PHYSICAL SCIENCES: PHYSICS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupPHYSICAL SCIENCES: PHYSICS
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your examination number and centre number in the appropriate spaces on the ANSWER BOOK.
- This question paper consists of 11 questions. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two subquestions, for example between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your FINAL numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, et cetera where required.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write down only the letter (A-D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.11 D.
1.1 The net (resultant) force acting on an object is equal to the ... of the object in the direction of the net force.
- change in momentum
- change in kinetic energy
- rate of change of momentum
- rate of change of kinetic energy (2)
1.2 A physical quantity that is described as a measure of the resistance of a body to a change in motion is called …
- inertia.
- force.
- acceleration.
- weight. (2)
1.3 The diagram below shows a section of the path of a stone projected vertically upwards.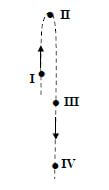
At which ONE of the positions indicated on the diagram will the magnitude of the momentum of the stone be the GREATEST? Ignore air resistance.
- I
- II
- III
- IV (2)
1.4 Two cars, P and Q, moving in a straight line, have the same momentum. The kinetic energy of Q is greater than the kinetic energy of P.
Which ONE of the following statements regarding the cars is CORRECT?
- Q has a smaller mass than P.
- Q has the same mass as P.
- Q is moving slower than P.
- Q is moving at the same speed as P. (2)
1.5 The net work done on an object to increase its speed from rest to v is W.
How much net work must be done on the same object to increase its speed from v to 2v?
- W
- 2W
- 3W
- 4W (2)
1.6 Which ONE of the following is NOT an application of the Doppler effect?
- A light meter
- A blood flow meter
- Detecting the heartbeat of a foetus using ultrasound
- Measuring the speed of an approaching car using radar (2)
1.7 Two small identical metal spheres, on insulated stands, carry charges -q and +3q respectively.
When the centres of the spheres are a distance d apart, the spheres exert an electrostatic force of magnitude F on each other.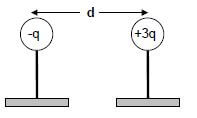
The spheres are now made to touch and are brought back to the same positions as before.
The magnitude of the electrostatic force which the spheres now exert on each other, in terms of F, is:
- 4 F
3 - 1 F
3 - 1 F
2 - 3F (2)
1.8 In the circuit below the battery has an emf (ε) and internal resistance r. With switch S open, readings are registered on the ammeter and voltmeter.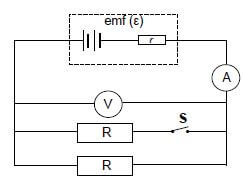
Switch S is now closed. How do the readings on the ammeter and voltmeter change? (2)
| AMMETER READING | VOLTMETER READING | |
| A | Increases | Remains the same |
| B | Increases | Decreases |
| C | Decreases | Remains the same |
| D | Decreases | Decreases |
1.9 A learner lists the following as factors that affect the magnitude of the current induced in an AC generator:
(i) The number of turns (windings) of the coil
(ii) The strength of the magnetic field
(iii) The speed of rotation of the coil
Which ONE of the combinations below is CORRECT?
- (i) and (ii) only
- (i) and (iii) only
- (ii) and (iii) only
- (i), (ii) and (iii) (2)
1.10 The graph below is obtained from an experiment on the photoelectric effect.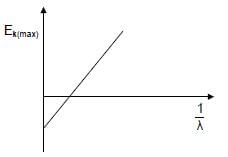
Which ONE of the following represents the gradient of the graph?
- hc
- h
- Ek(max)
λ - W0 (2) [20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a new page.)
Block P, of unknown mass, is placed on a rough horizontal surface. It is connected to a second block of mass 3 kg, by a light inextensible string passing over a light, frictionless pulley, as shown below.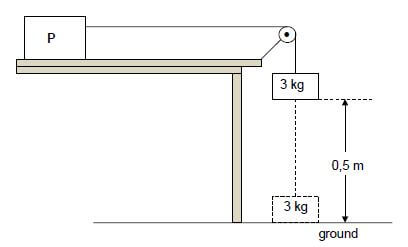
Initially the system of masses is held stationary with the 3 kg block, 0,5 m above the ground. When the system is released the 3 kg block moves vertically downwards and strikes the ground after 3 s. Ignore the effects of air resistance.
2.1 Define the term acceleration in words. (2)
Calculate the magnitude of the:
2.2 Acceleration of the 3 kg block using equations of motion (3)
2.3 Tension in the string (3)
The magnitude of the kinetic frictional force experienced by block P is 27 N.
2.4 Draw a labelled free-body diagram for block P. (4)
2.5 Calculate the mass of block P. (3) [15]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a new page.)
In the diagram below, point A is at the top of a building. Point B is exactly halfway between the point A and the ground. Ignore air resistance.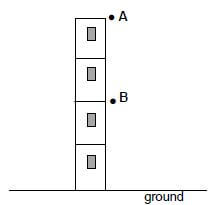
3.1 Define the term free fall. (2)
A ball of mass 0,4 kg is dropped from point A. It passes point B after 1 s.
