principle is correctly given.
1.6 Mathematical manipulations and change of subject of appropriate formulae carry no marks, but if a candidate starts off with the correct formula and then changes the subject of the formula incorrectly, marks will be awarded for the formula and correct substitutions. The mark for the incorrect numerical answer is forfeited.
1.7 Marks are only awarded for a formula if a calculation has been attempted, i.e. substitutions have been made or a numerical answer given.
1.8 Marks can only be allocated for substitutions when values are substituted into formulae and not when listed before a calculation starts.
1.9 All calculations, when not specified in the question, must be done to a minimum of two decimal places.
1.10 If a final answer to a calculation is correct, full marks will not automatically be awarded. Markers will always ensure that the correct/appropriate formula is used and that workings, including substitutions, are correct.
1.11 Questions where a series of calculations have to be made (e.g. a circuit diagram question) do not necessarily always have to follow the same order. FULL MARKS will be awarded provided it is a valid solution to the problem. However, any calculation that will not bring the candidate closer to the answer than the original data, will not count any marks. - UNITS
2.1 Candidates will only be penalised once for the repeated use of an incorrect unit within a question.
2.2 Units are only required in the final answer to a calculation.
2.3 Marks are only awarded for an answer, and not for a unit per se. Candidates will therefore forfeit the mark allocated for the answer in each of the following situations:- Correct answer + wrong unit
- Wrong answer + correct unit
- Correct answer + no unit
2.4 SI units must be used except in certain cases, e.g. V.m-1 instead of N.C-1, and cm•s-1 or km•h-1 instead of m•s-1 where the question warrants this.
- GENERAL
3.1 If one answer or calculation is required, but two are given by the candidate, only the first one will be marked, irrespective of which one is correct. If two answers are required, only the first two will be marked, etc.
3.2 For marking purposes, alternative symbols (s, u, t, etc.) will also be accepted.
3.3 Separate compound units with a multiplication dot, not a full stop, for example, m•s-1.
For marking purposes, m•s-1 and m/s will also be accepted. - POSITIVE MARKING
Positive marking regarding calculations will be followed in the following cases:
4.1 Subquestion to subquestion: When a certain variable is calculated in one subquestion (e.g. 3.1) and needs to be substituted in another (3.2 of 3.3), e.g. if the answer for 3.1 is incorrect and is substituted correctly in 3.2 or 3.3, full marks are to be awarded for the subsequent subquestions.
4.2 A multistep question the a subquestion: If the candidate has to calculate, for example, current in die first step and gets it wrong due to a substitution error, the mark for the substitution and the final answer will be forfeited. - NEGATIVE MARKING
Normally an incorrect answer cannot be correctly motivated if based on a conceptual mistake. If the candidate is therefore required to motivate in QUESTION 3.2 the answer given in QUESTION 3.1, and QUESTION 3.1 is incorrect, no marks can be awarded for QUESTION 3.2. However, if the answer for e.g. QUESTION 3.1 is based on a calculation, the motivation for the incorrect answer could be considered.
QUESTION 1:
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1 C ✓✓ (2)
1.2 A ✓✓ (2)
1.3 D ✓✓ (2)
1.4 A ✓✓(2)
1.5 D✓✓ (2)
1.6 C ✓✓ (2)
1.7 A ✓✓ (2)
1.8 D ✓✓ (2)
1.9 C ✓✓(2)
1.10 D ✓✓ (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1.1 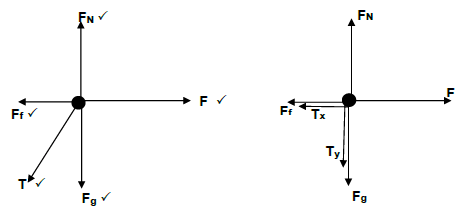
Mark awarded for arrow and label.
