ECONOMICS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - 2018 JUNE EXAM PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupECONOMICS PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
JUNE 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK.
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer TWO of the three questions.
SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions. - Write the question number above each answer.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Read the questions carefully and start each question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2−3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive levels of the questions.
- Only the required number of questions will be marked in the order in which they appear in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1 30 MARKS − 20 MINUTES
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–C) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.9 D.
1.1.1 Factors that originate from inside the domestic economic system are referred to as …
- exogenous.
- production.
- indigenous.
- endogenous.
1.1.2 In business cycles estimating something known from information that is unknown, is called …
- amplitude.
- extrapolation.
- trend.
- moving average.
1.1.3 The money market in the RSA is a market for … savings and loans.
- short-term
- medium-term
- long and short term
- medium and short term
1.1.4 One of the main problems in public sector provisioning is ...
- providing public goods.
- issues of conservation.
- marketing with public relations.
- a lack of accountability.
1.1.5 The trade balance is the net result of ...
- the trade in services.
- the trade in goods.
- exports and imports.
- export prices and import prices.
1.1.6 This is an argument in favour of free trade:
- Economic development
- Economic growth
- Economies of scale
- Infant industries
1.1.7 Putting laws in place to regulate activities:
- Regional government
- Regulation
- Central government
- Deregulation
1.1.8 The currency fluctuates in value according to demand and supply:
- Free floating
- Appreciation
- Fixed
- Revaluation (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Choose the correct description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A−I) next to the question number (1.2.1−1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.2.1 Market prices 1.2.2 Jugler cycles 1.2.3 Community goods 1.2.4 Transfer payment 1.2.5 Depression 1.2.6 Customs union 1.2.7 Non-rivalry 1.2.8 Real figures |
|
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
Acronyms and abbreviations will NOT be accepted.
1.3.1 The flow of goods and services between the participants in the circular flow
1.3.2 A diagram that shows expansion and contraction periods of economic activities
1.3.3 The curve that shows the relationship between tax rate and tax revenue
1.3.4 Taxes that are not shifted to the end user
1.3.5 A financing instrument distributed among member countries of the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
1.3.6 Withdrawal of capital investment from a company or country (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name TWO characteristics of fiscal policy. (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 How can the appreciation of the rand affect exports of goods and services? (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
| THE MULTIPLIER EFFECT The government has taken a decision to expand the national road network by R200 million a year. The tendency of households is to save 30 per cent of their income. |
2.2.1 Identify the concept in the above extract. (1)
2.2.2 What percentage of their income do households spend? (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term multiplier. (2)
2.2.4 What impact will a tax increase have on the multiplier? (2)
2.2.5 Calculate the size of the multiplier. Show ALL calculations. (4)
2.3 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow.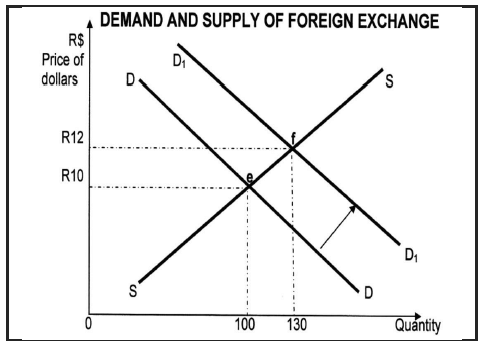
2.3.1 Identify the original equilibrium point on the above graph. (1)
2.3.2 What happens to the value of the Rand when the demand curve shifts from DD to D1D1? (1)
2.3.3 Briefly explain the floating exchange rate systems. (2)
2.3.4 What effect does globalisation have on international trade? (2)
2.3.5 How will demand influence foreign exchange? (4)
2.4 Briefly discuss any TWO arguments in favour of privatisation. (4 x 2) (8)
2.5 What effect does the term of trade have on the balance on the current account? (4 x 2) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name TWO demand reasons for international trade. (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 How important are national account aggregates for the country? (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow.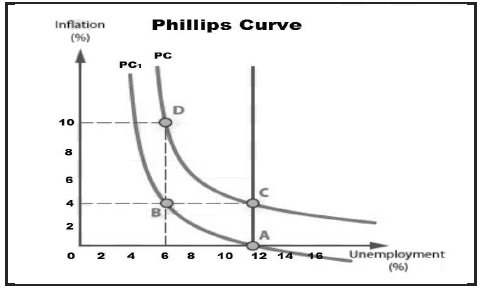