3.2 Calculate the height of point A above the ground. (3)
When the ball strikes the ground it is in contact with the ground for 0,2 s and then bounces vertically upwards, reaching a maximum height at point B.
3.3 Calculate the magnitude of the velocity of the ball when it strikes the ground. (3)
3.4 Calculate the magnitude of the average net force exerted on the ball while it is in contact with the ground. (6) [14]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a new page.)
A trolley of mass 1,5 kg is held stationary at point A at the top of a frictionless track. When the 1,5 kg trolley is released, it moves down the track. It passes point P at the bottom of the incline and collides with a stationary 2 kg trolley at point B. Refer to the diagram below. Ignore air resistance and rotational effects.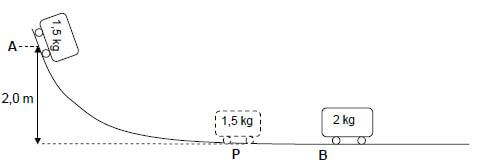
4.1 Use the principle of conservation of mechanical energy to calculate the speed of the 1,5 kg trolley at point P. (4)
When the two trolleys collide, they stick together and continue moving with constant velocity.
4.2 The principle of conservation of linear momentum is given by the incomplete statement below.
In a/an … system, the … linear momentum is conserved.
Rewrite the complete statement and fill in the missing words or phrases. (2)
4.3 Calculate the speed of the combined trolleys immediately after the collision. (4)
4.4 Calculate the distance travelled by the combined trolleys in 3 s after the collision. (3) [13]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a new page.)
A load of mass 75 kg is initially at rest on the ground. It is then pulled vertically upwards at a constant acceleration of 0,65 m⋅s-2 by means of a light inextensible rope.
Refer to the diagram below. Ignore air resistance, rotational effects and the mass of the rope.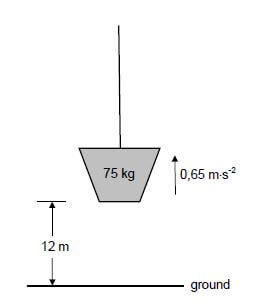
5.1Draw a labelled free-body diagram for the load while it moves upward. (2)
5.2 Name the non-conservative force acting on the load. (1)
5.3 Calculate the work done on the load by the gravitational force when the load has reached a height of 12 m. (3)
5.4 State the work-energy theorem in words. (2)
5.5 Use the work-energy theorem to calculate the speed of the load when it is at a height of 12 m. (5) [13]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a new page.)
A sound source, moving at a constant speed of 240 m∙s-1 towards a detector, emits sound at a constant frequency. The detector records a frequency of 5 100 Hz.
Take the speed of sound in air as 340 m∙s-1.
6.1 State the Doppler effect. (2)
6.2 Calculate the wavelength of the sound emitted by the source. (7)
Some of the sound waves are reflected from the detector towards the approaching source.
6.3 Will the frequency of the reflected sound wave detected by the sound sourcebe EQUAL TO, GREATER THAN or SMALLER THAN 5 100 Hz? (1) [10]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a new page.)
A particle, P, with a charge of + 5 x 10-6 C, is located 1,0 m along a straight line from particle V, with a charge of +7 x 10-6 C. Refer to the diagram below.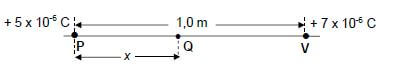
A third charged particle, Q, at a point x metres away from P, as shown above, experiences a net electrostatic force of zero newton.
7.1 How do the electrostatic forces experienced by Q due to the charges on P and V respectively, compare with each other? (2)
7.2 State Coulomb's law in words. (2)
7.3 Calculate the distance x. (5) [9]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a new page.)
A small metal sphere Y carries a charge of + 6 x 10-6 C.
8.1 Draw the electric field pattern associated with sphere Y. (2)
8.2 If 8 x 1013 electrons are now transferred to sphere Y, calculate the electric field at a point 0,5 m from the sphere. (7) [9]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a new page.)
9.1 In the circuit diagram below the battery has an unknown emf (ε) and an internal resistance (r) of 0,8 Ω.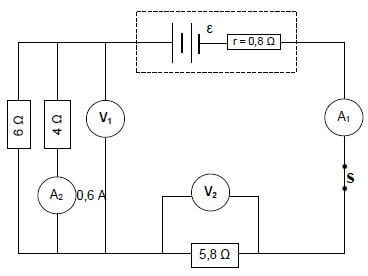
9.1.1 State Ohm's law in words. (2)
The reading on ammeter A2 is 0,6 A when switch S is closed.