Do not penalise for length of arrows since drawing is not drawn to scale
Any other additional force(s)4/5
If force(s) do not make contact with body.Max. 4/5 (5)
2.1.2 If the resultant/net force acts on an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the resultant/net force with an acceleration that is directly proportional to the resultant/net force ✓ and inversely proportional to the mass ✓ of the object. (2)
2.1.3 OPTION 1
Fnet = ma ✓
Fnet = Fapp - Tx - f any one
ma = Fapp - Tx - f
5,2a = 46,5 - Tx- 12 ✓
5,2a = 34,5 - Tx . . . . . . . . . . (1)
2a = Tx - 5,1 ✓ . . . . . . . . . . .(2)
a = 4,08m.s-2
2 x (4,08) ✓ = Tx - 5,1
Tx= 13,26
T = ??
???25?
T = 13,26
???25? ✓
T = 14,63 N ✓
OPTION 2
-5,2a = - 46,5 + Tx + 12 ✓
-5,2a = -34,5 + Tx. . . . . (1)
-2a =Tx + 51✓ . . . . . (2)
a = -4,08m.s-2
a = 4,08 m.s-2
(6)
2.2 g = ??
?2 ✓
g= 6,67 10−11? 6,39 1023
(3,39 106)2 ✓
g = 3,71 m.s-2 ✓ (3)
[16]
QUESTION 3
3.1.1 UPWARD POSITIVE
Δx = viΔt + ½aΔt2 ✓
- (48) ✓= vi x 2,8+ ½ x(- 9,8) x 2,82 ✓
Vi = -3,42
Vi = 3,42 m.s-1 ✓
DOWNWARD POSITIVE
Δx = viΔt + ½ aΔt2 ✓
(48) ✓ = vi x 2,8 + ½ x 9,8 x 2,82 ✓
Vi = 3,42 m.s-1 ✓ (4)
OPTION 1
3.1.2 UPWARD POSITIVE
Vf = Vi + aΔt ✓
Vf = -3,42 + (-9,8) (2,8) ✓
Vf = -30,86 m.s-1
Vf = 30,86 m.s-1 ✓
DOWNWARD POSITIVE
Vf = Vi + aΔt ✓
Vf = 3,42 + (9,8) (2,8) ✓
Vf = 30,86 m.s-1 ✓ (3)
OPTION 2
UPWARD POSITIVE
??2 = ??2 + 2aΔx ✓
??2 = -3,422 + 2 (-9,8) (-48) ✓
?? = 30,86 m.s-1 ✓
DOWNWARD POSITIVE
??2 = ??2 + 2aΔx ✓
??2 = 3,422 + 2 (9,8) (48)✓
?? = 30,86 m.s-1 ✓
OPTION 3
UPWARD POSITIVE
Δx = ??+?? Δt ✓
2
-(48) = ??−3,42 x 2,8 ✓
2
?? = - 30,87
?? = 30,87 m.s-1 ✓
DOWNWARD POSITIVE
Δ x = ??+?? Δt ✓
2
48 = ??+3,42 x 2,8 ✓
2
?? = 30,87 m.s-1✓
OPTION 4
EMi = EMi
mgh1 + ½ ???2 = mgh + ½ ???2 Any one ✓
gh1 + ½ ??2 = gh2 + ½ ??2
9,8 x 48 + ½ x 3,422 = 0 + ½ ??2✓
Vf = 30,86 m.s-1✓
OPTION 5
Fnet Δt = Δp
