GENETICS - LIFE SCIENCES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupActivity 1
Choose an item from COLUMN 2 that matches a description in COLUMN 1.
Write only the letter (A to I) next to the question number (1-5), for example 6. J.
| COLUMN 1 | COLUMN 2 |
| A. Gene B. Recessive C. Haemophilia D. Dominant E. Homologous F. Genotype G. Phenotype H. Alleles I. Karyotype |
[5]
Answers to activity 1
- B✔
- H✔
- C✔
- E✔
- G✔ (5 × 1) [5]
Activity 2
Question 1
Try solving this problem on your own before you look at the solution.
Fur colour in mice is controlled by a gene with two alleles. A homozygous mouse with black fur was crossed with a homozygous mouse with brown fur. All offspring had black fur. Using the symbols B and b to represent the two alleles for fur colour, show diagrammatically a genetic cross between a mouse that is heterozygous for fur colour and a mouse with brown fur. Show the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. (6)
Question 2
In rabbits the dominant allele (B) produces black fur and the recessive allele (b) produces white fur. Use a genetic cross to show the possible phenotypes and genotypes of the F1 generation for fur colour if two heterozygous rabbits are crossed. (6)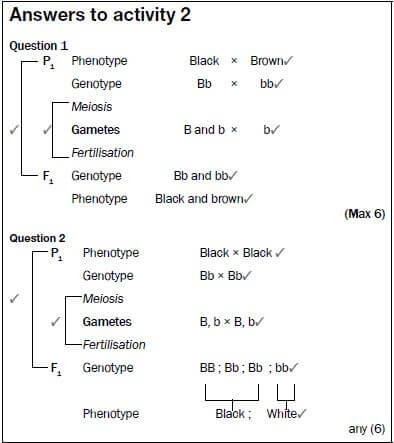
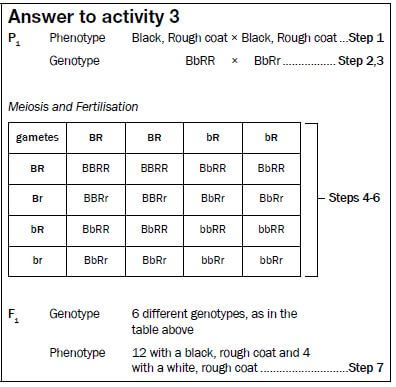
Activity 3
Question
In hamsters, the allele for black coat colour (B) is dominant over the allele for white coat colour (b). The allele for rough coat (R) is dominant over the allele for smooth coat (r). If you cross a hamster that is heterozygous black and homozygous rough, with one that is heterozygous black and heterozygous rough, what will be the phenotypes and genotypes of the offspring? (Use the steps 1-7 to arrive at an answer).
Activity 4
The pedigree diagram in Figure 5.1 shows inheritance of eye colour in humans over three generations of a family. Brown eye colour (B) is dominant over blue eye colour (b). Study the diagram and then answer the questions that follow.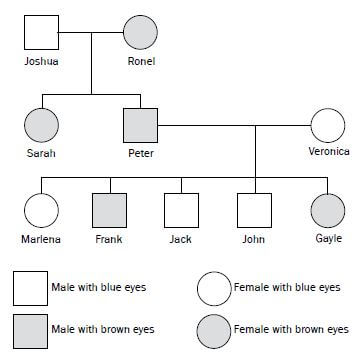
Figure 5.1 Pedigree diagram showing inheritance of eye colour
Note the following in the pedigree diagram on page 38:
- Squares represent males and circles represent females.
- The horizontal line between a square (Joshua) and a circle (Ronel) shows that they have mated.
- The vertical line flowing from the horizontal line represents the offspring (Sarah and Peter) of the two parents (Joshua and Ronel).
- Brown eye colour (B) is dominant over blue eye colour (b) - stated in problem Step 1
- Joshua, Jack and John are males with blue eyes.
- Veronica and Marlena are females with blue eyes.
- Peter and Frank are males with brown eyes. Step 2
- Ronel, Sarah and Gayle are females with brown eyes.
- Joshua, Veronica, Marlena, Jack and John will have the genotype ‘bb’. The recessive characteristic only shows up in the homozygous condition Step 3
- Example: The genotype of Peter is ‘Bb’ - working backwards from the offspring Marlena or Jack or John who are homozygous recessive.
This means that one of the recessive alleles of Marlena, Jack and John, i.e. ‘b’, must have come from parent Peter and the other one from parent Veronica Steps 4 and 5 - Ronel could be homozygous dominant (BB) or heterozygous dominant (Bb) Step 6
Questions
1. How many members of the family have blue eyes? (1)
2. Is Veronica homozygous or heterozygous for eye colour? (1)
3. Write down the genotype of:
a) Joshua (2)
b) Ronel (2)
c) Frank (2)
4. If Frank marries a woman with the same genetic composition as Sarah, what is the percentage probability of them having a child with brown eyes? (1) [9]
Answers to activity 4
1. 5✔ (1)
2. Homozygous✔(1)
3. a) bb✔✔ (2)
b) BB/Bb✔✔ (2)
c) Bb✔✔ (2)
4. 75%✔
Activity 5
Question
State FOUR disadvantages and FOUR advantages of genetic engineering. [8]
Answer to activity 5
Four disadvantages of genetic engineering:
- Expensive✔/research money could be used for other needs
- Interfering with nature✔/immoral
- Potential health impacts✔
- Unsure of long-term effects✔ (4)
Four advantages of genetic engineering:
- Production of medication/resources cheaply✔
- Control pests with specific genes inserted into a crop✔
- Using specific genes to increase crop yields✔/food security
- Selecting genes to increase shelf-life of plant products✔ (4) [8]
Activity 6
Question
A young couple wants to have a child, but they are aware of a serious genetic disorder in one of their families that could be carried through to their offspring. State THREE benefits of genetic counselling in this case. [3]
Answer to activity 6
Three benefits of genetic counselling:
- To be given advice on the risk of transferring the defective gene✔/ to find the probability of passing on the defective gene to the offspring
- To be given an explanation of the procedure involved in DNA testing✔
- To be given an explanation of the results of DNA testing✔ [3]