Calculate the:
9.1.2 Reading on voltmeter V1 (3)
9.1.3 Current through the 6 Ω resistor (2)
9.1.4 Reading on voltmeter V2 (2)
9.1.5 Emf (ε) of the battery (3)
9.1.6 Energy dissipated as heat inside the battery if the current flows in the circuit for 15 s (3)
9.2 A simplified circuit diagram for the windscreen wiper of a car consists of a variable resistor and a wiper motor connected to a 12 volt battery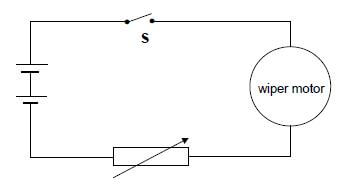
When switch S is closed, the potential difference across the variable resistor is 2,8 V and the current passing through it is 0,7 A.
9.2.1 Calculate the resistance of the variable resistor. (2)
The resistance of the variable resistor is now decreased.
9.2.2 State whether the speed at which the wiper turns will INCREASE, DECREASE or REMAIN THE SAME.
Give a reason for the answer. (3) [20]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a new page.)
10.1 The diagram below is a simplified representation of a DC motor. The current in the coil is in the direction XY.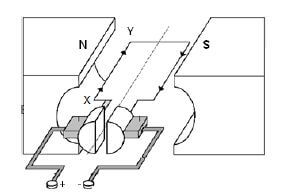
10.1.1 Name the component that ensures that the coil rotates continuously in ONE DIRECTION. (1)
10.1.2 In which direction will the coil rotate? Write down only CLOCKWISE or ANTICLOCKWISE. (2)
10.1.3Write down the energy conversion which takes place while the motor is working. (2)
10.2An AC generator, producing a maximum voltage of 320 V, is connected to a heater of resistance 35 Ω.
10.2.1 Write down the structural difference between an AC generator and a DC generator. (1)
Calculate the:
10.2.2 Root mean square (rms) value of the voltage (3)
10.2.3 Root mean square (rms) value of the current in the heater (4) [13]
QUESTION 11 (Start on a new page.)
A group of students investigates the relationship between the work function of different metals and the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons when the metals are irradiated with light of suitable frequency.
11.1 Define the term work function. (2)
During the investigation ultraviolet rays of wavelength 2 x 10-8 m are allowed to fall on different metal plates. The corresponding maximum kinetic energies of ejected electrons are measured.
The data obtained is displayed in the table below.
| METAL PLATE USED | MAXIMUM KINETIC ENERGY (Ek(max)) (x 10-18 J) |
| Lead | 9,28 |
| Potassium | 9,58 |
| Silver | 9,19 |
11.2 Write down the dependent variable for this investigation. (1)
11.3Write down ONE control variable for this investigation. (1)
11.4Using the information in the table, and without any calculation, identify the metal with the largest work function.
Explain the answer. (3)
11.5 Use information in the table to calculate the work function of potassium. (4)
11.6 State how an increase in the intensity of the ultraviolet light affects the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons. Choose from: INCREASES, DECREASES, REMAINS THE SAME.Explain the answer. (3) [14]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12
PAPER 1 (PHYSICS)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Acceleration due to gravity | g | 9,8 m•s-2 |
Universal gravitational constant | G | 6,67 × 10-11 N•m2•kg-2 |
Speed of light in a vacuum | c | 3,0 × 108 m•s-1 |
Planck's constant | h | 6,63 × 10-34 J•s |
Coulomb's constant | k | 9,0 × 109 N•m2•C-2 |
Charge on electron | e | -1,6 × 10-19 C |
Electron mass | me | 9,11 × 10-31 kg |
Mass of earth | M | 5,98 × 1024 kg |
Radius of earth | RE | 6,38 × 103 km |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE
MOTION
| vf = vi + aΔt | Δx = ViΔt + ½aΔt2 or Δy = ViΔt2 + ½aΔt2 |
Vf2 = Vi2 + 2aΔx or Vf2 = vi2 + 2aΔy | Δx = [Vi + Vf]Δt or Δy = [Vi + Vf]Δt |
FORCE
Fnet = ma | p= mv |
fsmax = µsN | fk = µkN |
FnetΔt = Δp | w =mg |
F = Gm1m2 | g = G M |
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
W =FΔxcosθ | U= mgh or EP = mgh |
K = ½mv2 or Ek = ½mv2 | Wnet = ΔK or Wnet = ΔEk ΔK = Kf −Ki or ΔEk =Ekf − Eki |
Wnc= ΔK + ΔU or Wnc= ΔEk + ΔEp | P = W Δt |
Pav = Fv |
WAVES, SOUND AND LIGHT
v = f λ | T =1/f |
fl = v ± vl fs fl = v ± vl fb | E = hf or E = h c |
E = W0 + Ek where | |
ELECTROSTATICS
| F = kQ1Q2 r2 | E = KQ |
E = V | E = F |
V = W | n = Q |
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
R = V | emf (ε) = I(R + r) |
RS = R1 + R2 + ....... | q = I Δt |
W = Vq | P= W |
ALTERNATING CURRENT
I rms = Imax | Paverage = VrmsIrms |