Fnet Δt = m (vf – vi) Any one
mgΔt = m (vf – vi)
g Δt = vf – vi
9,8 x 2,8 = vf – 3,42 ✓
Vf = 30,86 m.s-1 ✓
3.1.3 UPWARD POSITIVE
??2 = ??2 + 2aΔX ✓
0 = ??2 + 2 (-9,8)(8) ✓
VI = 12,52 m.s-1 upwards. ✓
DOWNWARD POSITIVE
??2 = ??2 + 2aΔx ✓
0 = ??2 + 2 (9,8)(--8) ✓
VI = 12,52 m.s-1
VI = 12,52 m.s-1 upwards. ✓ (3)
3.2 Positive marking from 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.1.3
CRITERIA FOR MARKING
- Initial velocity with which the ball was thrown. ✓
- Final velocity with which the ball hit the ground ✓
- Time taken to hit the ground. ✓
- The velocity with which the ball bounces off the ground. ✓
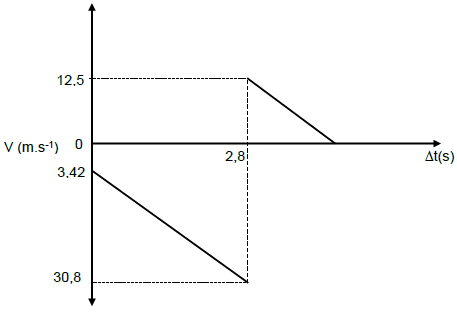
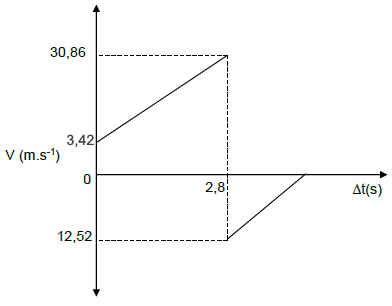
(4)
[14]
QUESTION 4
4.1 (?? + ?? ) ?? = ?? ??? + ?? ??? ✓
(1100 + 800) x( 45 ? 1000) ✓= 1100 V?? + 800 x 9,06 ✓
3600
??? = 15,00 m.s-1 ✓ (4)
4.2
4.2.1 The product of the net force acting on an object and the time the net force acts on the object. ✓✓(2)
Positive marking from QUESTION 4.1
4.2.2 OPTION 1
????Δt = m (?? - ?? ) ✓
???? x 0,2 ✓= 1100 (0 – (-15)✓
???? = 1,65 x 104 N left ✓
OPTION 2
????Δt = m (?? - ?? ) ✓
???? x 0,2 ✓= 1100 (0 – (15) ✓
???? = - 1,65 x 104
???? = 1,65 x 104 N left✓ (4)
[10]
QUESTION 5
5.1 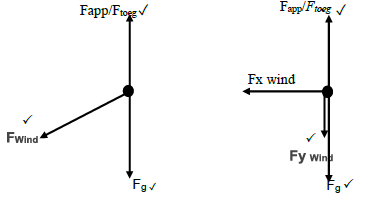
(3)
Mark awarded for arrow and label
Do not penalise for length of arrows since drawing is not drawn to scale
Any other additional force(s)2/3
If force(s) do not make contact with body./Indien krag(te) nie kontak maak met liggaam nie Max/Maks.2/3
5.2
5.2.1 OPTION 1
WFg = Fg ΔX cos? ✓
WFg = 245 x 9,8 x 12 cos180o ✓
WFg = - 28812 J ✓
OPTION 2
WFg = -ΔEp Any one ✓
WFg = - mg (h2 – h1)
WFg = - 245 x 9,8(12 – 0) ✓
WFg = - 28812 J ✓ (3)
5.2.2 OPTION 1
Fnet = FwindY + Fg + Fapp
Fnet = - (1870 cos 50o ) – (245 x 9,8) + 3000 ✓
Fnet = - 603,01 N Any one ✓
Wnet = Fnet .Δx cos?