3.2.1 What does the above curve represent? (1)
3.2.2 Name the point that represents the natural rate of unemployment. (1)
3.2.3 Explain the relationship between inflation and unemployment. (2)
3.2.4 What measures could be used by the government to reduce unemployment? (2)
3.2.5 What impact will an increase in commercial banks’ reserve requirements have on the aggregate money supply? (4)
3.3 Study the following cartoon and answer the questions that follow.
|
3.3.1 Identify the trade policy referred to in the cartoon above. (1)
3.3.2 Name ONE reason why the policy is beneficial. (1)
3.3.3 Briefly explain the term trade liberalisation. (2)
3.3.4 Explain the dangers of dumping to a country. (2)
3.3.5 Why should infant industries be protected? (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Illustrate in the form of a table how Gross Domestic Product at market prices is calculated using the income method. NO FIGURES NECESSARY. (8)
3.5 How can the South African government avoid public sector failure? (4 x 2) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name any TWO examples of injections. (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How are ad valorem duties used to limit imports? (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Read the following article and answer the questions that follow.
| ECONOMIC INDICATORS USED IN FORECASTING Decreases in newspaper job advertisements, a deterioration in the composite leading business cycle indicators of South Africa’s major trading partners, fewer hours worked in the manufacturing sector and softer commodity prices in the month all contributed to a fall. |
4.2.1 Identify an example of a leading economic indicator from the above extract. (1)
4.2.2 Name the factor that contributed to a fall in the manufacturing sector. (1)
4.2.3 Briefly explain the term composite indicator. (2)
4.2.4 Explain how leading economic indicators are used in forecasting. (2)
4.2.5 How can the government use fiscal policy to stimulate the economy? (4)
4.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
4.3.1 What is represented in the above cartoon? (1)
4.3.2 Identify the people most affected as a result of increased government spending. (1)
4.3.3 Name any reason why the government imposes taxes. (2)
4.3.4 Briefly explain how people benefit from taxes. (2)
4.3.5 How do community goods differ from collective goods? (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Explain direct and portfolio investments in the financial account. (2 x 4) (8)
4.5 Why are state owned enterprises (SOEs) seen as a problem in public sector provisioning? (4 x 2) (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
Your answer will be assessed as follows:
| STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
Introduction
| Max. 2 |
| Body Main part: Discuss in detail/In-depth discussion/Examine/Critically discuss/Analyse/Compare/Evaluate/Distinguish/Differentiate/ Explain Additional part: Give own opinion/Critically discuss/Evaluate/ Critically evaluate/Draw a graph and explain/Use the graph given and explain/Complete the given graph/Calculate/Deduce/ Compare/Explain/ Distinguish/ Interpret/Briefly debate/ How/Suggest | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
| TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
The new economic paradigm is embedded in the demand-and-supply side policies to influence the economy.
- Discuss in detail the use of monetary policy and fiscal policy to influence the supply in the smoothing of business cycles. (26 marks)
- Explain the effect of demand-side and supply-side policies using a graph (aggregate demand and aggregate supply). (10 marks)
[40]
QUESTION 6: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
South Africa’s international trade policy consists of export promotion and import
substitution.
Discuss export promotion as part of South Africa’s international trade policy under the following headings:
- Methods (8)
- Reasons (8)
- Disadvantages (10) (26 marks)
How can countries use lending and borrowing to correct the deficit and surpluses on the balance of payments? (10 marks)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
