GRADE12 MATHEMATICS PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2016
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMATHEMATICS P2
GRADE12
JUNE2016
MEMORANDUM
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
QUESTION
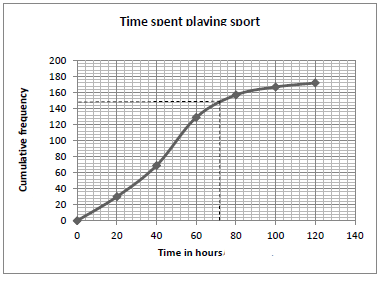
| 1.1 |
| (4) | ||||||||||||||
| 1.2 | 40 ≤ t < 60 | ✓answer (1) | ||||||||||||||
| 1.3 | 172 | ✓answer (1) | ||||||||||||||
| 1.4 | (72;148) ∴ 172-148 = 24 learners | ✓148 ✓24 (2) | ||||||||||||||
| 1.5 | Frequency: 30; 39; 60;28;10;5 30×10+39×30+60×50+28×70+10×90+5×110=7880 172 =7880 172 =45,81 | ✓frequency ✓midpoints ✓7880 172 ✓answer(4) |
[12]
QUESTION 2
| 2.1 | ?̅= 6772 20 ?̅=338,6 ?? | ✓ ?̅= 6772 20 ✓answer(2) |
| 2.2 | 2,71 ml | ✓✓ answer (2) |
| 2.3 | [338,6 – 2,71; 338,6 + 2,71] [335,89; 341.31] | ✓✓ interval (2) |
[6]
QUESTION 3
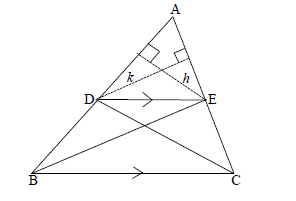
| 3.1 | ???= −1 ?−9=3(?−3) 3?−?=0 | ✓S ✓R ✓ subst, m = 3 & (3;9) in eqn. (3) |
| 3.1.2 | ?+3?=10……… .(1) 3?−?=0 …………(2) ?+3(3)=10 ?=1 | ✓equating two eqns ✓simplification ✓y = 3 ✓x = 1 (4) |
| 3.1.3 | 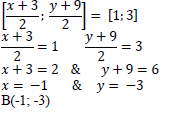 | ✓method using midpoint ✓ simplification ✓ coordinates of B (3) |
| 3.1.4 | AD =√(3−?)2+ (9−?)2 ∴ √50= √9−6?+?2+81−18?+ ?2 ∴ 50= ?2−6?+?2−18?+90 ∴ (10−3?)2−6(10−3?)+ ?2−18 ?+90=50 ∴ 100−60?+9?2−60+18?+?2−18?+90=50 | ✓ subst into eqn dist AD ✓ subst AD = √50 ✓subst x =10 - 3y ✓ simplification ✓standard form ✓values for y ✓values for x ✓coordinates (8) |
| 3.2.1 | ?PQ= 8 - 2= 6 = ¾ | ✓ subs into eqn ✓ answer (2) |
| 3.2.2 | tan?= ¾ ?=36,9 | ✓ tan ? ✓ answer |
| 3.2.3 | ?=¾?+? 0= ¾(8)+? ?= −6 ?= ¾?−6 | ✓subst. m = 34 ✓ answer |
[25]
QUESTION 4
| 4.1 | A(0; y) ∴?= 0+8=4 2 ∴D(4;4) | ✓midpt equation ✓coordinates of D (2) |
| 4.2 | Ay = ?+7=4 A(0; 1)2 ∴(?−0)2+(?−1)2= ?2 ∴(4−0)2+(4−1)2= ?2 ∴16+9= ?2 ∴?2+(?−1)2=25 ∴?2+ ?2−2?−24=0 | ✓ y-coordinate of A ✓ A(0; 1) ✓✓subst (0;1)and (4;4) into equation. ✓r2 (5) |
| 4.3 | ???×????= −1 [tan radius] | ✓S/R 3 ✓subst m and (4;4) into eqn |
| 4.4 | ?2+ ?2= ?2 (8)2+(7)2= ?2 ∴?2+ ?2=113 | ✓subst (8;7) into eqn ✓answer (2) |
[14]
QUESTION 5
| 5.1.1 | =sin?.cos?.tan?.cos? | ✓sin x ✓cos x ✓tan x ✓cos x ✓sin x ✓cos x ✓-tan x ✓-cos x (8) |
| 5.2 | sin? + 1 + cos? = 2 2+2cos? 2 = RHS/RK | ✓ denominator ✓ numerator ✓ simplification ✓ identity ✓ factorisation (5) |
| 5.3 | cos2?=cos(?+?) = cos?.cos?−sin?.sin? =cos2?−sin2? = cos2?−(1−cos2?) =2cos2?−1 | ✓ expansion ✓ identity (2) |