Wnet = 603,01 x 12 cos 180o ✓
Wnet = - 7236,12 J ✓
Positive marking from QUESTION 5.2.1
OPTION 2
Wnc = ΔEk + ΔEp Any one✓
WF + Wwind = ΔEk + ΔEp
3000 x 12 cos0o + 1870 x12 cos130o) ✓ = 28812 ✓+ ΔEk
ΔEk = - 7236,15 J
Wnet = - 7236,12 J ✓
Positive marking from QUESTION 5.2.1
OPTION 3
Wnet = WwindY + WFg + Wapp ✓
Wnet = (1870 x 12 cos130o) ✓ - 28812 + (3000 x 12 cos0o) ✓
Wnet = - 7236,15 J ✓ (4)
5.3 The net work done on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy ✓✓(2)
5.4Wnet = Δ Ek
Wnet = ½ m ??2 - ½ m ??2 Any one ✓
-7236,15 = ½ x 245 ??2 - ½ x 245 x 152 ✓
?? = 12,88 m.s-1 ✓ (3)
[15]
QUESTION 6
6.1
6.1.1 EQUAL TO. ✓There is no relative motion between the observers and the source of sound. ✓(2)
6.1.2 GREATER THAN ✓ (1)
6.1.3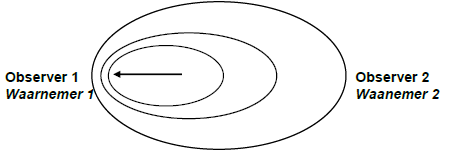
| Criteria | Mark |
| Wave compressed towards observer 1 | ✓ |
| Wave stretched away from observer 2 | ✓ |
| Direction of motion indicated | ✓ |
(3)
6.1.4 Doppler effect ✓ (1)
6.1.5 ?? = ? ± ?? ??
?±??
1730 ✓= 340 ??
340−25
?? = 1602,79 Hz ✓(5)
6.1.6 Star C, ✓ it shows a greater red shift. ✓ (2)
[14]
QUESTION 7
7.1 The electrostatic force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges ✓and inversely proportional to the square of the
distance between them. ✓ (2)
7.2.1 OPTION 1
Factor = 1920 ✓ = 16
120
OR
Factor = 120 = 1
1920 16
Factor decreases by 16.
Factor by which r increased = √16 = 4 ✓
X + 6 = 4X ✓
X = 2m ✓
OPTION 2
F = ??1?2
?2 ✓
1920✓= 9?109??2
?2 ✓
?2 = 1920 ? ?2 . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . (1)
9 ? 109
120 = 9 ? 109 ? ?2
(?+6)2 ✓
?2 = 120 ? (?+6)2 . . . . . . . . . . . (2)
9 ? 109
1920 ? ?2 = 120 ? ( ?+6)2
9 ? 109 9 ? 109
x = 2m ✓ (5)
Positive marking from QUESTION 7.2.1
7.2.2 OPTION 1
F = ??1?2
?2 ✓
1920 ✓ = 9 ? 109 ? ?2
22 ✓
Q = 9,24 x10-4 C ✓
OPTION 2
F = ??1?2
?2 ✓
120 ✓ = 9 ? 109 ? ?2
82 ✓
Q = 9,24 x10-4 C✓ (4)
Positive marking from QUESTION 7.2.1
7.3.1
E = ??
?2 ✓
E1 = 9 ? 102 ? 9,24 ?10−4
2.22 ✓
E1 = 1718181,818 N.C-1 (1,72 X 106 N.C-1) Right
E2 = 9 ? 102 ? 9,24 ?10−4
0.22 ✓
E2 = 207900000 NC-1 (2,08 X 108 N.C-1) Right
Enet = 1718181,818 + 207900000
(1,72 X 106 N.C-1 + 2,08 X 108 N.C-1) ✓
Enet = 2,10 x 108 N.C-1 ✓ (5)
Positive marking from QUESTION 7.3.1
7.3.2 OPTION 1
E = ?
? ✓
2,10 x 108 = ?
1,6 ? 10−19 ✓
F = 3,36 x 10-11 N ✓
OPTION 2
F = ??1?2
?2 ✓
F= 9 ? 109 ? 9,24 ? 10−4 ? 1,6 ? 10−19 + 9 ? 109 ? 9,24 ? 10−4 ? 1,6 ? 10−19
2.22 0.22 ✓
F = 3,35 x 10-11 N ✓(3)
[19]
QUESTION 8
8.1.1 Diagram A represents Exp 2. ✓ (1)
8.1.2 ε = I(R+r) ✓
= 14,4 + 4,8r✓. . . . . . . . (1)
= 20,58 + 1,71r ✓. . . . . .(2)
3,09 r = 6,18
∴r = 2 Ω✓(4)
8.1.3 OPTION 1
ε = I(R+r)
= 4,8 x 2 + 14,4 ✓
= 24 V✓
OPTION 2
ε = I(R+r)
= 1,71 x 2 + 20,5 ✓
= 24 V ✓ (2)
Positive marking from QUESTION 8.2.1 and 8.2.2
8.1.4 OPTION 1
R = ?
?
R = 20,58
1,71
R = 12
R = R1 + R2
12 = 2R1
R = 6 Ω ✓
OPTION 2
R = ?
?
R = 14,4
4,8
R = 3 Ω
1 = 1 + 1
R// R1 R2
1 = 1 + 1 = (R1 + R2 = R)
3 R R
R = 6 Ω ✓
OPTION 3
? = I (R + r) ✓
24 = 4,8 (R + 2) ✓
R = 3 Ω
1 = 1 + 1
R// R1 R2
1 = 1 + 1 = (R1 + R2 = R)
3 R R
R = 6 Ω ✓
OPTION 4
? = I (R + r) ✓
24 = 1,71(R + 2) ✓
R = 12,04 Ω
R = R1 + R2
12,04 = 2R✓
R = 6,02 Ω ✓ (4)
8.1.5 OPTION 1
DECREASE, ✓otal external resistance will increase, the current will decrease ✓
P ∝ I2 ✓ therefore power decreases.
OPTION 2
DECREASE, ✓total external resistance will increase, the current will decrease, the lost volt will decrease. ✓
P ∝ ?????2 ✓ therefore power decreases. (3)
8.2 P = I2R ✓
P = 165 x 52 ✓
P = 13 312 W
kWh = 13,312 x 6
kWh = 79,872
Cost = 79,872 x 1,20 ✓
= R95,85 ✓(4)
[18]
QUESTION 9
9.1 9.1.1 Mechanical energy to Electrical energy. ✓✓ (2)
9.1.2 P to Q.✓ (1)
9.2
9.2.1 Vrms = V max ✓
√2
230 = Vmax ✓
√2
Vmax = 325,27 V ✓ (3)
9.2.2
1 = 1 + 1
R// R1 R2
1 = 1 + 1
R// 12 24
R// = 8 Ω
OPTION 1
Paverage = V2rms
R
Paverage = 2302
8
Paverage = 6612,5 W (6,61 kW) ✓ (5)
OPTION 2
Irms = Vrms
R
Vrms = IrmsR
Irms = 230
8
= 28,75 A
Pavg = Vrms.Irms ✓
= (230)(28,75) ✓
= 6612,5 W (6,61 kW) ✓
65OPTION 3
Irms = Vrms
R
Vrms = IrmsR
Irms = 230
8
= 28,75 A
Paverage = I2rms R
= (28,75)2(8) ✓
= 6612,5 W (6,61 kW) ✓ (5)
[11]
QUESTION 10
10.1 The minimum energy (of incident photons) that can eject electrons from a metal (surface). ✓✓(2)
10.2 Wo = 3,51 x 10-19 J ✓ (1)
10.3 EQUAL to ✓ The gradient is Plank’s constant. ✓ (2)
Positive marking from QUESTION 10.1.2
10.4 Wo = hfo ✓
3,51 x 10-19 = 6,63 x 10-34 fo ✓
fo = 5,29 x 1014 Hz ✓ (3)
Positive marking from QUESTION 10.1.2
10.5 E = Wo + Ek Any one ✓
ℎ? = Wo + ½ mv2
?
6,63? 10−34 ? 3 108 ✓ = 3,51 x 10-19+ ½ x 3,83 x 10-19 ✓
?
? = 2,71 x 10-7m ✓(5)
[13]
TOTAL: 150