| 5.4 | cos2?+3sin?=2 1−2sin2?+3sin?=2 2sin2?−3sin?+1=0 (2sin?−1)(sin?−1)=0 | ✓ identity ✓ standard form ✓factors ✓ sin x = ½ sin x = 1 (both eqns) ✓ x = 30° ✓ x = 150° ✓ x = 90° (7) |
| 5.5 | sin?cos?+cos?sin?=sin(?+?) = sin90° = 1 | ✓ identity ✓ subst ✓ answer (3) |
[25]
QUESTION 6
| 6.1 | 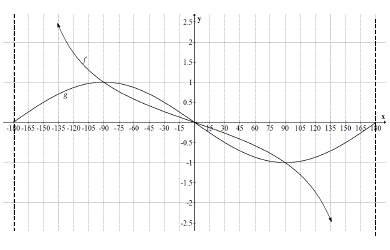 | ✓shape g ✓intercepts ✓min & max value ✓shape f ✓asymptotes ✓ intercept (6) |
| 6.2 | −180°<?≤−90° or/of 0°≤?≤90° | ✓critical values ✓ notation (2) |
[8]
QUESTION 7
| 7.1 | MN2=PN2+PM2−2PN.PMcos MP̂N = 122+102−2(12)(10)cos126,9° =144+100−240(−0,6) =388,1 MN=19,7 ? MN=AD=19,7 ? | ✓ correct subst into cos rule ✓ simplification ✓ answer (3) |
| 7.2 | ½MN.PT= ½PN.PMsinMP̂N [Both equal Area of ΔPMN] PT=12.sin126,9° | ✓ Equating Area form ✓ correct subst ✓ simplification ✓ answer (4) |
[7]
QUESTION 8
| 8.1 | Supplementary | ✓ answer (1) |
| 8.2.1 | EF̂O=90° [tan radius] EF̂O+EĜO=180° | ✓ S ✓R ✓S ✓R ✓ R (5) |
| 8.2.2 | Ĝ1= Ĥ=? [ tan chord] K̂1= Ĥ=? [ corresp angles; EK || FH] ∴Ĝ1= K̂1 EG is a tangent [angle between line and chord] | ✓S ✓R ✓S ✓R ✓R (5) |
| 8.2.3 | Ô1=2Ĥ [ angle at centre] = 2x ∴FÊG=180°−2? [ opp angles of cyclic quad] | ✓S ✓R ✓R (3) |
[14]
QUESTION 9
| 9.1 | B̂2 = Â2 = x [ angles opp equal sides] Â1 = B̂2 = x [ tan chord] Ŝ1 = Â1 = x [ corresp; AD||SC] ?̂3 = ?̂2 = x [ alt int; AD|| SC] AD̂C = B̂3 = x [ ext angle of cyclic quad] | ✓ S/R ✓ S/R ✓ S/R ✓ S/R ✓ S/R (5) |
| 9.2 | Â1 = AD̂C [ from 8.1] AS || DC [alt angles equal] DA || CS [given] ASCD is a parallelogram [opp sides ||] | ✓ S ✓ S/R ✓ S ✓ R (4) |
| 9.3 | ΔSAB ||| ΔADB [ A,A,A]/[H,H,H] | ✓ ΔSAB (1) |
| 9.4 | SA = SB [from 8.3.1] ∴AD.SB=SA.AB | ✓ S ✓ S ✓ S/R ✓ S/R ✓ R (5) |
[15]
QUESTION10
| 10.1.1 | In proportion | ✓ Answer (1) |
10.1.2
| RTP: PROOF: But Area ΔBDE=Area Δ CED (same base and same height) ∴ areaΔADE = area ΔADE | ✓ ratio of area of ΔADE: ΔBDE ✓AD BD ✓ratio of area of ΔADE : ΔCED ✓AE EC ✓equating two areas(5) |
| 10.2.1 | QT=QW prop thm; TW || VR ∴ 15 = ?+4 ?2−9?+8=0 ∴(?−8)(?−1)=0 ∴?=8 or ?=1 | ✓QT=QW TP WR ✓R ✓ substitution ✓ std form ✓factors ✓ both values for x (6) |
| 10.2.2 | PV = PT prop thm TV || QR PV = 10 PV = 12units | ✓ S/R ✓ substitution ✓ answer (3) |
[15]
QUESTION11
| 11.1 | ?2=90° [ line from centre to midpoint of chord] ∴ΔABC |||ΔDOC [AAA/???] | ✓ S/R ✓ S/R ✓ S (3) |
| 11.2 | OC = DC ΔABC |||ΔDOC OC = DC.BC
| ✓ S/R (1) |
| 11.3 | AC2=BC2−AB2 [Pythagoras] ??=??.?? ?? = 15 × 30=18,8 ?? 24 | ✓ S/R ✓ subst in eqn ✓ AC = 24 ✓ subst ✓ answer (5) |
[9]
TOTAL: 150